Flare fittings are unsung heroes in the world of plumbing, hydraulics, and automotive systems. These unassuming components play a critical role in ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of countless applications. From transporting fluids and gases to creating robust connections in high-pressure environments, flare fittings deliver exceptional performance and reliability.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of flare fittings, exploring their design, materials, installation, and applications. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast tackling a plumbing project or a professional working in a demanding industrial setting, understanding flare fittings is essential for achieving optimal results.
Let’s embark on a journey to uncover the secrets behind these indispensable connectors.
What is a Flare Fitting
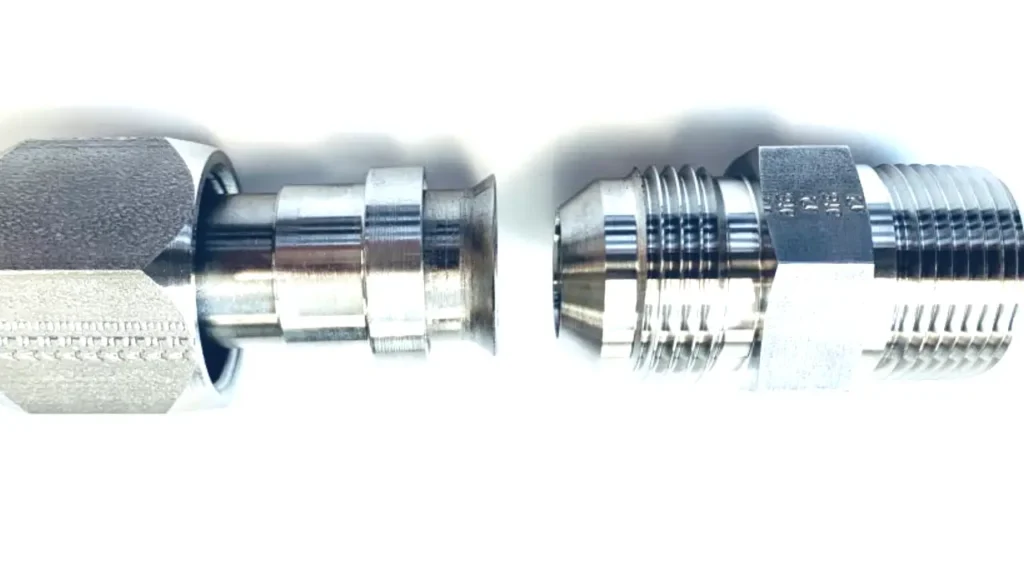
Flare fittings are a type of compression fitting commonly used to join metal tubing, primarily soft steel, ductile copper, and aluminum, although other materials are also compatible. The unique feature of these fittings lies in the flaring process: the end of the tube is expanded and deformed into a conical shape, which is then pressed against a matching conical surface on the fitting. A nut secures the connection, ensuring a leak-tight seal.
What Does Inverted Flare Mean?
An “inverted flare” refers to a specific type of metal fitting design used to create a strong, leak-proof seal in tubing connections, commonly found in automotive brake lines, fuel systems, and hydraulic applications.
What is a Double Flare Fitting?
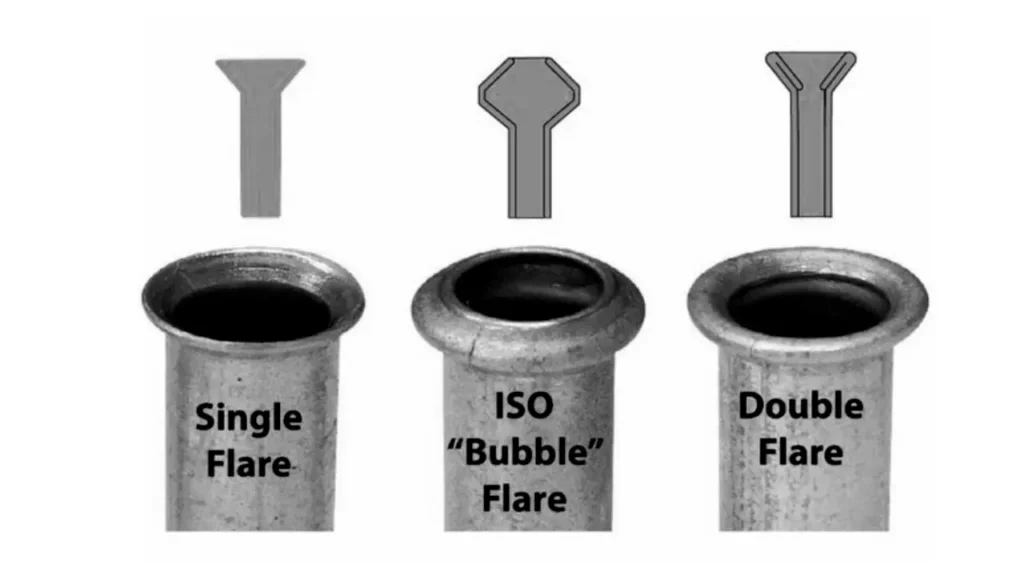

A double flare fitting is a type of compression fitting that employs a reinforced connection for enhanced durability and pressure resistance.
