Choosing the right hydraulic hose is about more than just size and pressure rating; media compatibility is equally critical. The fluid that flows through your hydraulic system can be highly corrosive or chemically active. If your hose material is not compatible with the fluid, it will degrade, leading to leaks, bursts, and catastrophic system failure.
Understanding the chemical resistance of your hydraulic hoses is a cornerstone of a reliable and safe system. This guide will explore why media compatibility is so vital and how a mismatch can cause expensive downtime and equipment damage. By making an informed choice, you can significantly extend the life of your entire hydraulic system.
What is Media in Hydraulic Hoses?
In the industry of hydraulic hoses, media refers to the fluid that is being conveyed through the hose. This is a crucial factor because the hose material must be chemically compatible with the fluid to prevent degradation, swelling, or premature failure. Incompatible fluids can break down the inner tube of the hose, leading to contamination of the hydraulic system, leaks, and potential safety hazards.
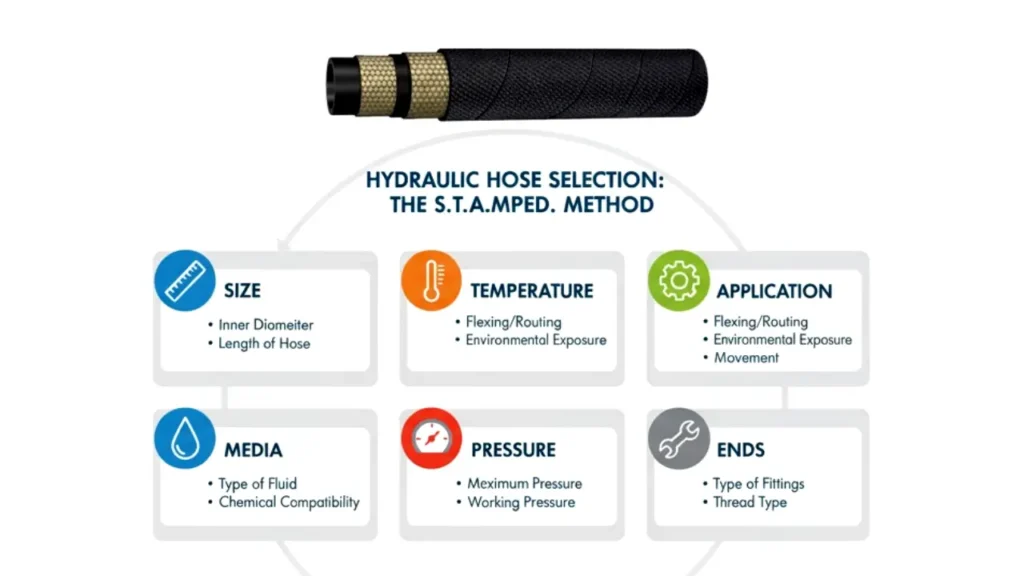
The industry uses a helpful acronym, STAMPED, to ensure all critical factors are considered when selecting a hydraulic hose.
- Size: The inner diameter and length of the hose.
- Temperature: The temperature of both the fluid and the surrounding environment.
- Application: How the hose will be used, including flexing, routing, and environmental exposure.
- Media: The type of fluid being conveyed.
- Pressure: The maximum and working pressure of the system.
- Ends: The type of fittings required to connect the hose.
- Delivery: The delivery or volume requirements of the fluid.
What Media Can Hydraulic Hose Convey
A hydraulic hose is specifically engineered to convey high-pressure hydraulic fluid, which is typically a mineral or synthetic oil. However, its applications extend beyond just hydraulic systems. The hose’s reinforced construction with multiple layers of steel wire or textile braid allows it to handle and transfer various other media safely, provided the fluid is compatible with the hose’s inner tube and outer cover materials. This makes them suitable for a wide range of industrial and mobile applications where high pressure is a factor.
- Hydraulic Fluid: This is the primary medium for which hydraulic hoses are designed. They are built to withstand the high pressures needed to power hydraulic systems in machinery, vehicles, and industrial equipment.
- Petroleum-Based and Synthetic Oils: Beyond standard hydraulic fluid, these hoses can also convey various types of lubricating oils and transmission fluids, which are essential in many industrial and automotive systems.
- Water and Water-Based Fluids: Some hydraulic hoses are specifically rated to handle water or water-based fluids, such as water-glycol solutions. These are often used in systems that require fire-resistant fluids or in applications where oil contamination is a concern.
- Compressed Air and Gases: While not their primary function, certain hydraulic hoses are also designed to convey high-pressure compressed air and some gases, which are required for specific industrial and pneumatic tools.
- Select Chemicals: Depending on the specific hose material (e.g., inner tube lining), a hydraulic hose can be resistant to a limited range of chemicals. However, it is crucial to verify chemical compatibility with the manufacturer’s specifications to prevent material degradation and failure.
What is Hydraulic Hose Media Compatibility?
