Hydraulic hoses play a crucial role in various industries, enabling the transfer of hydraulic fluid to power machinery and equipment.
When it comes to hydraulic hoses, understanding their pressure ratings is essential to ensure safe and reliable operation. Two critical terms associated with hydraulic hoses are working pressure and bursting pressure.
In this article, we will delve into the difference between these hydraulic hose pressure ratings, their significance, and how they impact the selection and usage of hydraulic hoses.
What is Hydraulic Hose Working Pressure?
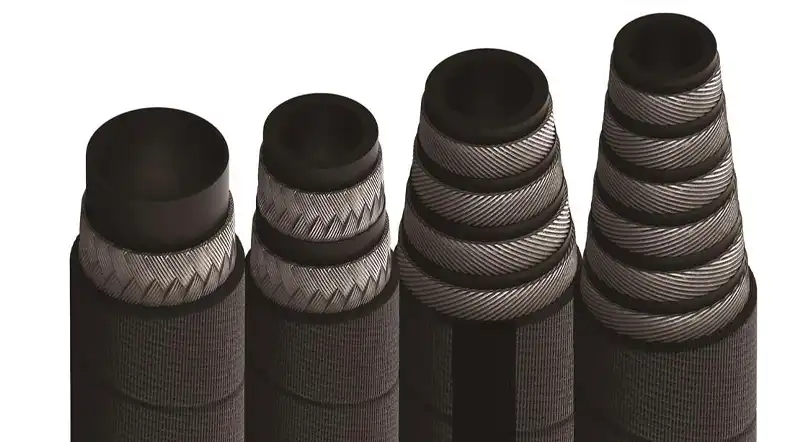

Working pressure refers to the maximum pressure that a hydraulic hose can safely handle during normal operation. It represents the continuous pressure that a hose is designed to withstand without experiencing any significant deformation or failure. Working pressure is typically expressed in pounds per square inch (psi) or bar.
The Importance of Working Pressure
The working pressure of a hydraulic hose is a critical specification that directly impacts the safety, efficiency, and longevity of any hydraulic system. Its importance cannot be overstated, as selecting a hose with an inappropriate working pressure can lead to severe consequences.
- System Safety: Foremost among the reasons for its importance is safety. Using a hose rated below the system’s maximum operating pressure significantly increases the risk of hose rupture. A burst hose can release high-pressure fluid, causing severe injuries (e.g., injection injuries, burns) to personnel, as well as property damage, environmental contamination, and costly downtime.
- Preventing Premature Failure: Hoses constantly operating at or near their maximum rated working pressure will experience accelerated wear and fatigue. This leads to premature material degradation, reduced flexibility, and an increased likelihood of failure, even if an immediate burst doesn’t occur. Proper working pressure selection ensures the hose operates within its design limits, extending its service life.
- Optimizing System Performance: A hose that is appropriately rated for the system’s working pressure ensures efficient power transmission and fluid flow. If the hose is constantly stressed, it can lead to internal damage that restricts flow, causes pressure drops, and reduces the overall efficiency of the hydraulic machinery.
- Compliance and Standards: Adhering to the specified working pressure is crucial for compliance with industry standards and regulations (e.g., ISO, SAE). These standards are established to ensure safe and reliable operation of hydraulic equipment. Non-compliance can lead to legal liabilities, warranty invalidation, and operational restrictions.
- Cost-Effectiveness in the Long Run: While it might seem tempting to opt for a cheaper hose with a lower pressure rating, the potential costs associated with hose failures (repairs, downtime, injuries, environmental cleanup) far outweigh any initial savings. Investing in hoses with the correct working pressure for the application is a cost-effective decision that ensures long-term reliability and minimizes unexpected expenses.
- Minimizing Maintenance and Downtime: Properly selected hoses are less prone to failure, which reduces the frequency of maintenance and the associated downtime for repairs and replacements. This directly contributes to higher operational efficiency and productivity.
Factors Affecting Hydraulic Hose Working Pressure
The working pressure of a hydraulic hose, representing the maximum pressure it can safely handle during normal operation, is influenced by several critical factors. Understanding these is essential for proper hose selection and system safety.
