Installing hydraulic fittings correctly is paramount for the safety and efficiency of any hydraulic system. Improper installation can lead to dangerous leaks, system failure, and costly downtime. This guide will walk you through the essential steps to ensure a secure and reliable connection, transforming what might seem like a complex task into a manageable one.
Whether you’re replacing a worn-out hose or building a new hydraulic circuit, understanding the nuances of fitting installation is crucial. By following these best practices, you’ll minimize the risk of operational issues and maximize the lifespan of your hydraulic components, ensuring your machinery runs smoothly and safely.
When to Use Hydraulic Fittings?
Hydraulic fittings are essential components used in various scenarios where fluid power needs to be transmitted efficiently and safely. Their primary purpose is to connect hoses, tubes, and pipes to hydraulic components like pumps, cylinders, and valves, ensuring a sealed and robust pathway for high-pressure hydraulic fluid.
- When assembling new hydraulic systems: Every new hydraulic setup, whether for industrial machinery or mobile equipment, requires fittings to create the necessary fluid pathways. These fittings are crucial for connecting all the individual components into a functional, pressurized circuit, allowing for proper operation.
- During repairs or maintenance: When a hydraulic hose or component fails, fittings are used to replace the damaged part and restore system integrity. This often involves disconnecting old fittings and installing new ones, which is critical for bringing machinery back online quickly and safely after a breakdown.
- For system modifications or upgrades: If a hydraulic system needs to be expanded, reconfigured, or upgraded for different performance requirements, new fittings are indispensable. They enable the integration of additional components or the rerouting of fluid lines, adapting the system to new operational demands without compromising pressure.
- To connect different types of hydraulic lines: Hydraulic systems often utilize a combination of rigid pipes and flexible hoses. Fittings provide the necessary transitions between these different line types, allowing for secure connections that can accommodate both stationary and moving parts within the complex hydraulic circuit.
How to Install Hydraulic Fittings?
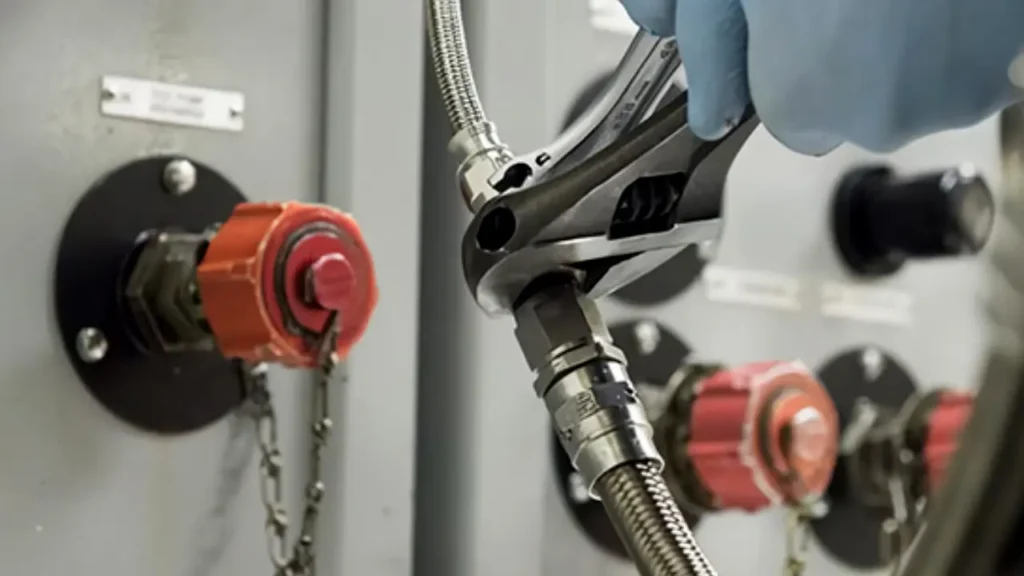

Installing hydraulic fittings correctly is paramount for the safe and efficient operation of any hydraulic system. Improper installation can lead to leaks, system failure, and even hazardous conditions due to high-pressure fluid.
