Hydraulic hose pressure testing is a critical aspect of ensuring the safety and efficiency of hydraulic systems. Among the key parameters evaluated, working pressure and burst pressure stand out as fundamental indicators of a hose’s performance and reliability. Understanding the distinction between these two pressure ratings is essential for selecting the appropriate hose and maintaining system integrity.
This blog delves into the intricacies of hydraulic hose pressure testing, with a focus on working versus burst pressure. We’ll explore the definitions of these terms, their significance in real-world applications, and the importance of adhering to industry standards. By demystifying these concepts, we aim to provide valuable insights for professionals and enthusiasts alike, empowering them to make informed decisions regarding hydraulic hose selection and maintenance.
What Is Hydraulic Hose Pressure Testing
-
 SAE 100R14 / Teflon Hose(Inner Corrugated Tube)
SAE 100R14 / Teflon Hose(Inner Corrugated Tube) -
 SAE 100R6 | Hydraulic Hose
SAE 100R6 | Hydraulic Hose -
 SAE 100R15 | Hydraulic Hose
SAE 100R15 | Hydraulic Hose -
 SAE 100R13 | Hydraulic Hose
SAE 100R13 | Hydraulic Hose -
 SAE 100R12 | 4 Wire Spiral Hydraulic Hose
SAE 100R12 | 4 Wire Spiral Hydraulic Hose -
 SAE 100 R14 / Teflon Hose (Inner Smooth Tube)
SAE 100 R14 / Teflon Hose (Inner Smooth Tube) -
 SAE 100R17 | Hydraulic Hose
SAE 100R17 | Hydraulic Hose -
 SAE 100R16 | Hydraulic Hose
SAE 100R16 | Hydraulic Hose -
 SAE 100R2A / DIN EN853 2ST
SAE 100R2A / DIN EN853 2ST -
 SAE 100R1A/DIN EN853 1ST
SAE 100R1A/DIN EN853 1ST -
 SAE 100R1AT/ DIN EN853 1SN
SAE 100R1AT/ DIN EN853 1SN
Hydraulic hose pressure testing is a critical procedure that involves subjecting hydraulic hoses to controlled levels of pressure to evaluate their structural integrity and performance. This type of hydraulic hose testing is essential to ensure that hoses can withstand the pressures they will encounter during operation, preventing failures that could lead to equipment damage, fluid leaks, and safety hazards.
The primary goal of pressure testing is to verify that hoses meet industry standards and manufacturer specifications, guaranteeing their reliability in real-world applications. By simulating operating conditions, testers can identify weaknesses or defects in the hose’s construction, such as leaks, bulges, or ruptures. This process is vital for maintaining the safety and efficiency of hydraulic systems across various industries.
Hydraulic Hose Testing Standards
Hydraulic hose testing standards are essential for guaranteeing the safety and reliability of hydraulic systems. These standards outline the procedures and parameters for conducting various tests, ensuring hoses meet specific performance criteria.
Adherence to these standards is crucial for preventing failures, minimizing downtime, and protecting personnel from potential hazards. Organizations like the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) develop and maintain these standards.
Here are some key aspects covered by hydraulic hose testing standards:
- Proof Pressure Test: Verifies the hydraulic hose’s ability to withstand a pressure significantly higher than its working pressure without permanent deformation.
- Burst Pressure Test: Determines the maximum pressure the hydraulic hose can withstand before rupturing, providing a safety margin.
- Impulse Test: Evaluates the hose’s resistance to repeated pressure fluctuations, simulating the cyclic stresses of real-world applications.
- Leakage Test: Checks for any leaks under pressure, ensuring the hydraulic hose’s integrity and preventing fluid loss.
- Temperature Test: Assesses the hydraulic hose’s performance under extreme temperature conditions, ensuring it maintains its properties.
- Flexibility and Bend Radius Test: Evaluates the hydraulic hose’s ability to bend and flex without damage, ensuring proper installation and operation.
- Dimensional Stability Test: Checks for changes in hydraulic hose dimensions after hydraulic hose pressure testing, ensuring it maintains its shape and size.
