As a leading hose fitting manufacturer, we understand the importance of choosing the right fitting for the job. When it comes to threaded pipe connections, two of the most common standards you’ll encounter are BSP (British Standard Pipe) and NPT (National Pipe Thread). While they may seem similar at first glance, key differences between them can impact compatibility and performance.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of BSP vs. NPT fittings, exploring their characteristics, applications, and how to identify them to ensure a secure and leak-free connection in your project.
What Are BSP Fittings

BSP, or British Standard Pipe, is a family of pipe thread standards originating in the United Kingdom. It encompasses several sub-types, with the most common being:
- BSP Parallel (BSPP): This type features a straight cylindrical thread with a flat flank. It’s commonly used for low-pressure applications where a tight seal isn’t critical.
- BSP Tapered (BSPT): This type features a tapered thread that creates a tighter seal as the fitting is screwed together. It’s the most widely used BSP fitting and is suitable for a broader range of pressures.
Key characteristics of BSP fittings:
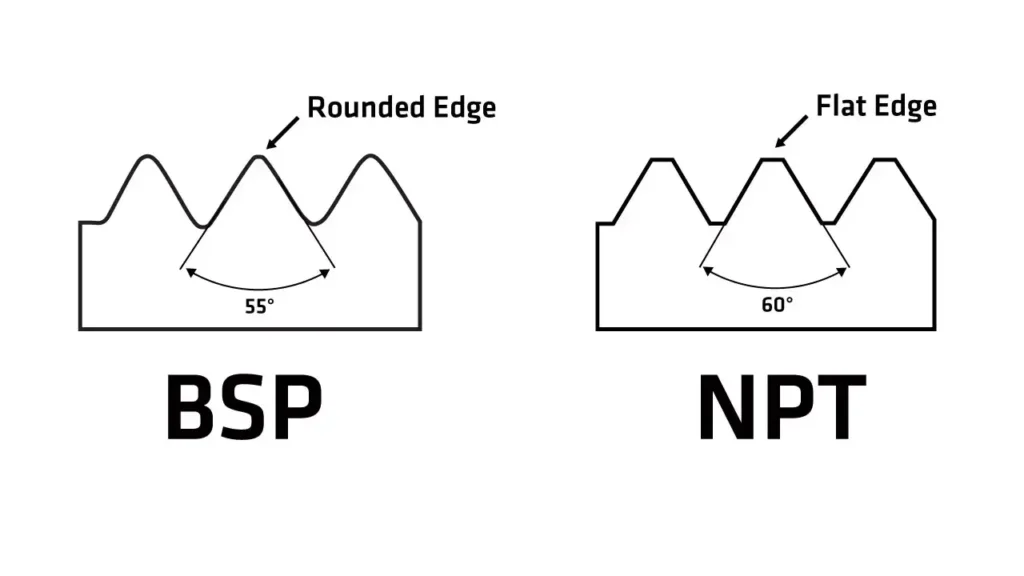
- Thread profile: Rounded peaks and valleys (compared to NPT’s sharp profile)
- Thread angle: 55 degrees (compared to NPT’s 60 degrees)
- Sealing mechanism: Primarily relies on the threads for sealing in BSPP, while BSPT utilizes a combination of threads and a sealant like PTFE tape for tighter connections.
Applications of BSP fittings:
- Common in plumbing and heating systems in Europe, Asia, Australia, and New Zealand
- Used in hydraulic and pneumatic systems
- Often found in industrial machinery and equipment
What Are NPT Fittings

NPT, or National Pipe Thread, is an American standard for threaded pipe connections. It’s widely used in North America and other regions that have adopted American plumbing practices.
Key characteristics of NPT fittings:
- Thread profile: Flat and sharp peaks and valleys
- Thread angle: 60 degrees
- Sealing mechanism: Primarily relies on a tapered thread and sealant like PTFE tape to create a tight seal.
Applications of NPT fittings:
- Dominant standard in plumbing and heating systems in North America
- Widely used in hydraulic and pneumatic systems
- Common in industrial and commercial applications across various industries
BSP vs NPT Fittings
Distinguishing between BSP and NPT fittings can be crucial for ensuring a leak-free connection.