- Hydraulic Hose Construction and Materials: The type and quality of materials used for the inner tube, reinforcement layers, and outer cover significantly impact pressure ratings. Hoses with multi-spiral wire reinforcement generally offer higher pressure capabilities than those with single or double-braided wire. The strength and elasticity of the rubber or thermoplastic compounds also play a vital role.
- Inner Diameter (ID): As the inner diameter of a hydraulic hose increases, its working pressure rating typically decreases. This is because a larger cross-sectional area experiences greater force at the same pressure, requiring stronger reinforcement to maintain the same pressure capacity.
- Operating Temperature: Both the temperature of the hydraulic fluid and the ambient environmental temperature can severely affect a hose’s working pressure. High temperatures can degrade hose materials, reducing their strength and flexibility, while extremely low temperatures can make hoses brittle, increasing the risk of cracking and failure. Manufacturers provide specific temperature ranges for their hoses, and exceeding these limits can necessitate a reduction in the rated working pressure.
- Fluid Type and Compatibility: The chemical composition and viscosity of the hydraulic fluid can influence the hose’s performance and pressure rating. Certain fluids may be incompatible with specific hose materials, leading to degradation, swelling, or shrinking, which compromises the hose’s ability to hold pressure.
- Dynamic vs. Static Pressure and Pressure Spikes: Systems with dynamic pressure (fluctuations, pulses, and temperature changes) place greater stress on hoses than those with static, constant pressure. The working pressure rating should account for potential pressure spikes that can occur during system operation, as these brief, high-pressure events can be detrimental if not properly anticipated.
- Safety Factor: A crucial aspect of working pressure is its relationship to burst pressure. Most hydraulic hoses adhere to a minimum 4:1 safety factor, meaning the burst pressure (the pressure at which the hose will rupture) is at least four times its working pressure. This safety margin accounts for unforeseen pressure surges and material degradation over time.
- Environmental Conditions: Beyond temperature, other environmental factors like exposure to UV radiation, ozone, moisture, and abrasive surfaces can degrade the outer cover and internal components, potentially reducing the hose’s effective working pressure over its lifespan.
Hydraulic Hose Bursting Pressure

Bursting pressure refers to the maximum pressure that a hydraulic hose can withstand before rupturing or bursting. Unlike working pressure, bursting pressure represents a short-term peak pressure that a hose can endure without catastrophic failure. Similar to working pressure, bursting pressure is also expressed in psi or bar.
Significance of Bursting Pressure
While working pressure indicates the maximum pressure a hydraulic hose can handle during normal operation, bursting pressure serves as a safety margin. It provides an extra level of protection against unexpected pressure spikes or system malfunctions. A hydraulic hose with a high bursting pressure can tolerate sudden pressure increases without failure.
Factors Influencing Hydraulic Hose Bursting Pressure
The bursting pressure of a hydraulic hose is the absolute maximum pressure it can withstand before physical rupture or catastrophic failure. It’s a critical safety metric, distinct from working pressure, and is influenced by a combination of material science, manufacturing precision, and design considerations.
- Hose Construction and Reinforcement: The most significant factor influencing burst pressure is the hose’s reinforcement. Hoses with multiple layers of high-tensile steel wire, especially those with spiral-wound designs (like 4-wire or 6-wire spiral hoses), exhibit significantly higher burst pressures than those with single or double-braided wire reinforcement. The strength, number, and angle of these reinforcement layers directly determine how much internal pressure the hose can contain before failure.
- Material Quality and Type: The inherent strength and integrity of the materials used for the inner tube, reinforcement, and outer cover are paramount. High-quality synthetic rubbers (like nitrile, neoprene) or thermoplastics, coupled with robust steel wire, are essential. Inferior materials or those not suited for the fluid or temperature can degrade, weakening the hose’s ability to resist extreme pressure.
- Inner Diameter (ID) and Wall Thickness: For a given material and reinforcement, a smaller inner diameter generally corresponds to a higher burst pressure, as there’s less surface area for the pressure to act upon. Conversely, increasing the wall thickness of the inner tube and outer cover can also contribute to a higher burst pressure, provided the reinforcement is adequate.