This guide outlines the essential steps about how to install hydraulic hose fittings in the following:
Step 1: Prioritize Safety and Preparation
Before beginning any installation, always ensure the hydraulic system is completely depressurized and locked out to prevent accidental activation. This critical safety measure eliminates the risk of high-pressure fluid injection injuries or unexpected machinery movement during the installation process. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety glasses, gloves, and sturdy work boots, to protect against potential hazards.
Tools Needed for Hydraulic Fitting Installation
Proper installation of hydraulic fittings necessitates a specific set of tools to ensure secure, leak-free connections and prevent damage to components. Using the right tools is crucial for both efficiency and safety in hydraulic system assembly and maintenance.
- Cleaning Brushes/Compressed Air: Used to clean hoses and fittings, removing debris that could contaminate the hydraulic system.
- Hose Cutters: Specialized tools designed to make clean, square cuts on hydraulic hoses, preventing fraying and ensuring proper fitting seating.
- Wrenches (Open-end, Adjustable, or Hydraulic Fitting Wrenches): Used to tighten fittings to the correct torque. Hydraulic fitting wrenches are designed to grip multiple sides of the fitting for better leverage and to prevent rounding.
- Crimping Machines: Essential for installing crimp-style hydraulic fittings, these machines apply precise pressure to secure the fitting onto the hose according to manufacturer specifications.
- Skiving Tools: Used to remove outer covers or inner tubes of hydraulic hoses, exposing reinforcement layers for specific fitting types.
- Torque Wrenches: Critical for tightening fittings to the manufacturer’s recommended torque specifications, preventing overtightening (which can damage fittings) or undertightening (which can lead to leaks).
- Thread Sealant/Tape: Applied to male threads of fittings to create a leak-proof seal and prevent fluid escape.
Step 2: Prepare the Hydraulic Hose
Accurate hose length is crucial. Measure the required length carefully, accounting for bends, movement, and potential routing constraints within the machinery. Use a sharp, specialized hose cutter to make a clean, square cut. A ragged or uneven cut can compromise the seal and reduce the fitting’s ability to grip the hose securely.
Once the hose is cut, ensure the inside is free of any debris from the cutting process. Use compressed air to blow out any particles, or a dedicated cleaning brush. For certain types of fittings, skiving (removing a portion of the hose’s outer cover or inner tube) might be necessary to expose the reinforcement layer. Always refer to the fitting manufacturer’s instructions for precise skiving specifications, as incorrect skiving can lead to premature hose failure.
Step 3: Install the Hydraulic Fitting onto the Hydraulic Hose
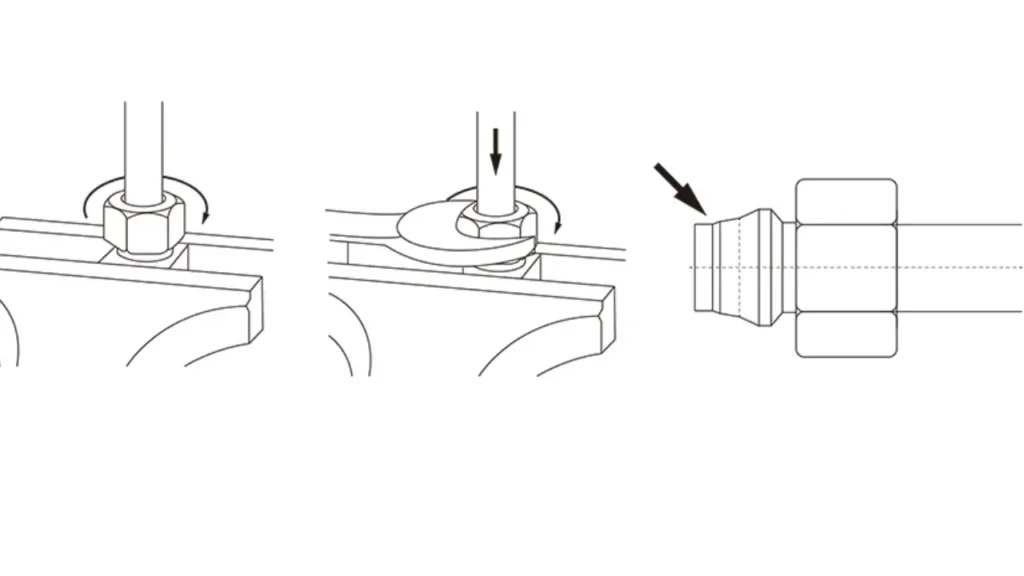
For reusable fittings, lubricate the threads of the fitting and the hose with a compatible hydraulic fluid to ease assembly and prevent damage to the hose inner tube. Carefully thread the fitting onto the hose, ensuring it goes on straight to avoid cross-threading. For two-piece reusable fittings, thread the collar onto the hose first, then insert the stem of the fitting into the hose and tighten.