Here are some key methods to know NPT thread vs BSP thread:
- Thread profile: Run your fingers along the threads. BSP threads will feel smoother and rounded, whereas NPT threads will feel sharper and more defined.
- Thread angle: While a precise measurement tool might be needed for absolute confirmation, visually comparing the thread angle can offer a good indication. NPT threads have a slightly wider angle (60 degrees) compared to BSP (55 degrees).
- Size and designation: BSP and NPT fittings may have different size designations. Consult a reference chart to compare size markings for the specific fitting you’re working with.
Important Note: Never attempt to force an NPT fitting into a BSP thread or vice versa. These differences can cause leaks and even damage the fittings. It’s crucial to use the correct fitting type for your application.
BSP vs NPT Fittings Comparison Chart
| Feature | BSP | NPT |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | British Standard Pipe | National Pipe Thread (American Standard) |
| Dominant Region | Europe, Asia, Australia, New Zealand | North America, South America (areas with American plumbing practices) |
| Thread Profile | Rounded peaks and valleys | Flat and sharp peaks and valleys |
| Thread Angle | 55 degrees | 60 degrees |
| Sealing Mechanism | Primarily threads for BSPP (parallel), threads and sealant (PTFE tape) for BSPT (tapered) | Primarily tapered threads and sealant (PTFE tape) |
| Common Types | BSPP (Parallel), BSPT (Tapered) | N/A (only tapered threads) |
| Applications | Plumbing & Heating, Hydraulic & Pneumatic Systems, Industrial Machinery | Plumbing & Heating, Hydraulic & Pneumatic Systems, Industrial & Commercial Applications |
| Identification Methods | Thread feel (smoother for BSP, sharper for NPT), Thread angle (slightly wider for NPT), Size & Designation (consult reference chart) | Thread feel, Thread angle, Size & Designation |
| Compatibility | Not compatible with NPT. Requires matching thread type. | Not compatible with BSP. Requires matching thread type. |
| Adapter Availability | Yes (BSP to NPT and vice versa) | N/A (only one type) |
Additional Notes:
- For high-pressure applications, NPT’s tapered thread and reliance on sealant generally offer a more secure seal compared to BSPP’s reliance solely on threads.
- When working with existing plumbing or equipment, ensure the new fitting matches the thread type already present.
- Using adapters adds complexity and potential leak points, so prioritize direct compatibility whenever possible.
BSP VS NPT Compatibility
BSP and NPT threads are NOT compatible.
Here’s why:
- Different Thread Profiles: BSP threads have a 55-degree included angle, while NPT threads have a 60-degree included angle.
- Different Tapers: BSP threads have a 1 in 20 taper, while NPT threads have a 3/4 inch per foot taper.
- Different Thread Pitches: The number of threads per inch also differs between BSP and NPT for the same nominal size.
Attempting to force a BSP and NPT connection will likely result in:
- Cross-threading: The threads will not align properly, leading to damage.
- Leaks: Even if the connection appears to be made, it will likely leak due to the mismatched thread profiles and tapers.
- Stripped Threads: The threads may become damaged or stripped due to the misalignment and excessive force required to connect them.
To avoid these issues:
- Always use the correct fittings and adapters. If you need to connect BSP and NPT systems, use appropriate adapters designed for this purpose.
- Double-check thread compatibility before attempting any connections.
- Consult with a qualified professional if you are unsure about thread compatibility.
BSP and NPT are distinct thread standards with significant differences. Using them interchangeably can lead to serious problems, including leaks and damage to the threads.