Unlike single flare fittings where the tube is flared once, a double flare involves an additional step: the end of the tube is folded over itself before being flared into a conical shape. This creates a thicker, more robust connection that can withstand higher pressures and repeated tightening and loosening.
Key characteristics of double flare fittings:
- Enhanced durability: The folded-over tube wall provides extra strength and resistance to wear.
- Higher pressure rating: Suitable for applications that require higher fluid pressures.
- Common in automotive brake systems: Often used in brake lines due to their ability to handle the forces involved in braking.
- Also known as inverted flares: Sometimes referred to as inverted flares due to the way the tube is folded.
Benefits of double flare fittings:
- Superior seal: The reinforced connection provides a more secure and reliable seal.
- Resistance to leaks: Less prone to leaks compared to single flare fittings, especially under high pressure conditions.
- Longer lifespan: The increased durability extends the life of the fitting.
Applications of double flare fittings:
- Automotive brake systems
- Hydraulic systems
- Fuel lines
- Other high-pressure applications
Comparison of single and double flare fittings:
| Feature | Single Flare | Double Flare |
|---|---|---|
| Tube preparation | Flared once | Folded over and flared |
| Durability | Less durable | More durable |
| Pressure rating | Lower pressure | Higher pressure |
| Common applications | Low-pressure systems | Brake lines, hydraulic systems |
While double flare fittings offer superior performance in many applications, they require specialized tools and techniques for installation. It’s essential to use the correct flaring tool and follow proper procedures to ensure a secure and leak-free connection.
Flare Fitting Angle
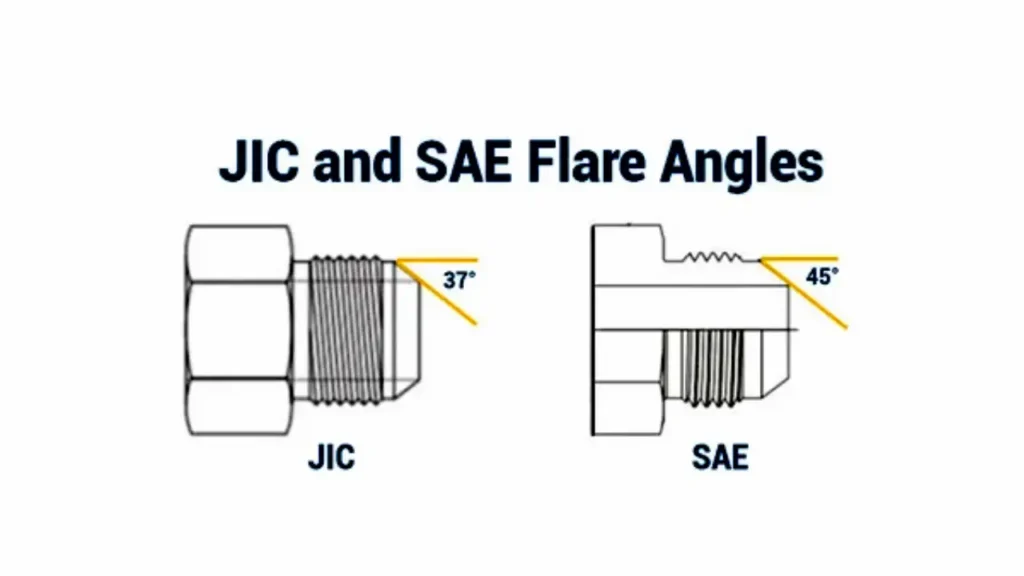
Flare fitting angles are a critical design feature determining the integrity of a seal in fluid systems. This specific angle, usually 37° or 45°, ensures metal-to-metal contact, preventing leaks and maintaining system pressure. Understanding this angle is fundamental for correct component matching.
- Crucial for Sealing: The flare angle is paramount for creating a reliable metal-to-metal seal in flare fittings. An incorrect angle prevents proper seating, leading to leaks even if other dimensions are accurate, compromising the entire hydraulic or fluid system’s integrity.
