Choosing the right type of thread for your project is critical for ensuring a secure and leak-free connection. Two common thread standards you might encounter are SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) and NPT (National Pipe Taper). While both are used for joining pipes and fittings, they have distinct characteristics that make them suitable for different applications.
This blog post will delve into the key differences between SAE and NPT threads, helping you understand their unique features and make informed decisions for your projects.
What Is SAE Thread
SAE threads are a family of thread standards developed by the Society of Automotive Engineers. They are widely used in the automotive and hydraulics industries.
Here are some key characteristics of SAE threads:
- Straight Threads: Unlike tapered threads like NPT, SAE threads are typically straight.
- O-Ring Seal: SAE threads often incorporate an O-ring for sealing, providing a reliable and reusable connection.
- Various Types: There are different types of SAE threads, including:
- Straight Thread O-Ring Boss (ORB): A common type with a straight thread and an O-ring groove.
- SAE 45° Flare: Used in brake and fuel systems, featuring a 45-degree flare for sealing.
- JIC 37° Flare: Similar to SAE 45° Flare but with a 37-degree flare angle.
Key Advantages of SAE Threads:
- Reliable Sealing: The O-ring provides a consistent and effective seal, even in high-pressure applications.
- Reusable Connections: The threads themselves are not relied upon for sealing, allowing for multiple connections and disconnections without damaging the threads.
- Ease of Assembly: Straight threads are generally easier to assemble and disassemble compared to tapered threads.
Applications:
SAE threads are commonly found in:
- Hydraulic systems
- Automotive brake lines and fuel systems
- Industrial machinery
- Aerospace applications
If you’re working with hydraulic or automotive systems, understanding SAE thread standards is essential for ensuring proper component selection and assembly.
What Is PNT Thread
PNT does not refer to a specific thread standard.
- PNT most commonly stands for Positioning, Navigation, and Timing, as explained earlier.
- PT on the other hand, often refers to Pipe Thread, which is a British Standard for tapered pipe threads.
It’s possible there might be a very niche or industry-specific use of “PNT” to denote a particular thread type, but without further context, it’s unlikely to be a widely recognized term in the field of threads and fasteners.
SAE Thread vs NPT
| Feature | SAE Thread | NPT Thread |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Profile | Straight | Tapered |
| Taper | None | 3/4 inch per foot |
| Sealing | Primarily O-ring | Primarily sealing tape or compound |
| Common Usage | Automotive, Hydraulics | General Plumbing, Gas |
| Interchangeability | Not directly interchangeable with NPT | Not directly interchangeable with SAE |
SAE Threads:
- Straight thread design
- Rely on O-rings for sealing
- Commonly used in automotive and hydraulic systems
NPT Threads:
- Tapered thread design
- Rely on sealing tape or compound
- Widely used in general plumbing and gas applications
Incompatibility: Due to their different thread profiles and sealing mechanisms, SAE and NPT threads are not directly interchangeable. Attempting to force a connection can lead to leaks, damage to the threads, and potential safety hazards.
1/4 SAE vs 1/4 NPT
| Feature | 1/4 SAE Thread | 1/4 NPT Thread |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Profile | Straight | Tapered |
| Taper | None | 3/4 inch per foot |
| Sealing | Primarily O-ring | Primarily sealing tape or compound |
| Common Usage | Automotive, Hydraulics | General Plumbing, Gas |
| Interchangeability | Not directly interchangeable with 1/4 NPT | Not directly interchangeable with 1/4 SAE |
Key Points:
- Thread Design: 1/4 SAE threads are straight, while 1/4 NPT threads are tapered.
- Sealing: 1/4 SAE threads typically rely on an O-ring for sealing, whereas 1/4 NPT threads use sealing tape or compound.
- Applications: 1/4 SAE threads are commonly found in automotive and hydraulic systems, while 1/4 NPT threads are prevalent in general plumbing and gas applications.
- Incompatibility: Due to their distinct thread profiles and sealing mechanisms, 1/4 SAE and 1/4 NPT threads are not directly interchangeable. Attempting to connect them can lead to leaks, damage, or even safety hazards.