BSPT vs BSBP Fittings
BSPT and BSPP, though both falling under the British Standard Pipe (BSP) family, cater to different needs. Here’s a detailed breakdown to help you understand their nuances:
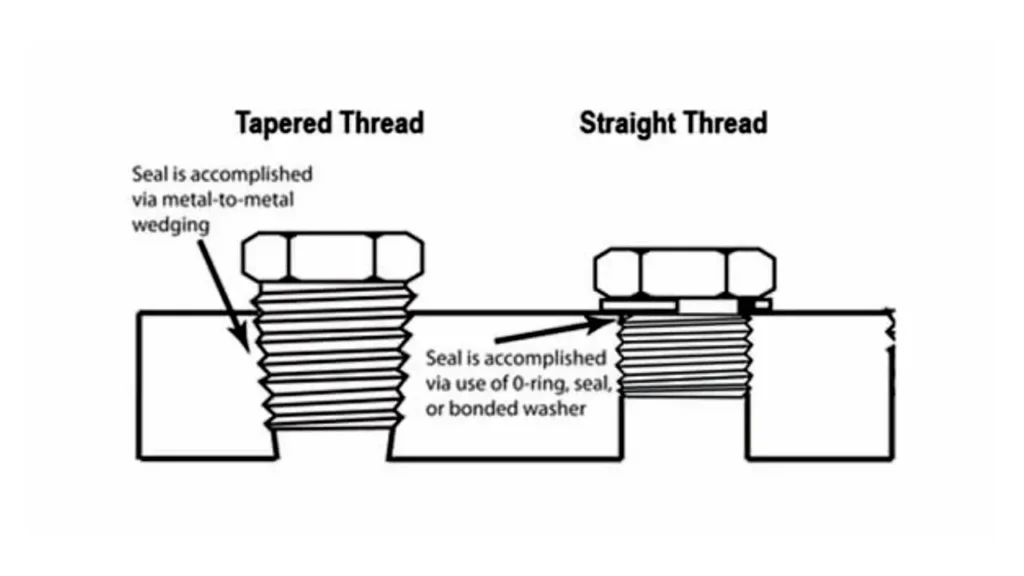
Thread Profile:
- BSPP (Parallel): Features a straight, cylindrical thread with a flat flank. Think of it like a screw that maintains a consistent width throughout its length.
- BSPT (Tapered): Boasts a tapered thread, meaning the diameter gets narrower as you move towards the end. Imagine a cone-shaped thread where the base is wider than the tip.
Sealing Mechanism:
- BSPP (Parallel): Primarily relies on the threads themselves for sealing. This makes it suitable for low-pressure applications where a leak-proof connection isn’t as critical.
- BSPT (Tapered): Creates a much tighter seal due to the tapered threads. As you screw the fitting together, the threads become increasingly engaged, compressing the fitting and creating a stronger seal. This makes BSPT ideal for a broader range of pressures, including moderate to high-pressure applications. To further enhance the seal, using a sealant like PTFE tape is recommended with BSPT.
Applications:
- BSPP (Parallel): Commonly found in:
- Low-pressure plumbing systems (think water supply lines within a house)
- Air conditioning systems (especially for low-pressure refrigerant lines)
- Instrumentation and control systems (where pressure isn’t a major concern)
- BSPT (Tapered): Widely used in:
- Hydraulic and pneumatic systems (where fluids are under moderate to high pressure)
- High-pressure water lines (industrial applications)
- Oil and gas pipelines
- Machinery and equipment requiring secure connections under pressure
Advantages and Disadvantages:
- BSPP (Parallel):
- Advantages: Simple design, easy to assemble and disassemble, no need for sealant (in low-pressure applications).
- Disadvantages: Not suitable for high-pressure applications due to potential leaks.
- BSPT (Tapered):
- Advantages: Creates a more secure and leak-resistant seal, suitable for a wider range of pressures.
- Disadvantages: Requires proper tightening to ensure a good seal, needs sealant for optimal performance (adds an extra step).
Choosing Between BSPT and BSPP:
The key factor influencing your choice is the pressure involved in your application.
- For low-pressure applications: BSPP is a cost-effective and straightforward option.
- For moderate to high-pressure applications: BSPT is the preferred choice due to its superior sealing capabilities.
Additional Considerations:
- Regional Compatibility: BSP is the dominant standard in Europe, Asia, Australia, and New Zealand. Ensure compatibility with existing components in your system.
