Peristaltic pumps, also known as tube pumps or hose pumps, are positive displacement pumps that use a unique mechanism to transfer fluids. Unlike traditional pumps that use impellers or gears, peristaltic pumps operate by squeezing and releasing a flexible tube or hose to create a vacuum that draws fluid through it.
This design offers several advantages, such as precise control, gentle pumping action, and the ability to handle abrasive or shear-sensitive materials.
In this guide, you will get to know how to use peristaltic pump.
Components of A Peristaltic Pump
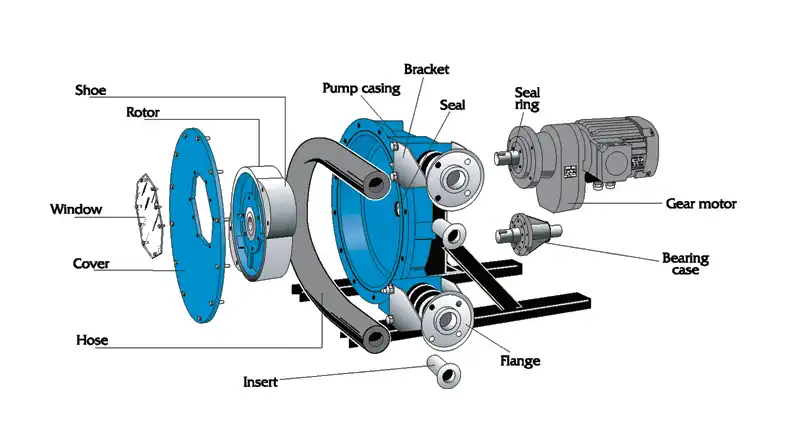
Pump Head
The pump head is the core component of a peristaltic pump. It consists of rollers or shoes that compress and release the tubing, creating the peristaltic action. The number of rollers can vary depending on the pump’s design.
Tubing
The tubing is the conduit through which the fluid flows. It is typically made of materials like silicone, PVC, or rubber, depending on the type of fluid being pumped. Tubing selection is crucial to prevent chemical reactions and ensure compatibility.
Motor
The motor drives the rollers in the pump head, creating the peristaltic motion. It’s essential to choose a motor that suits your application’s flow rate and pressure requirements.
How to Use Peristaltic Pump
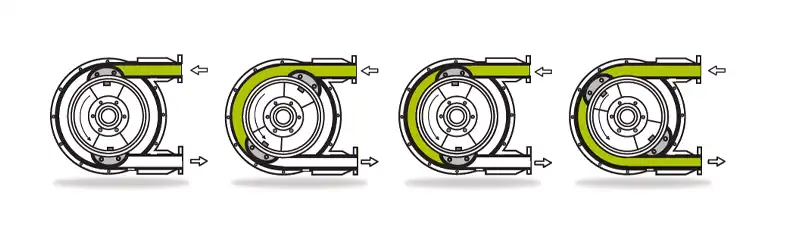
Using a peristaltic pump effectively involves several key steps to ensure accurate and reliable fluid transfer. Whether you’re working in a laboratory, an industrial setting, or any other application that requires precise fluid handling, follow these guidelines on how to use a peristaltic pump:
- Inspect the Pump: Before you begin, visually inspect the peristaltic pump to ensure it’s clean and in good working condition. Check for any loose or damaged parts, and make sure the power source is connected and functioning correctly.
- Prepare Your Workspace: Set up your work area with all the necessary materials, including the peristaltic pump, tubing, and the container or system you’ll be transferring fluid to or from.
- Select the Right Tubing: Choose the appropriate tubing for your specific application. Consider factors such as the type of fluid being pumped, chemical compatibility, temperature resistance, and flexibility. Ensure that the tubing is of the correct size to fit the pump head and connectors.
- Calibrate the Pump: If your peristaltic pump has calibration settings, configure them to achieve the desired flow rate and accuracy. Calibration is especially crucial for applications that require precise fluid delivery, such as laboratory experiments.
- Prime the Pump: Priming is the process of filling the tubing and pump head with the fluid you intend to transfer. This step removes any air bubbles and ensures a continuous and consistent flow. To prime the pump, follow these steps:
- Disconnect the tubing from the pump head.
- Submerge the tubing and the pump head in the fluid reservoir.
- Gradually increase the pump speed until the fluid fills the tubing and exits the pump head.