- Manufacturing Process and Quality Control: Precision in manufacturing is crucial. Defects such as inconsistent material thickness, poor bonding between layers, improper crimping of fittings, or imperfections in the reinforcement winding can create weak points that drastically reduce the hose’s actual burst pressure compared to its theoretical rating. Strict quality control and adherence to industry standards during production are vital.
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures, both high and low, can compromise hose materials. High temperatures can cause the material to soften, swell, or degrade chemically, while very low temperatures can make the hose brittle. In either case, the material’s ability to withstand pressure is reduced, thus lowering the effective burst pressure.
- Fluid Compatibility: The chemical compatibility between the hydraulic fluid and the hose’s inner tube material is critical. Incompatible fluids can cause the inner tube to swell, harden, soften, or delaminate, leading to a loss of structural integrity and a reduced burst pressure.
- Aging and Fatigue: Over time, even correctly specified hoses will experience material fatigue due to repeated pressure cycles, flexing, and environmental exposure. This aging process can lead to microscopic cracks or degradation of the reinforcement, gradually lowering the burst pressure and increasing the risk of failure well below the original rating.
- External Damage: Abrasions, cuts, kinks, or crushing from external forces can compromise the structural integrity of the hose, especially its reinforcement layers. Such damage can create localized stress concentrations, leading to a burst at a pressure far below the hose’s original burst rating.
Hydraulic Hose Proof Pressure (Test Pressure/Overpressure)

Hydraulic hose proof pressure, sometimes referred to as overpressure or over-range capacity, is a critical test pressure that a hose assembly must withstand without permanent deformation, leakage, or other signs of damage.
Unlike burst pressure, which is a destructive test to determine the point of rupture, proof pressure is a non-destructive test typically performed by the manufacturer on a hose or hose assembly. It’s usually set at a multiple of the hose’s maximum working pressure, commonly 1.5 to 2 times the working pressure, and is held for a specified duration (e.g., 30-60 seconds).
The purpose of this test is to verify the structural integrity of the hose and its fittings under a pressure significantly higher than its normal operating conditions, providing an additional layer of assurance for safety and reliability in the field, and confirming that the hose meets industry standards like SAE or ISO.
Hydraulic Hose Working Pressure vs Bursting Pressure
Understanding the difference between hydraulic hose working pressure and bursting pressure is essential for safe and efficient hydraulic system performance. These two pressure ratings define the hose’s strength, durability, and suitability for specific applications, ensuring proper operation under varying load and environmental conditions.
- Working Pressure: The working pressure is the maximum pressure a hydraulic hose can handle during regular operation. It is determined with a built-in safety margin to prevent failures. Manufacturers usually recommend a working pressure four times lower than the hose’s burst pressure to ensure reliable performance and safety.
- Bursting Pressure: The bursting pressure is the maximum pressure a hydraulic hose can withstand before catastrophic failure occurs. It represents the hose’s ultimate strength under extreme stress. Bursting pressure is typically four times higher than the working pressure and helps determine the safety factor used in
| Pressure Rating | Working Pressure | Bursting Pressure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The maximum pressure that a hydraulic hose is designed to safely handle during normal operation. | The pressure at which a hydraulic hose may rupture or burst due to excessive pressure or failure of the hose assembly. |
| Measurement Unit | The difference between the working pressure and the bursting pressure, ensures the hose operates within safe limits. | PSI (Pounds per Square Inch) or bar (1 bar = 14.5 PSI) |
| Magnitude | Usually a fraction or a percentage of the bursting pressure. It is typically lower than the bursting pressure. | The highest pressure value that a hydraulic hose can withstand before it fails catastrophically. It is significantly higher than the working pressure. |
| Safety Margin | The difference between the working pressure and the bursting pressure, ensuring the hose operates within safe limits. | No safety margin is included since the bursting pressure is the maximum pressure a hose can handle before failure. |
| Application | The pressure at which a hydraulic system operates under normal conditions. | A safeguard against sudden pressure spikes, system malfunctions, or excessive pressure due to blockages, which can cause a hose to burst. |
| Importance | Critical to consider ensuring proper hose selection and avoid premature failure. | Primarily used as a safety factor to provide a buffer against potential failure under extreme conditions. |
The primary difference between working pressure and bursting pressure lies in their duration and purpose. Working pressure represents the continuous pressure a hydraulic hose can handle during normal operation while bursting pressure indicates the short-term peak pressure a hose can withstand without failure. It is crucial to choose a hydraulic hose with a working pressure rating higher than the maximum expected pressure and ensure the bursting pressure provides an additional safety margin.