- Safety: When dealing with high-pressure applications, prioritize using BSPT and following proper assembly procedures to ensure a safe and leak-free connection.
| Feature | BSPP (Parallel) | BSPT (Tapered) |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Profile | Straight, Cylindrical | Tapered |
| Sealing Mechanism | Primarily Threads | Threads and Sealant (PTFE tape recommended) |
| Applications | Low-Pressure Systems (Plumbing, Air Conditioning, Instrumentation) | Broader Range of Pressures (Hydraulics, Pneumatics, High-Pressure Water Lines, Oil & Gas) |
| Advantages | Simple Design, Easy Assembly, No Sealant (low pressure) | More Secure Seal, Wider Pressure Range |
| Disadvantages | Not Suitable for High Pressure | Requires Proper Tightening, Needs Sealant (extra step) |
| Choosing Factor | Pressure in Application (Low Pressure) | Pressure in Application (Moderate to High Pressure) |
| Additional Notes | Cost-effective for low pressure | Prioritize for safety in high-pressure applications |
By understanding the distinct characteristics and applications of BSPT and BSPP, you can make informed decisions when selecting the right fitting for your project. If you’re unsure about the pressure requirements or need further guidance, consulting a plumbing or hydraulics professional is always recommended.
Choosing Between BSP and NPT Fittings
Selecting the right fitting depends on several factors:
- Regional compatibility: Consider the prevalent standard in your location. If unsure, consult with a plumbing professional.
- Application pressure: For high-pressure applications, NPT’s tapered thread and reliance on sealant generally offer a more secure seal.
- Existing components: If you’re working with existing plumbing or equipment, ensure the new fitting matches the thread type already present.
Adapting Between BSP and NPT
In situations where you need to connect components with different thread standards, adapters are available. These fittings convert from one thread type to another, allowing for compatibility between BSP and NPT systems. However, using adapters adds complexity and potential leak points, so it’s best to prioritize direct compatibility whenever possible.
Does BSP fit NPT
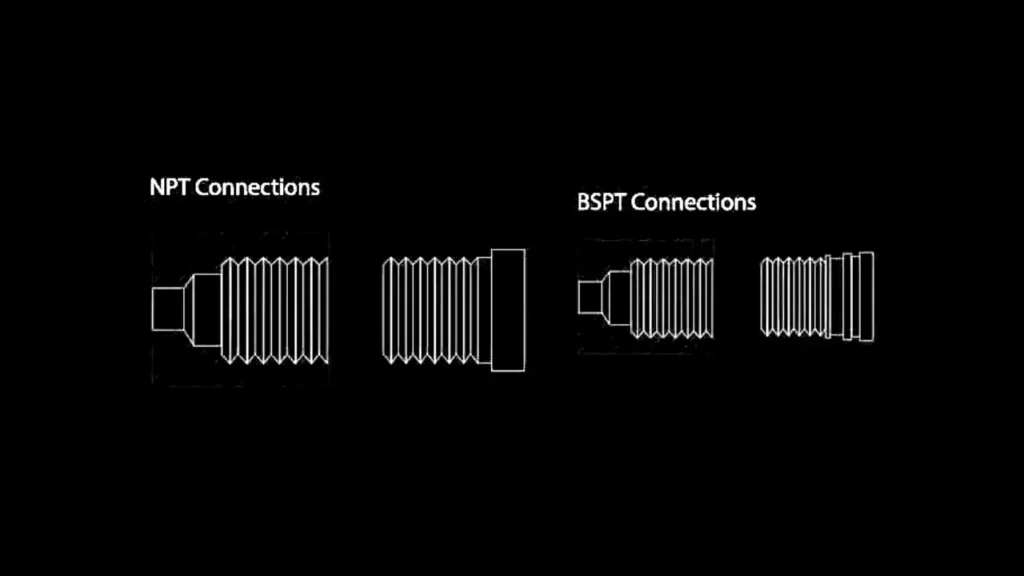
So are BSP fittings compatible with NPT fittings?
No, BSP and NPT fittings are not directly interchangeable.
While they may appear similar at first glance, there are key differences in thread profile, angle, and pitch that prevent them from creating a secure seal.
- Thread angle: BSP threads have a 55-degree angle, while NPT threads have a 60-degree angle.