- Reconnect the tubing to the pump head.
- Adjust Flow Rates: Peristaltic pumps allow you to adjust flow rates easily. You can control the flow by changing the pump’s speed or adjusting tubing dimensions. Be sure to set the flow rate to the desired level for your application.
- Start the Pump: Turn on the peristaltic pump to begin fluid transfer. Monitor the process to ensure that the pump is operating smoothly and that the fluid is flowing as expected.
- Maintenance and Cleaning: Regular maintenance is crucial to prolong the life of your peristaltic pump. This includes cleaning the tubing, inspecting the pump head, and lubricating moving parts as needed. Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines to prevent contamination and ensure optimal performance.
- Safety Precautions: Always observe safety precautions when using peristaltic pumps. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) as needed, especially when handling chemicals or potentially hazardous fluids. Follow safety guidelines for chemical handling and disposal.
- Shut Down Properly: When you have completed your fluid transfer task, turn off the peristaltic pump and disconnect the tubing. Properly clean and store the tubing, and ensure that the pump is in a safe and secure location.
By following these steps and considering the specific requirements of your application, you can effectively use a peristaltic pump for precise and reliable fluid transfer. Remember that regular maintenance and adherence to safety guidelines are essential for the efficient and safe operation of peristaltic pumps.
Choosing the Right Peristaltic Hose
Selecting the appropriate peristaltic hose is essential to prevent contamination and ensure efficient fluid transfer. Consider factors like chemical compatibility, temperature resistance, and flexibility when choosing tubing for your peristaltic pump.
Calibrating the Pump
Calibrating the pump involves configuring it to achieve the desired flow rate and accuracy. This step is crucial for applications that require precise fluid delivery, such as laboratory experiments or medical procedures.
Prime the Pump
Before you start pumping your desired fluid, it’s essential to prime the pump. Priming involves filling the tubing and pump head with the fluid to remove any air bubbles and ensure a consistent flow.
Adjusting Flow Rates
Peristaltic pumps allow you to adjust the flow rate easily. This flexibility is valuable when dealing with varying fluid requirements. You can control the flow by changing the pump’s speed or adjusting tubing dimensions.
Maintenance and Cleaning
To ensure your peristaltic pump lasts, follow manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines. This includes regular cleaning, inspection, and lubrication of moving parts.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Tubing Blockage
Tubing blockage can occur due to debris or improper tubing installation. To resolve this issue, disassemble the pump head, remove the tubing, and clean or replace it.
Pump Leakage
Leakage can result from damaged tubing or loose connections. Inspect the tubing for cracks or wear and tighten any loose fittings.
Motor Malfunctions
If the motor fails to operate correctly, check the power source and connections. If the problem persists, consult the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide or contact customer support.
Safety Precautions
When using peristaltic pumps, observe safety precautions to protect yourself and the equipment. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and follow chemical handling guidelines.
Applications of Peristaltic Pumps

Peristaltic pumps find a wide range of applications across various industries due to their unique capabilities and advantages. Here’s a more detailed explanation of their applications:
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Peristaltic pumps are extensively used in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes. They provide precise and contamination-free fluid transfer, making them ideal for handling sensitive drugs and chemicals. These pumps are commonly employed for filling vials, transferring fluids during drug formulation, and controlling the flow of reagents in research and development.
- Food and Beverage Industry: In the food and beverage sector, peristaltic pumps play a crucial role in applications where maintaining product integrity is paramount. They are used for pumping liquids with particulates, such as fruit juices with pulp, dairy products, and sauces. The gentle pumping action ensures that delicate food products are not damaged during processing.
- Environmental and Water Treatment: Peristaltic pumps are valuable tools in water and wastewater treatment facilities. They are used for chemical dosing, adding coagulants, flocculants, and pH adjustment agents accurately. The ability to handle aggressive chemicals and adjust flow rates makes them essential in maintaining water quality.
- Laboratory and Scientific Research: Peristaltic pumps are indispensable in laboratory settings, especially for experiments that require precise fluid delivery. They are commonly used in analytical instruments like HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) and for continuous culture feeding in biotechnology research.
- Medical and Healthcare: Peristaltic pumps are vital in medical applications, including drug infusion, dialysis, and blood circulation during surgeries. Their ability to deliver fluids at a controlled and consistent rate is crucial for patient safety and treatment efficacy.
