When selecting hydraulic fittings, distinguishing between SAE and JIC is crucial for system integrity and safety. While both are prevalent in fluid power applications, they have distinct design specifications that prevent direct interchangeability. This guide will clarify the key differences, ensuring you choose the right fitting for your specific needs.
Understanding these distinctions is vital for preventing costly leaks and system failures. This blog post will delve into the technical characteristics, common applications, and identification methods for SAE and JIC fittings, helping you make informed decisions for reliable hydraulic connections.
What are SAE Fittings?
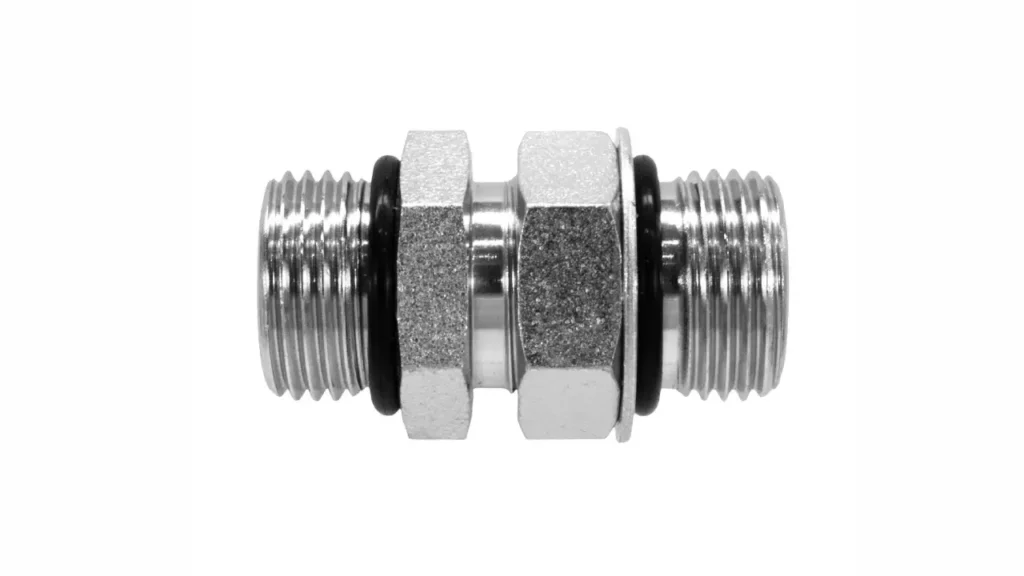

SAE fittings refer to hydraulic connectors designed and manufactured according to standards set by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE). This organization develops a wide array of technical standards for various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and commercial vehicles.
SAE fitting standards govern critical aspects such as dimensions, materials, thread forms, pressure ratings, and performance criteria, ensuring compatibility, safety, and reliability across different hydraulic systems and equipment. Common examples of SAE fitting types include JIC (37-degree flare), SAE 45-degree flare, and O-Ring Face Seal (ORFS) fittings, each with specific design characteristics and applications.
What are JIC Fittings?



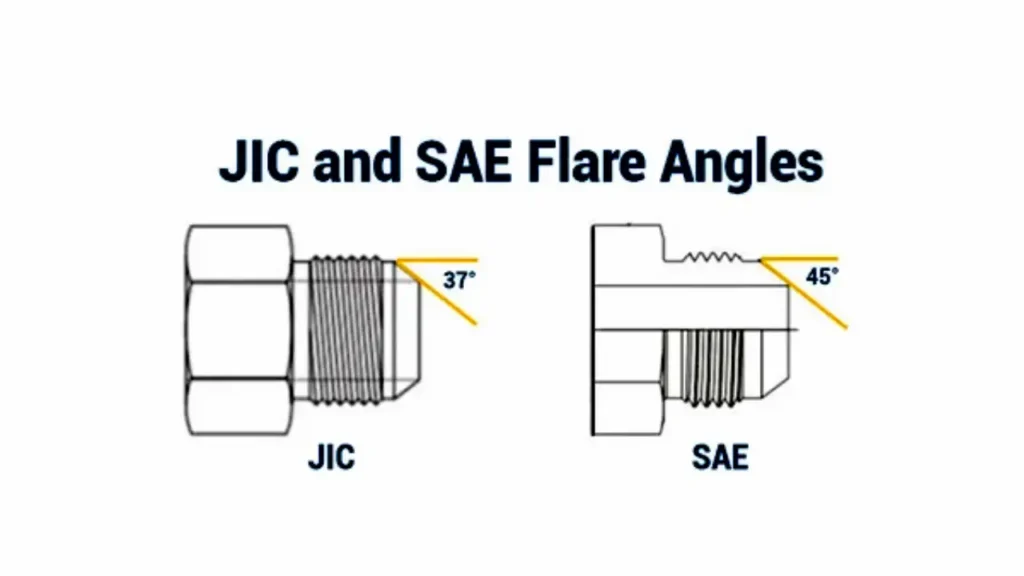
JIC (Joint Industry Council) fittings are a type of hydraulic fitting commonly used in North America and other regions, defined by the SAE J514 standard. They are characterized by a 37-degree flare seating surface, which creates a metal-to-metal seal when the male and female components are tightened together.
This design makes them highly effective for creating leak-free connections in fluid power systems, especially in high-pressure applications within industries like agriculture, construction, and automotive. JIC fittings typically consist of three main parts: the fitting body, a flare nut, and a sleeve that supports the tubing, ensuring a robust and reliable connection.
SAE vs JIC Fittings
Understanding the relationship between SAE and JIC fittings is essential for hydraulic system design. While JIC is a specific type, SAE encompasses broader standards. This comparison will clarify their differences in design, sealing, and application, ensuring proper selection for reliable fluid connections.