For crimp-style fittings, this step involves using a crimping machine. Follow the manufacturer’s crimping specifications precisely, including the correct die size and crimp diameter. An incorrect crimp can result in a weak connection prone to leaks or a fitting that damages the hose, leading to early failure. Always perform a visual inspection of the crimped fitting to ensure it is symmetrical and securely attached.
Step 4: Connect the Hydraulic Hose Assembly to the Component
Before making the final connection, ensure the threads on both the fitting and the component port are clean and free of any debris or old sealant. If required, apply a compatible thread sealant (e.g., PTFE tape or liquid sealant) to the male threads of the fitting. Be careful not to apply too much, as excess sealant can enter the hydraulic system and cause blockages.
Carefully thread the hose assembly onto the component port by hand to ensure proper alignment and avoid cross-threading. Once finger-tight, use the appropriate wrenches to tighten the connection to the manufacturer’s recommended torque specifications. Overtightening can damage threads or distort the fitting, while undertightening can lead to leaks. Always use a torque wrench when specified to achieve the correct tightness.
Step 5: Final Inspection and Testing
After installation, conduct a thorough visual inspection of all connections to ensure they are secure and properly aligned. Check for any signs of thread damage or improper seating. Ensure hoses are routed correctly, avoiding sharp bends, abrasive surfaces, and heat sources that could compromise their integrity over time.
Before putting the system back into full operation, pressurize the hydraulic system slowly and carefully. Monitor all newly installed connections for any signs of leaks. Address any leaks immediately by re-tightening the fitting slightly or, if necessary, disassembling and re-installing the fitting. A leak-free system is essential for safety, efficiency, and the longevity of hydraulic components.
What is the Most Common Method of Attaching Reusable Fittings to Hydraulic Hose?
The most common method for attaching reusable fittings to hydraulic hoses involves a two-piece design that is assembled by hand and then tightened with wrenches. This method is often favored for its convenience in field repairs or when specialized crimping equipment is not readily available. Reusable fittings are designed to be disassembled and reassembled, allowing for hose replacement without needing to discard the entire fitting.
This attachment typically involves a socket (or ferrule) and a nipple (or stem) that thread together. The hose is first inserted into the socket, and then the nipple is screwed into the socket, compressing the hose between the two components to create a secure, leak-tight seal.
- Thread-On Assembly: The most widespread method involves threading the hose into a female socket with a left-hand thread until it bottoms out. Then, a male stem or nipple, which typically has a right-hand thread, is screwed into the socket, forcing it into the hose’s inner diameter. This process compresses the hose wall between the socket and the nipple, creating a mechanical grip and a fluid-tight seal.
- Lubrication and Wrenching: Proper lubrication of the hose and fitting threads is crucial to facilitate assembly and prevent damage to the hose’s inner tube during the threading process. Once hand-tight, wrenches are used to fully tighten the connection. The socket usually has an external hex or square for gripping with a wrench, while the nipple often has an internal hex or a shaped end for another wrench, allowing for counter-rotation to fully engage the threads and create a secure assembly.
How to Select the Right Hydraulic Fittings?