Understanding the distinct roles of proof pressure and burst pressure is crucial for hydraulic system design and safety. While both relate to a hose’s pressure-handling capabilities, they represent different types of tests and safety benchmarks.
Definition and Purpose
Proof pressure is a non-destructive test pressure applied to a hose assembly to verify its integrity without causing damage. Its purpose is to ensure the hose can safely withstand pressures above its normal working range. Burst pressure, conversely, is the pressure at which a hose catastrophically fails or ruptures. It’s a destructive test conducted to determine the absolute maximum pressure the hose can contain before breakdown, establishing a critical safety limit for the hose’s design.
Test Nature
Proof pressure testing is non-destructive, meaning the hose is expected to return to its original state after the test without any signs of leakage or permanent deformation. It’s often a quality control measure applied to every hose or a sample during manufacturing. Burst pressure testing, by its very nature, is destructive. The hose is pressurized until it fails, providing data on its ultimate pressure resistance but rendering the tested hose unusable.
Relationship to Working Pressure
Proof pressure is typically a multiple of the working pressure, commonly 1.5 to 2 times, providing a safety margin for occasional pressure surges in a hydraulic system. Burst pressure, on the other hand, is significantly higher than the working pressure, often by a factor of 4:1 (meaning burst pressure is at least four times the working pressure), forming the foundation of the hose’s safety factor to prevent catastrophic failure under extreme conditions.
Application in Design and Manufacturing
Proof pressure testing is a routine quality assurance step in the manufacturing process, ensuring that each produced hose or a representative sample meets specified performance and safety standards before leaving the factory. Burst pressure data, however, is primarily used during the design and development phase of a hydraulic hose. It helps engineers establish the fundamental strength of the hose and set appropriate working pressure ratings based on established safety factors.
Importance for Safety
Both pressures are vital for safety, but in different ways. Proof pressure guarantees that a hose can handle temporary overloads without immediate failure or compromise, adding a layer of operational reliability. Burst pressure defines the ultimate limit of the hose’s pressure containment, acting as the final safety barrier against catastrophic failure, protecting personnel and equipment from dangerous high-pressure fluid releases.
Proof Pressure vs Burst Pressure
| Feature | Proof Pressure | Burst Pressure |
| Definition | Test pressure hose can withstand without damage | Pressure at which hydraulic hose ruptures/catastrophically fails |
| Test Nature | Non-destructive | Destructive |
| Purpose | Quality assurance, verify integrity | Determine ultimate strength, establish safety factor |
| Relationship to Working Pressure | 1.5x – 2x Working Pressure | ≥ 4x Working Pressure (Safety Factor) |
| Application | Manufacturing quality control | Design and development, safety rating |
Selecting the Right Hydraulic Hose

Choosing the correct hydraulic hose is crucial for system safety, performance, and longevity. The right selection depends on pressure requirements, temperature, fluid compatibility, and environmental conditions. Proper hose choice prevents leaks, bursts, and downtime, ensuring smooth operation in demanding hydraulic applications across various industries and environments.
- Pressure Rating – Always match the hose’s working pressure with the system’s maximum operating pressure. Using a hose with inadequate pressure tolerance can lead to leaks or rupture. A proper pressure margin ensures stable performance under peak loads and extends the service life of your hydraulic components.
- Temperature Range – Select a hose designed for both the fluid and ambient temperature conditions. Excessive heat can degrade rubber compounds, while extreme cold can cause stiffness or cracking. A temperature-resistant hose maintains flexibility and sealing integrity, preventing performance loss and premature wear in hydraulic systems.