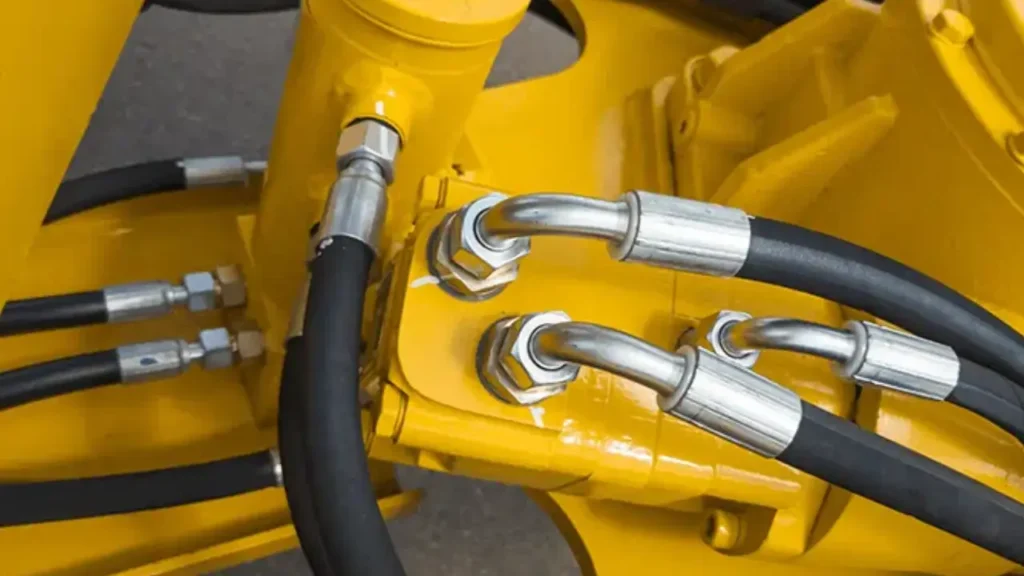

Hydraulic hose media compatibility refers to the ability of the hose’s inner tube, fittings, and seals to resist chemical degradation from the fluid flowing through them. This is a crucial factor in hydraulic system design because using a hose that is incompatible with the fluid can cause the hose material to swell, soften, or crack. This leads to reduced flow, leaks, and potential system failure.
- Chemical Resistance: Different hose materials, such as synthetic rubber or thermoplastics, have varying levels of resistance to specific chemicals, including hydraulic oils, water, and various solvents. A hose that is compatible with one type of fluid may not be with another.
- Degradation: When an incompatible fluid flows through a hose, it can break down the inner tube, creating particles that contaminate the entire hydraulic system and damage sensitive components like pumps and valves.
- Safety: A compromised hose due to chemical incompatibility is a significant safety hazard. A burst hose under high pressure can cause serious injury and lead to dangerous fluid spills.
Factors Influencing Hydraulic Hose Media Compatibility
Several factors influence the media compatibility of a hydraulic hose, and understanding them is crucial for preventing hose degradation and system failure. The interaction between the fluid and the hose material is not simple and can be affected by various environmental and operational conditions. A mismatch in compatibility can lead to the hose’s inner tube swelling, hardening, or cracking, which compromises its ability to contain the fluid and maintain pressure.
Fluid Composition:
The specific chemical makeup of the hydraulic fluid is the primary factor. Different fluids—such as petroleum-based oils, synthetic fire-resistant fluids, or water-based emulsions—have varying chemical properties that require specific hose materials for resistance. For example, a nitrile hose is generally excellent for petroleum-based fluids, but it may not be suitable for phosphate ester-based fluids, which require materials like Viton.
Operating Temperature:
Both the temperature of the fluid and the surrounding environment affect compatibility. Higher temperatures can accelerate chemical reactions between the fluid and the hose material, causing degradation to happen much faster. A hose that is compatible with a fluid at room temperature may fail quickly when exposed to the same fluid at an elevated temperature.
Pressure and Flow Rate:
The pressure and velocity of the fluid can also influence compatibility. High-pressure cycles and rapid fluid flow can cause stress on the hose material, and if the hose is already weakened by chemical incompatibility, this can lead to premature failure.
Additives and Contaminants:
The presence of additives in the fluid or external contaminants can alter the fluid’s chemical properties and affect its compatibility with the hose material. Even small amounts of an incompatible substance can start a degradation process over time.