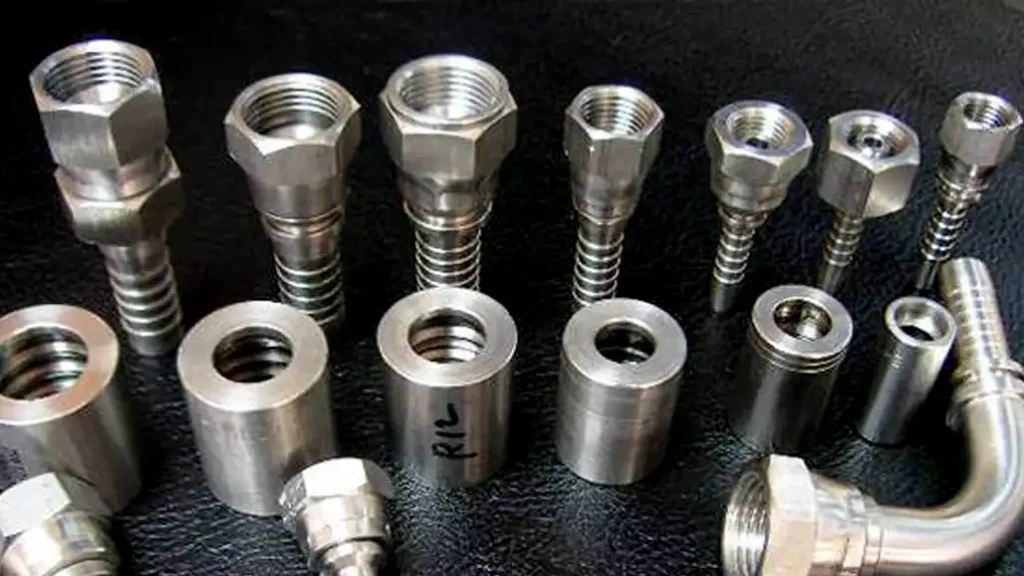

Selecting the right hydraulic fittings is a critical decision that directly impacts the safety, efficiency, and longevity of any hydraulic system. An incorrect fitting can lead to leaks, system failure, reduced performance, and even catastrophic accidents due to the high pressures involved. This process requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure optimal compatibility and functionality within your specific application.
The selection process involves matching the fitting to the hose, the component port, the fluid type, and the operating environment. A systematic approach, considering each variable, will ensure you choose fittings that create secure, leak-free connections capable of withstanding the demands of your hydraulic system.
- Hose Type and Size: The most fundamental factor is matching the fitting to the specific hydraulic hose. Hoses have varying inner diameters (ID), outer diameters (OD), and construction (e.g., single-braid, multi-spiral). Fittings are designed to work with particular hose types and sizes, ensuring a proper seal and secure grip. Always refer to the hose manufacturer’s specifications for compatible fittings.
- Pressure Rating: Hydraulic systems operate at a wide range of pressures. It is crucial to select fittings that have a pressure rating equal to or greater than the maximum operating pressure of your system. Using fittings rated below the system’s maximum pressure can lead to dangerous ruptures and leaks, posing significant safety risks.
- Fluid Compatibility: The type of hydraulic fluid used in the system dictates the material compatibility required for the fitting’s seals (O-rings, etc.) and sometimes the fitting material itself. Incompatible materials can degrade, swell, or dissolve, leading to leaks and system contamination. Always check that the fitting’s seals are compatible with your hydraulic fluid.
- Connection Type and Thread Style: Hydraulic components use various connection types and thread styles (e.g., JIC, ORFS, NPT, BSPP, SAE). The fitting must match the thread style of the component port it’s connecting to. Mismatched threads will not seal properly and can cause irreparable damage to both the fitting and the component.
- Application and Environment: Consider the environmental conditions where the hydraulic system will operate. Factors like temperature extremes, vibration, corrosive elements, or abrasive dust can influence the choice of fitting material or protective coatings. For instance, stainless steel fittings might be preferred in corrosive marine environments.
- Material and Construction: Fittings are made from various materials like carbon steel, stainless steel, and brass. Carbon steel is common for general industrial use, while stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance. The construction (e.g., one-piece crimp, two-piece reusable) also plays a role, influencing ease of assembly and reusability.