Hydraulic Hose Pressure Test Procedure
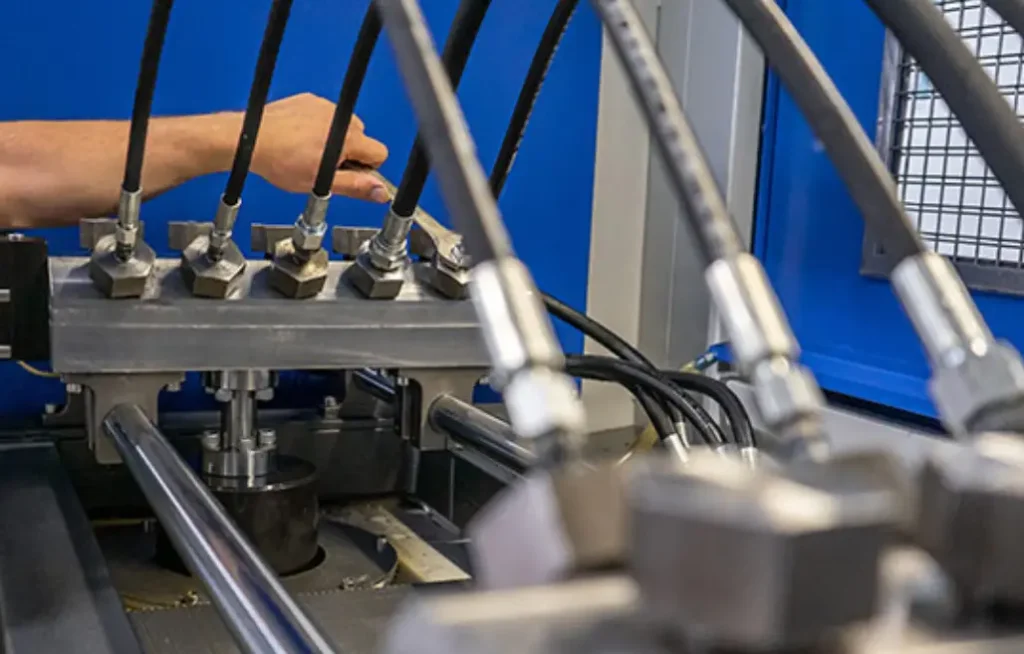
Hydraulic hose pressure testing is essential for verifying the integrity and safety of hydraulic systems. Following a structured procedure ensures accurate results and minimizes the risk of failures. This guide outlines the steps involved in conducting a hydraulic hose pressure test.
Tools Needed for Hydraulic Hose Pressure Testing:
- Hydraulic test pump with pressure gauge
- Appropriate fittings and adapters
- Hydraulic fluid compatible with the hose
- Safety enclosure or shields
- Measuring tools (calipers, tape measure)
- Leak detection spray or solution
- Safety glasses and gloves
- Timer or stopwatch
Step 1: Preparing the Test Hose and System
The initial phase involves meticulous preparation. Begin by visually inspecting the hydraulic hose for any signs of damage, such as cracks, abrasions, or deformities. Ensure the hose is clean and free of debris that could interfere with the test. Select the correct fittings and adapters to connect the hose to the test pump, ensuring a secure and leak-free connection. Fill the hydraulic test pump with the appropriate hydraulic fluid, and calibrate the pressure gauge to ensure accurate readings.
Proper preparation is paramount to avoid errors that could compromise the test’s outcome. It is essential to double-check all connections and to be sure that the proper fluid is used.
The safety enclosure or shields should be positioned around the test setup to contain any potential hose ruptures or fluid sprays. This protective measure safeguards personnel from high-pressure fluid hazards.
Step 2: Executing the Pressure Test
With the setup complete, initiate the pressure test by gradually increasing the pressure in the hose using the test pump. Adhere to the specified test pressure, as defined by industry standards or manufacturer guidelines. Maintain this pressure for a predetermined duration, typically several minutes, to assess the hose’s ability to withstand sustained pressure. Throughout the test, carefully monitor the pressure gauge for any pressure drops, which could indicate leaks or hose expansion.
Visually inspect the hose for any signs of deformation, bulging, or leakage during the test. Use a leak detection spray or solution to identify any subtle leaks at the fittings or along the hose length. Record all pressure readings and observations meticulously.
Careful observation of the hose, and the pressure gauge, is very important. Any abnormalities need to be recorded.
Step 3: Recording and Interpreting Test Results
Upon completion of the pressure test, meticulously record all data, including pressure readings, duration, and any observed anomalies. Compare the test results with the acceptance criteria outlined in industry standards or manufacturer specifications. Document any instances of leaks, deformations, or failures, noting their location and severity.
Generate a comprehensive test report that details the test setup, procedure, and results. This report should include pressure readings, observations, and any deviations from the acceptance criteria. The test report serves as a crucial document for evaluating the hose’s performance and determining its suitability for the intended application.
Accurate documentation of all test results is vital for determining the quality of the hydraulic hose, and for future reference.