Common Hydraulic Fluids and Their Compatibility
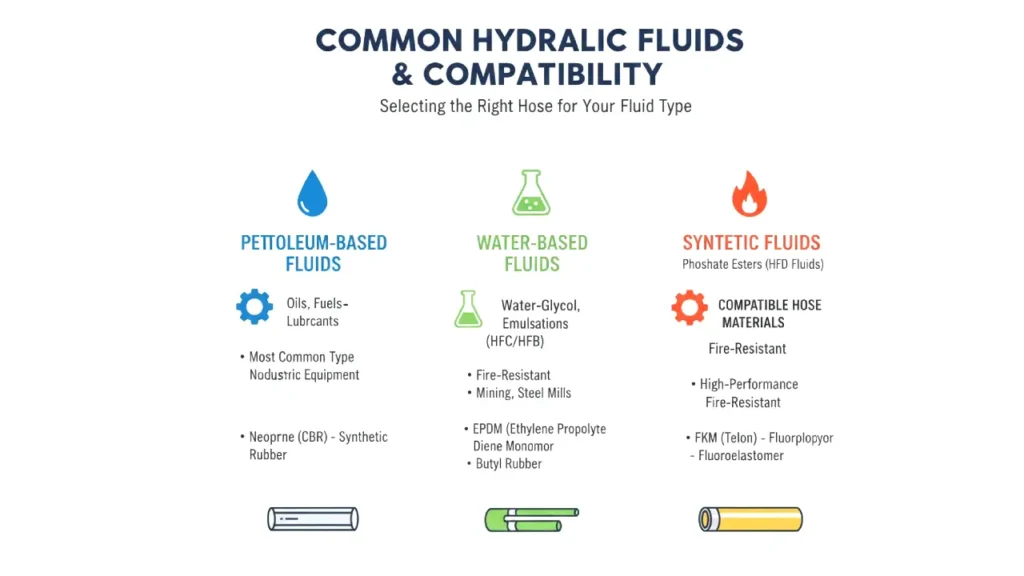
Matching a hydraulic hose to the fluid it will carry is a fundamental step in ensuring system safety and longevity. The most common hydraulic fluids fall into a few key categories, each with specific compatibility requirements for the hose’s inner tube material. A mismatch can lead to rapid hose degradation, resulting in leaks, system contamination, and even catastrophic failure.
Therefore, it is essential to consult manufacturer compatibility charts before selecting a hose for your application.
- Petroleum-Based Fluids: The most common type of hydraulic fluid, these are typically compatible with synthetic rubber materials like Nitrile (NBR) and Neoprene (CR). These hoses are widely available and used in a vast majority of industrial and mobile equipment.
- Water-Based Fluids: This category includes water-glycol and water-oil emulsions (HFC, HFB fluids) and is often used where fire resistance is a priority, such as in mining or steel mills. These fluids require specialized hoses, often with inner tubes made of Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM), as standard petroleum-compatible rubber would swell and fail.
- Synthetic Fluids: These fluids, such as phosphate esters or polyol esters, are engineered for high-performance or fire-resistant applications (HFD fluids). They are highly aggressive and require specific hose materials, most commonly PTFE (Teflon) or specially formulated fluoropolymer elastomers like Viton, as they would destroy standard rubber hoses.
How to Test Hydraulic Hose Media Compatibility?
Even when using a manufacturer’s chart, it’s wise to test media compatibility in-house, especially for new or custom applications. This process ensures the hydraulic hose will perform reliably with the specific fluid and conditions of your unique system, preventing unforeseen failures.
Consult Hydraulic Hose Manufacturer‘s Data
Begin by thoroughly reviewing the hose manufacturer’s official compatibility charts and data sheets. These documents provide the baseline information on which fluids are compatible with the hose’s inner tube and cover materials, giving you a strong starting point for your selection.
While charts are helpful, they are often for ideal conditions. It is crucial to consider how your operating temperatures, pressures, and potential fluid contaminants might affect compatibility beyond what is listed in the standard data sheets.
Conduct Immersion Testing
For critical applications or where data is unavailable, conduct a controlled immersion test. Place a small sample of the hose material into a sealed container filled with the fluid. The container should be heated to the maximum operating temperature of your system.
After a set period (e.g., 72 hours), remove the sample and check for changes in weight, volume, hardness, and elasticity. Any significant changes, such as swelling or softening, indicate a poor compatibility match that could lead to premature failure.
Perform Live System Testing
The final and most comprehensive step is to test the hose within the actual operating system. Install the hose and monitor its performance under real-world conditions, including system pressure, temperature cycles, and duty cycles.
Regularly inspect the hose for any signs of degradation, such as cracking, leaking, or changes in flexibility. This live test provides the most accurate assessment of the hose’s durability and ensures it can withstand the combined stresses of your specific application.
Conclusion
In conclusion, prioritizing hydraulic hose media compatibility is a fundamental step in ensuring the longevity and safety of your hydraulic system. By carefully matching the hose material to the specific properties of the fluid, you can prevent chemical attacks that lead to premature wear, leaks, and catastrophic failure. This practice is an essential safeguard for your equipment and personnel.
The quality of your hydraulic hoses is directly tied to the overall performance and reliability of your operations. Using substandard or incompatible hoses will inevitably lead to costly and dangerous failures. Investing in a durable hose with the correct media compatibility is a smart financial decision that prevents downtime and protects your valuable assets.
For all your hydraulic needs, including hoses with proven media compatibility, trust Kingdaflex. Our wholesale hydraulic hoses are manufactured to the highest standards, ensuring they can withstand even the most demanding chemical and physical conditions. Contact us today to find the perfect hose solution that guarantees the longevity of your hydraulic system.