Tips for Hydraulic Fitting Installation
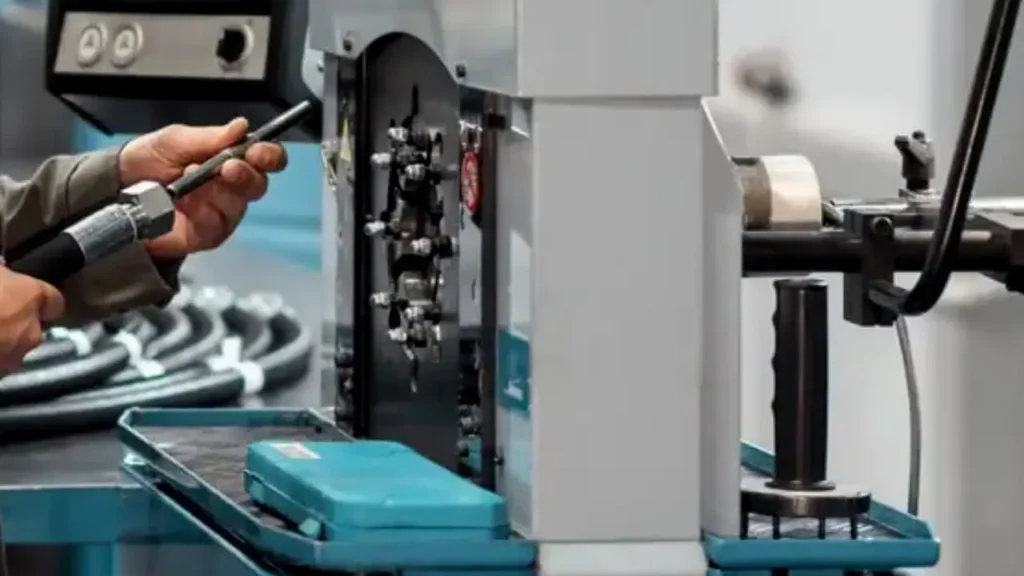

Proper installation of hydraulic fittings is paramount for system integrity and safety, minimizing leaks and maximizing operational lifespan. Adhering to best practices during installation can prevent costly downtime and premature component failure.
- Always Depressurize the System: Before starting any work, ensure the hydraulic system is fully depressurized and locked out. This prevents accidental fluid injection injuries or unexpected machinery movement.
- Use the Right Tools: Employ specialized hydraulic wrenches, hose cutters, and crimping machines (if applicable). Using incorrect tools can damage fittings, hoses, and lead to unsafe connections.
- Cleanliness is Crucial: Ensure hoses, fittings, and component ports are meticulously clean. Even small particles of dirt or debris can contaminate the hydraulic fluid, leading to component wear and system failure.
- Measure and Cut Hoses Accurately: Precise hose length and a clean, square cut are vital for proper fitting engagement and sealing. Ragged cuts can compromise the seal and reduce fitting grip.
- Lubricate Threads and Hoses: Apply a compatible hydraulic fluid to the threads of reusable fittings and the inner diameter of the hose. This eases assembly, prevents damage to the hose, and helps achieve proper torque.
- Avoid Cross-Threading: Always start threading fittings by hand to ensure proper alignment. Cross-threading can permanently damage threads on both the fitting and the component port, leading to leaks.
- Torque to Manufacturer Specifications: Use a torque wrench to tighten fittings to the recommended torque. Overtightening can weaken or damage components, while undertightening leads to leaks.
- Inspect and Test Thoroughly: After installation, visually inspect all connections for proper seating and alignment. Slowly pressurize the system and carefully check for any leaks before putting the equipment back into full service.
- Proper Hose Routing: Route hoses to avoid sharp bends, kinks, abrasion points, and exposure to excessive heat or corrosive materials. Proper routing extends hose life and prevents premature failure.
Conclusion
Successfully installing hydraulic fittings is a fundamental skill for anyone working with hydraulic systems, ensuring optimal performance and safety. By carefully following each step, from proper hose preparation to correct torquing, you can create reliable, leak-free connections that stand the test of time and pressure.
Paying attention to detail throughout the installation process minimizes the risk of system failures, fluid leaks, and costly downtime. A well-installed fitting contributes directly to the efficiency and longevity of your hydraulic equipment, safeguarding both your investment and operational continuity.
For all your hydraulic system needs, including a comprehensive selection of high-quality wholesale hydraulic fittings, we are your trusted partner. Our extensive inventory ensures you’ll find the right components to complete your projects efficiently and effectively.