Hydraulic Hose Working Pressure and Burst Pressure
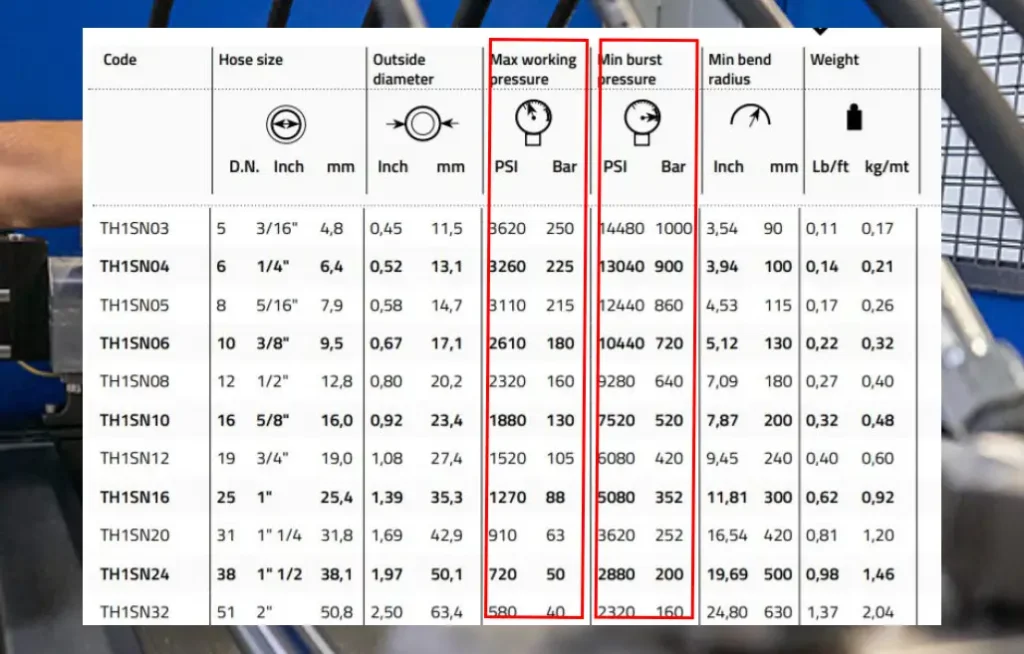
Hydraulic hose working pressure and burst pressure are vital specifications for safe and efficient hydraulic system operation.
Working Pressure: This is the maximum pressure a hydraulic hose is designed to handle continuously under normal operating conditions. It’s the upper limit for sustained pressure without risking premature failure or degradation. Operating above the working pressure can lead to leaks, reduced hose lifespan, and potential safety hazards.
Burst Pressure: This is the absolute maximum pressure a hydraulic hose can withstand before it ruptures. It’s significantly higher than the working pressure, providing a crucial safety margin. As you pointed out, a common industry standard is that the burst pressure should be at least four times the working pressure. This 4:1 safety factor accounts for pressure spikes, surges, and other unexpected events that can occur in hydraulic systems.
Here’s a recap of the importance of these pressures:
- Safety: The 4:1 safety factor is paramount for preventing catastrophic failures and protecting personnel and equipment.
- Reliability: Operating within the working pressure range ensures a longer, more predictable hose lifespan and reduces the risk of downtime.
- Performance: Proper selection of hoses with appropriate working and burst pressures optimizes hydraulic system performance and efficiency.
Hydraulic Hose Pressure Rating

The hydraulic hose pressure rating is a crucial specification that indicates the maximum pressure a hydraulic hose can safely handle during operation. This rating is typically expressed in pounds per square inch (psi) or bar and is determined by the hose’s construction, materials, and reinforcement layers. Selecting a hose with an appropriate pressure rating is essential to prevent failures, leaks, and potential safety hazards in hydraulic systems.
The pressure rating is influenced by several factors, including the number and type of reinforcement layers (e.g., steel wire braids or spirals), the hose’s inner diameter, and the materials used in its construction. Industry standards, such as those published by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), define specific pressure ratings for various hydraulic hose types. Understanding these standards is critical for choosing the right hose for a given application.
Here is a simplified chart showing common SAE hydraulic hose types and their general pressure ratings:
| SAE Hose Type | Description | Typical Working Pressure (psi) |
| SAE 100R1 | Single wire braid reinforced rubber hydraulic hose | 1,000 – 3,000 |
| SAE 100R2 | Double wire braid reinforced rubber hose | 3,000 – 6,000 |
| SAE 100R7 | Thermoplastic hydraulic hose | 1,000 – 3,000 |
| SAE 100R12 | Four spiral wire reinforced rubber hose | 4,000 – 6,000 |
| SAE 100R13 | Multi spiral wire reinforced very high pressure | 5,000 – 8,000+ |
| SAE 100R15 | Multi spiral wire reinforced extreme high pressure | 6,000 – 10,000+ |
Conclusion
In conclusion, comprehending the distinction between hydraulic hose working pressure and burst pressure is crucial for ensuring hydraulic system safety and efficiency. Operating within the working pressure parameters guarantees longevity and reliability, while the burst pressure acts as a vital safety buffer against unexpected pressure surges. This understanding minimizes the risk of catastrophic failures and maximizes system uptime.
Adhering to industry standards and recommended safety factors, like the 4:1 ratio between burst and working pressure, is essential for preventing accidents and equipment damage. Regular pressure testing and informed hose selection are paramount in maintaining a secure and productive hydraulic environment.
For reliable, high-quality hydraulic hoses that meet stringent pressure requirements, consider Kingdaflex. We offer a diverse range of wholesale hydraulic hoses designed to withstand demanding applications. Contact us today to explore our product offerings and ensure your hydraulic systems operate with optimal safety and performance.