Relationship and Definition
SAE, or the Society of Automotive Engineers, is a global organization that develops and publishes technical standards for various engineering fields, including hydraulic components. Therefore, “SAE fittings” is a broad category encompassing many different types of fittings that adhere to SAE-defined specifications.
JIC (Joint Industries Council) fittings are a specific type of hydraulic fitting that falls under the umbrella of SAE standards, specifically SAE J514. When people refer to “SAE vs. JIC,” they are often contrasting the JIC 37-degree flare fitting with other distinct SAE fitting designs, such as the SAE 45-degree flare or SAE O-ring face seal (ORFS) fittings.
Sealing Mechanism and Flare Angle
JIC fittings are characterized by their 37-degree flare angle. The sealing mechanism relies on a metal-to-metal contact where the flared end of the male fitting or tube presses against the coned seat of the female fitting, creating a robust and reliable seal.
Other SAE fitting types employ different sealing mechanisms. For instance, SAE 45-degree flare fittings, commonly found in automotive and refrigeration systems, use a 45-degree flare for sealing. SAE O-ring Face Seal (ORFS) fittings, another SAE standard, utilize an O-ring compressed against a flat face to create a leak-tight seal, offering excellent performance in high-pressure and high-vibration applications.
Thread Type and Standards
JIC fittings utilize Unified National Fine (UNF) straight threads, and their design and performance are standardized under SAE J514. This standardization ensures dimensional consistency and interchangeability among JIC fittings produced by different manufacturers.
Beyond JIC, various other SAE standards dictate thread types and forms for different fitting designs. For example, SAE J512 covers 45-degree flare fittings, which also typically use UNF threads but are distinct from JIC due to their different flare angle and intended applications. ORFS fittings, defined by SAE J1453, also use straight threads, but their sealing is primarily achieved by the O-ring.
Applications
JIC fittings are widely adopted in high-pressure hydraulic systems across industries such as construction, agriculture, and heavy machinery. Their metal-to-metal seal and robust design make them suitable for demanding environments where secure and leak-free connections are critical.
Other SAE fitting types serve diverse applications. SAE 45-degree flare fittings are common in lower-pressure automotive and refrigeration systems. SAE O-ring Face Seal (ORFS) fittings are preferred in mobile equipment and other high-pressure applications where superior vibration resistance and zero leakage are paramount due to their elastomeric seal.
Interchangeability
JIC fittings are inherently designed for interchangeability among themselves due to their strict adherence to the SAE J514 standard. This means a JIC fitting from one manufacturer should reliably connect with a JIC fitting from another, provided both meet the standard.
However, JIC fittings are generally not directly interchangeable with other SAE fitting types (e.g., SAE 45-degree flare, ORFS). Despite some shared thread sizes, the differing flare angles or sealing mechanisms prevent a proper, leak-free connection. Conversion adapters are necessary to connect components designed for different SAE fitting standards.
| Aspect | JIC Fittings (SAE J514) | Other Common SAE Fittings (e.g., SAE 45°, ORFS) |
| Relationship to SAE | A specific type within SAE standards | Other distinct types within SAE standards |
| Sealing Mechanism | 37-degree metal-to-metal flare | 45-degree metal-to-metal flare (SAE 45°), O-ring (ORFS) |
| Thread Type | UNF straight threads | UNF straight threads (SAE 45°, ORFS) |
| Primary Applications | High-pressure hydraulics, construction | Automotive, refrigeration (SAE 45°); High-pressure, vibration-resistant (ORFS) |
| Direct Interchangeability | Yes (among JIC fittings) | No (with JIC fittings, requires adapters) |
How to Choose SAE and JIC Fittings
Choosing between various SAE and JIC fittings primarily depends on the specific application requirements, including pressure, temperature, fluid type, and environmental conditions. Given that JIC is a type of SAE fitting (SAE J514), the decision often boils down to selecting the most appropriate SAE standard for your hydraulic system.
When making your selection, consider the following:
Pressure and Flow Requirements:
- JIC (37-degree flare) fittings are excellent for high-pressure hydraulic applications due to their robust metal-to-metal seal.
- SAE O-Ring Face Seal (ORFS) fittings are also well-suited for high-pressure systems and excel in applications with high vibration due to their elastomeric seal’s ability to absorb shock.
- SAE 45-degree flare fittings are typically used in lower-pressure applications, such as automotive or refrigeration lines.
Sealing Method and Leak Resistance:
- JIC offers a reliable metal-to-metal seal that can be re-made multiple times.
- ORFS fittings provide superior leak-free performance, especially in dynamic applications, due to the positive O-ring seal.
- SAE 45-degree flare fittings are generally less robust against leakage compared to JIC or ORFS in high-pressure or high-vibration scenarios.
Environmental Factors:
Consider temperature ranges, exposure to corrosive substances, and the need for vibration resistance. Different fitting types and materials perform better under specific environmental stresses.
Industry Standards and Compatibility:
Ensure the chosen fitting type aligns with industry standards or equipment specifications for compatibility and ease of maintenance. Mixing different fitting standards without proper adapters can lead to system failure.
Get Hydraulic Fittings from Kingdaflex
JIC fittings are a specific design under the broader SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) standards, particularly SAE J514. Thus, “SAE fittings” is a general category, while “JIC fittings” refers to the distinct 37-degree flare type within that framework.
The crucial takeaway is that JIC is an SAE standard for hydraulic fittings. When discussing “SAE vs. JIC,” it’s often a distinction between the specific 37-degree flare design (JIC) and other fitting types that also conform to various SAE standards, such as O-ring face seal (ORFS) fittings.
For reliable and compatible hydraulic connections, precise identification is key. For all your diverse hydraulic fitting needs, get wholesale hydraulic fittings from Kingdaflex.