SAE vs NPT Fittings
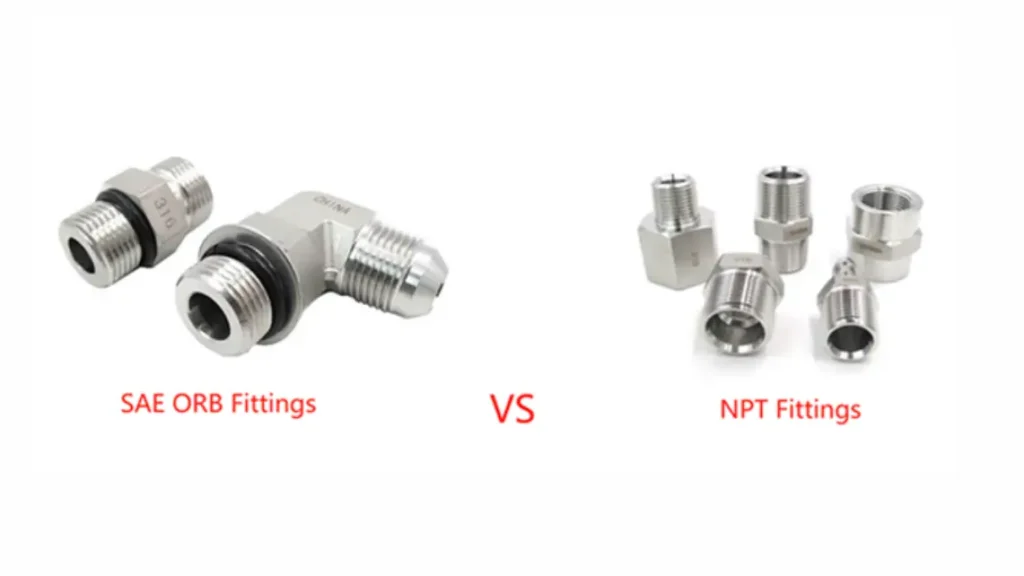

What is the difference between SAE and NPT fittings? Here are the things explained in the following:
SAE Fittings
- Thread Profile: Straight
- Sealing: Primarily rely on O-rings
- Common Usage: Automotive, Hydraulics, and other high-pressure applications
- Advantages:
- Reusable connections
- Easier assembly and disassembly
- Reliable sealing in high-pressure environments
NPT Fittings
- Thread Profile: Tapered
- Sealing: Primarily rely on sealing tape or compound
- Common Usage: General plumbing, gas lines, and other low-pressure applications
- Advantages:
- Relatively simple and inexpensive to assemble
Key Differences
| Feature | SAE Fittings | NPT Fittings |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Profile | Straight | Tapered |
| Sealing | O-ring | Sealing tape/compound |
| Pressure Applications | High-pressure | Low-pressure |
| Reusability | Highly reusable | Limited reusability |
| Assembly | Easier | More difficult |
Incompatibility:
- SAE and NPT fittings are not directly interchangeable.
- Attempting to connect them can lead to leaks, damage to the threads, and potential safety hazards.
Choosing the Right Fitting:
- Application: Consider the specific application and the required pressure and temperature ranges.
- Reusability: If frequent disassembly and reassembly are needed, SAE fittings are generally preferred.
- Cost: NPT fittings are often more cost-effective.
Remember: Always consult the relevant standards and consult with qualified professionals for specific applications.
SAE Straight Thread vs NPT
Here’s a breakdown of the key differences between SAE straight threads and NPT threads:
| Feature | SAE Straight Thread | NPT Thread |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Profile | Straight | Tapered |
| Taper | None | 3/4 inch per foot |
| Sealing | Primarily O-ring | Primarily sealing tape or compound |
| Common Usage | Automotive, Hydraulics | General Plumbing, Gas |
| Interchangeability | Not directly interchangeable with NPT | Not directly interchangeable with SAE |
Key Points:
- Thread Design: SAE straight threads have a parallel profile, while NPT threads have a tapered profile.
- Sealing: SAE threads rely on an O-ring for sealing, providing a reliable and reusable connection. NPT threads typically use sealing tape or compound to create a seal.
- Applications: SAE straight threads are commonly used in automotive and hydraulic systems, while NPT threads are prevalent in general plumbing and gas applications.
- Incompatibility: Due to their distinct thread profiles and sealing mechanisms, SAE straight threads and NPT threads are not directly interchangeable. Attempting to connect them can lead to leaks, damage to the threads, and potential safety hazards.
Visual Comparison:
Remember: Always use the correct fittings and adapters when working with different thread types to ensure proper connections and avoid potential issues.
Related: BSP Fittings vs NPT: Detailed Guide for Selecting the Right Fit
Is NPT compatible with SAE?
Are SAE and NPT threads compatible? No, SAE and NPT threads are not compatible.
Here’s why:
Different Thread Profiles: SAE threads are straight, while NPT threads are tapered.
Different Sealing Mechanisms: SAE threads typically use O-rings for sealing, while NPT threads rely on sealing tape or compound.
Attempting to connect SAE and NPT fittings can lead to:
Leaks: The mismatched thread profiles and sealing methods will likely result in leaks.
Damage: The threads themselves may become damaged due to the incompatibility.
Safety Hazards: In high-pressure applications, leaks can pose serious safety risks.
To ensure compatibility:
Use the correct fittings and adapters: If you need to connect systems with different thread types, use appropriate adapters designed for the specific combination (e.g., an SAE to NPT adapter).
Always consult the relevant standards and specifications to ensure proper installation and compatibility.
In Summary: SAE and NPT are distinct thread standards with significant differences. Using them interchangeably can lead to serious problems, including leaks and damage to the threads.
Conclusion
SAE and NPT are distinct thread standards with significant differences in their thread profiles, tapers, and sealing mechanisms. SAE, being a parallel thread, offers advantages in high-pressure applications and ease of assembly. NPT, with its tapered design, relies heavily on sealing compounds and is widely used in general plumbing and gas applications.
Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right fittings and ensuring proper installation. Using incompatible threads can lead to leaks, damage to equipment, and potential safety hazards.
Need high-quality hydraulic hose fittings?
Contact us today for a free consultation and let our experts help you choose the right components for your specific application. We offer a wide range of SAE and other industry-standard fittings to meet your exact requirements.