- Thread profile: The shape of the thread peaks and valleys differs between the two standards.
- Thread pitch: The number of threads per inch is different for BSP and NPT, even for the same nominal size.
Attempting to force a BSP fitting onto an NPT thread or vice versa can result in leaks, damage to the threads, or even failure of the connection.
If you need to connect BSP and NPT systems, you’ll need to use appropriate adapters or conversion fittings.
BSPT Vs NPT
BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper) and NPT (National Pipe Taper) are both tapered pipe thread standards used to connect pipes and fittings. While they serve a similar purpose, there are key distinctions:
Key Differences
| Feature | BSPT | NPT |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | British Standard | American Standard |
| Thread Profile | 55° included angle | 60° included angle |
| Taper | 1 in 20 | 3/4 in per foot |
| Sealing Mechanism | Primarily metal-to-metal contact | Primarily sealing tape or compound |
| Common Usage | Primarily used in Europe and countries influenced by British standards | Primarily used in North America |
Incompatibility
Due to the differences in thread profile, taper, and sealing mechanisms, BSPT and NPT threads are not interchangeable. Attempting to connect them can lead to leaks, damage to the threads, or even failure of the connection.
Important Note: While this table provides a general overview, there can be slight variations within each standard. Always refer to the specific standards documents for precise dimensions and tolerances.
Difference Between NPT and BSPT Threads
NPT (National Pipe Taper) and BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper) are two common types of tapered pipe threads used to connect pipes and fittings. While they serve a similar purpose, they have key differences that make them incompatible:
BSPT vs PNT thread
| Feature | NPT | BSPT |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | American Standard | British Standard |
| Thread Profile | 60° included angle | 55° included angle |
| Taper | 3/4 inch per foot | 1 in 20 |
| Sealing Mechanism | Primarily sealing tape or compound | Primarily metal-to-metal contact |
| Common Usage | North America | Europe and countries influenced by British standards |
Incompatibility: Due to these differences, NPT and BSPT threads cannot be interchanged. Attempting to connect them can lead to leaks, damage to the threads, or even failure of the connection.
Is NPT and BSPT the Same?
No, NPT and BSPT are not the same.
- NPT (National Pipe Taper):
- Originates from the United States
- Has a 60-degree included angle
- Tapered 3/4 inch per foot
- Primarily relies on sealing tape or compound
- BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper):
- Originates from the United Kingdom
- Has a 55-degree included angle
- Tapered 1 in 20
- Primarily relies on metal-to-metal contact for sealing
These differences make NPT and BSPT threads incompatible. Attempting to connect them will likely result in:
- Cross-threading
- Leaks
- Damaged threads
BSPP vs NPT
BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel) and NPT (National Pipe Taper) are both pipe thread standards, but with key differences:
| Feature | BSPP | NPT |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Profile | Parallel (no taper) | Tapered |
| Sealing Mechanism | Primarily relies on sealing compounds (e.g., PTFE tape) | Primarily relies on sealing compounds (e.g., PTFE tape) |
| Common Usage | Primarily used in hydraulic and pneumatic systems | Primarily used in general plumbing and gas applications |
| Interchangeability | Not interchangeable with NPT | Not interchangeable with BSPP |
Key Takeaways:
- BSPP threads are parallel, while NPT threads are tapered.
- Both standards typically rely on sealing compounds for a tight seal.
- BSPP and NPT threads are not compatible and cannot be interchanged.
Visual Comparison:
Remember: Always refer to the specific standards documents for precise dimensions and tolerances.
Related: SAE vs NPT: What Are Differences Between Them?
Conclusion
By understanding the key differences between BSP and NPT fittings, you can ensure a secure and reliable connection in your project. Remember to consider regional compatibility, application pressure, and existing components when selecting.
If you’re unsure about the appropriate fitting or need assistance with finding the right solution for your specific needs, don’t hesitate to contact our team of experts at Kingdaflex.
As a leading hose fitting manufacturer with a global reach, we offer a wide range of BSP and NPT fittings in various sizes and materials to cater to diverse applications. We’re committed to providing you with the right tools and expertise to