- Fluid Compatibility – Ensure the hose material is compatible with the hydraulic fluid used. Incompatible materials can cause swelling, softening, or corrosion, leading to leakage or failure. Checking compatibility charts helps maintain optimal chemical resistance and durability, especially when handling synthetic, petroleum-based, or biodegradable hydraulic fluids.
- Environmental Factors – Consider external conditions such as abrasion, UV exposure, and chemical contact. Hoses with protective covers or specialized materials withstand harsh surroundings better. Choosing the right outer layer enhances protection, minimizes wear, and guarantees dependable operation even in rugged or outdoor hydraulic applications.
Proper Maintenance and Inspection

Regular hydraulic hose maintenance and inspection of hydraulic hoses are vital to identify any signs of wear, damage, or degradation. Hoses should be visually inspected for cracks, leaks, bulges, or any other visible abnormalities.
Performing pressure tests and considering the service life of hoses can help prevent unexpected failures and ensure the safe operation of hydraulic systems.
Understanding the difference between working pressure and bursting pressure is crucial for selecting and using hydraulic hoses in various applications.
Working pressure represents the continuous pressure a hose can handle during normal operation while bursting pressure serves as a safety margin against pressure spikes. By considering these pressure ratings and following safety guidelines, it is possible to ensure the reliable and safe operation of hydraulic systems.
Hydraulic Hose Dynamic Pressure vs Static Pressure
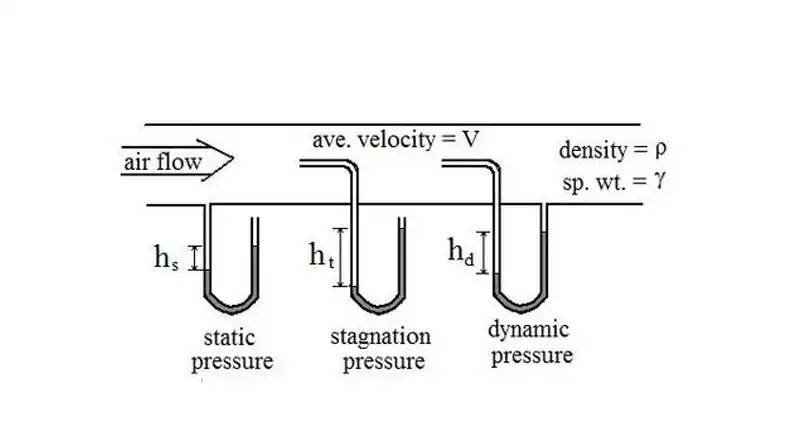
Hydraulic hoses are essential components used in hydraulic systems to transmit fluid power. They are designed to withstand high pressures and carry fluid between hydraulic components. When discussing hydraulic hose pressure, two important concepts to understand are dynamic pressure and static pressure.
Dynamic Pressure:
Dynamic pressure refers to the pressure exerted by a fluid when it is in motion. In the context of hydraulic hoses, dynamic pressure occurs when the hydraulic system is operational, and fluid is flowing through the hose. Dynamic pressure is typically higher than static pressure due to the added energy of fluid movement. It is influenced by factors such as flow rate, fluid viscosity, hose diameter, and system design.
Static Pressure:
Static pressure, on the other hand, refers to the pressure exerted by a fluid when it is at rest or not in motion. In the case of hydraulic hoses, static pressure exists when the hydraulic system is at rest or when fluid flow is blocked. Static pressure is typically lower than dynamic pressure because there is no additional energy from fluid movement. It is influenced by factors such as system design, fluid properties, and the weight of the fluid column above the point of measurement.
Both dynamic pressure and static pressure are important considerations when selecting hydraulic hoses for a specific application. Hoses need to be designed and rated to withstand the maximum pressures experienced during both dynamic and static conditions. The pressure rating of a hydraulic hose specifies the maximum pressure it can safely handle, taking into account both dynamic and static pressure situations.
It’s crucial to ensure that the selected hydraulic hose has a pressure rating that exceeds the maximum dynamic and static pressures expected in the hydraulic system. Operating a hose beyond its pressure rating can lead to hose failure, leaks, or other safety hazards.
Hydraulic Hose Maximum Pressure

Hydraulic hose maximum pressure is a vital specification that determines the maximum operating pressure a hose can withstand without failing. Exceeding this pressure limit can lead to catastrophic consequences, such as leaks, ruptures, and equipment damage.