- Chemical Industry: The chemical industry relies on peristaltic pumps for transferring and dosing a wide range of chemicals. These pumps are preferred for applications where chemical compatibility and accuracy are essential, such as in the production of specialty chemicals and petrochemicals.
- Mining and Minerals: Peristaltic pumps are used in mining operations to handle abrasive and corrosive slurries. They can transport tailings, mineral concentrates, and chemical reagents efficiently while minimizing maintenance downtime.
- Biotechnology: In biotechnology and biopharmaceutical processes, peristaltic pumps are employed for cell culture media transfer, fermentation, and harvesting. Their sterile fluid transfer capabilities are critical for maintaining the integrity of biologically sensitive materials.
- Analytical Chemistry: Peristaltic pumps are used in various analytical chemistry applications, including sample introduction in atomic absorption spectroscopy and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS).
- Environmental Monitoring: Environmental monitoring stations often use peristaltic pumps to collect and transport water samples for analysis. Their reliability and ability to handle different sample types make them ideal for long-term data collection.
These diverse applications demonstrate the versatility and reliability of peristaltic pumps across multiple industries. Their ability to provide precise and contamination-free fluid transfer makes them indispensable tools for ensuring product quality, research accuracy, and efficient processes.
Advantages of Peristaltic Pumps
- Precise and Consistent Flow Rates: Peristaltic pumps offer exceptional control over flow rates. Their design, based on the compression and release of tubing, allows for highly accurate and consistent fluid delivery. This precision is invaluable in applications where even minor variations can lead to significant consequences, such as in medical dosing or chemical reactions.
- Gentle Pumping Action: The gentle squeezing action of peristaltic pumps is a standout feature. It is especially beneficial when handling shear-sensitive or fragile fluids. Traditional pumps with impellers or gears might cause damage or alter the properties of these fluids, whereas peristaltic pumps maintain their integrity.
- Suitable for Shear-Sensitive Fluids: Peristaltic pumps are known for their ability to handle shear-sensitive materials like blood, certain pharmaceuticals, and biological samples. The absence of moving parts within the fluid path minimizes the risk of damaging these delicate substances during transfer.
- Minimal Risk of Contamination: Contamination is a critical concern in industries such as food and pharmaceuticals. Peristaltic pumps excel in this regard. Since the fluid only comes into contact with the tubing, there is a lower risk of contamination from the pump itself, making them ideal for hygienic processes.
- Easy Maintenance and Tubing Replacement: Maintenance is a breeze with peristaltic pumps. When it’s time to replace tubing (which is the primary wear component), it can be done quickly and with minimal disruption to operations.
- Versatility: Peristaltic pumps are versatile and widely used in healthcare, laboratories, wastewater treatment, and manufacturing, allowing for easy adjustment of flow rates.
- Chemical Compatibility: The choice of tubing material in peristaltic pumps allows for compatibility with a broad spectrum of chemicals. This makes them suitable for transferring aggressive or corrosive substances, which might pose challenges for other pump types.
- Low Risk of Cross-Contamination: In applications where cross-contamination must be avoided at all costs, peristaltic pumps shine. Each fluid passes through a dedicated section of tubing, minimizing the risk of mixing or contamination between different fluids.
In summary, peristaltic pumps offer a plethora of advantages, making them indispensable in various industries. Their ability to provide precise control, maintain fluid integrity, and minimize the risk of contamination sets them apart as a reliable and versatile choice for fluid transfer applications.
Conclusion
Peristaltic pumps are valuable tools for fluid transfer in various industries. Their unique design and advantages make them a preferred choice for applications requiring precise control and gentle handling of fluids.
FAQs
Are peristaltic pumps suitable for high-pressure applications?
Peristaltic pumps are not ideal for high-pressure applications due to their design limitations. They excel in low to moderate pressure situations.
Can I use peristaltic pumps for abrasive fluids?
Yes, peristaltic pumps are well-suited for pumping abrasive fluids, thanks to their gentle squeezing action on the tubing.
How often should I replace the tubing in my peristaltic pump?
Tubing replacement frequency depends on factors like the type of fluid, operating conditions, and manufacturer recommendations. It’s best to monitor the tubing for signs of wear and replace it as needed.
Are peristaltic pumps easy to clean?
Yes, peristaltic pumps are relatively easy to clean. Regular maintenance and proper tubing selection can help prevent contamination and simplify cleaning procedures.