Factors Affecting Hydraulic Hose Maximum Pressure:
- Hose Construction: The materials used in the hose’s construction, including the rubber core, reinforcement layers, and outer cover, significantly influence its pressure rating.
- Reinforcement Type: The type and quality of reinforcement within the hose, such as steel wire or braided fabric, determine its strength and ability to withstand high pressure.
- Hose Diameter: The diameter of the hose also affects its pressure rating. Larger diameter hoses generally have higher pressure ratings.
- Operating Temperature: The temperature at which the hose operates can influence its pressure capacity. Higher temperatures can reduce the strength of the hose material.
- Fluid Type: The type of hydraulic fluid being used can also impact the hose’s pressure rating. Some fluids may be more corrosive or abrasive than others.
Importance of Adhering to Maximum Pressure Ratings:
- Preventing Failures: Operating a hydraulic hose above its maximum pressure rating can lead to premature wear, leaks, or even catastrophic ruptures.
- Ensuring Safety: Exceeding the pressure limit can pose a serious safety hazard, potentially causing injuries or property damage.
- Protecting Equipment: Hydraulic system failures can result in costly equipment damage and downtime.
- Maintaining Efficiency: Proper hydraulic hose maintenance and adherence to pressure limits can help ensure optimal system performance and efficiency.
When selecting hydraulic hoses, it is essential to carefully consider the maximum pressure requirements of your application and choose hoses that are rated to handle the expected pressures.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between working pressure and bursting pressure is vital for maintaining hydraulic system safety and efficiency. By knowing how these ratings function, you can prevent equipment failure, extend hose life, and ensure your machinery performs reliably under all operating conditions. Proper pressure awareness safeguards both performance and personnel.
Selecting hoses based on accurate pressure ratings also minimizes downtime and maintenance costs. Always verify the hose specifications align with your system’s requirements, considering both maximum operating pressure and safety margins. A well-matched hydraulic hose provides consistent results, protecting your investment and enhancing productivity across demanding industrial environments.
At Kingdaflex, we supply wholesale hydraulic hoses designed to meet diverse working and bursting pressure needs. Whether for construction, agriculture, or manufacturing, our durable hoses ensure optimal performance and safety. Contact us today to get the best deals on reliable, pressure-tested hydraulic hoses for your business.
What is the difference between working pressure and bursting pressure?
Working pressure refers to the continuous pressure a hydraulic hose can handle during normal operation while bursting pressure indicates the short-term peak pressure a hose can withstand without failure.
Why is working pressure important for hydraulic hoses?
Working pressure ensures that a hydraulic hose can handle the pressure exerted by the system without compromising safety or performance.
What factors affect the bursting pressure of hydraulic hoses?
The construction, reinforcement layers, wall thickness, and materials used in the hose influence its bursting pressure.
Can I exceed the working pressure of a hydraulic hose?
Exceeding the working pressure of a hydraulic hose can lead to hose failure, leaks, or accidents. It is essential to select a hose with a suitable working pressure rating.
How can I select the right hydraulic hose for my application?
Consider factors such as working pressure requirements, application conditions, temperature range, fluid compatibility, and environmental considerations when selecting a hydraulic hose.
What happens if I exceed the working pressure of a hydraulic hose?
Exceeding the working pressure of a hydraulic hose can result in hose failure, leaks, or even accidents. It is essential to select a hose with a working pressure rating that exceeds the expected pressure in the application.
Can I use a hydraulic hose with a lower bursting pressure?
It is not recommended to use a hydraulic hose with a lower bursting pressure than the maximum pressure expected in the system. The bursting pressure serves as a safety margin against pressure spikes and unexpected events.
How often should hydraulic hoses be inspected?
Hydraulic hoses should be visually inspected regularly for signs of wear, damage, or degradation. The frequency of inspection may vary depending on the operating conditions and application.
Can I repair a damaged hydraulic hose?
It is generally recommended to replace a damaged hydraulic hose rather than attempt repairs. Proper installation of new hoses ensures optimal performance and safety.
Conclusion