- JIC vs. SAE 45-Degree: The two most common flare angles are JIC’s 37 degrees and SAE’s 45 degrees. It’s critical to distinguish between them, as they are not interchangeable. Mismatched angles will result in severe leaks and potential system failure due to improper seating.
- Use a Flare Gauge: Accurately identifying the flare angle requires a dedicated flare gauge. This tool confirms if the angle is precisely 37 or 45 degrees, eliminating guesswork. Visual inspection alone is often insufficient and can lead to costly fitting errors.
- Impacts System Performance: The correct flare angle ensures optimal flow and pressure integrity within the system. A properly matched flare prevents turbulence and pressure drops at the connection point, contributing to the overall efficiency and longevity of the hydraulic or fluid transfer system.
- Not Thread Dependent: While flare fittings have threads, the flare angle is independent of the thread size or pitch. Two fittings can have identical threads but different flare angles, making angle verification a distinct and essential step in proper fitting identification and selection.
Double Flare vs Single Flare
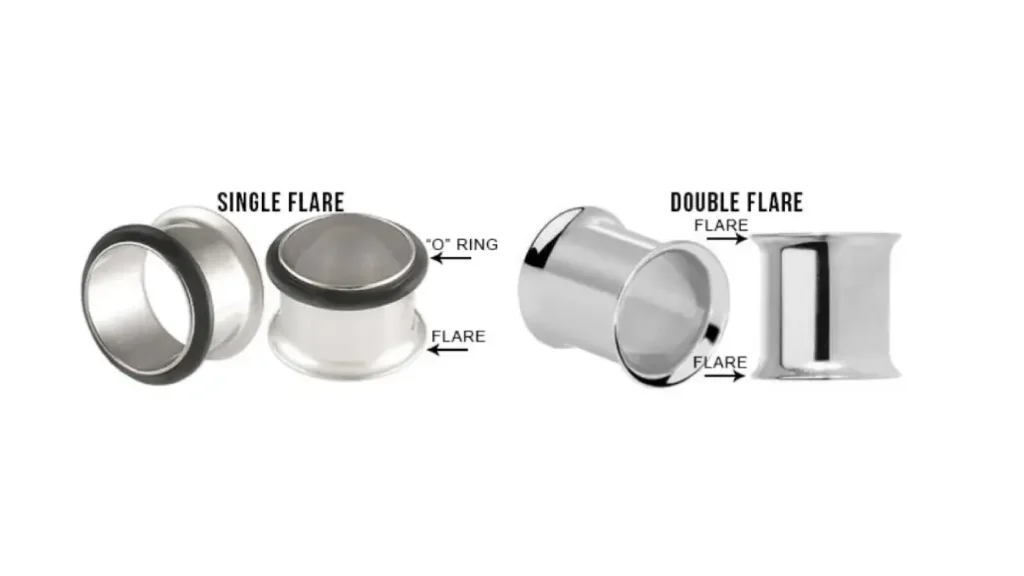

Single Flare Plugs
- Design: Have a flared edge on one side and a non-flared edge on the other.
- Insertion: The non-flared side is inserted first, making them easier to put in, especially when stretching.
- Security: Held in place by an O-ring on the non-flared side.
- Pros: Easier to insert, good for stretching and healing.
- Cons: O-rings can be lost or break, potential for plug to fall out, especially at larger sizes.
Double Flare Plugs
- Design: Have flared edges on both sides.
- Insertion: Requires some technique to insert, often involving angling the plug and gently working it in.
- Security: More secure once in, as the flared edges help hold it in place.
- Pros: Secure fit, less likely to fall out.
- Cons: Can be more difficult to insert, not ideal for fresh stretches.
Here’s a tables showing the key differences between double vs single flare:
| Feature | Single Flare | Double Flare |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Flared edge on one side | Flared edges on both sides |
| Insertion | Easier, non-flared side goes in first | More difficult, requires technique |
| Security | Held by O-ring | More secure once in |
| Best for | Stretching, healing, those new to plugs | Secure fit, once healed |
| Potential issues | O-rings can be lost, may fall out | Difficult to insert, not for fresh stretches |
- Stretching: Single flares are generally recommended for stretching as they’re easier to insert.
- Healing: Single flares are also better for healing stretches as they allow for more airflow and less irritation.
- Experience: Double flares are often preferred by those with more experience and who are confident in their insertion technique.
Inverted Flare vs Double Flare
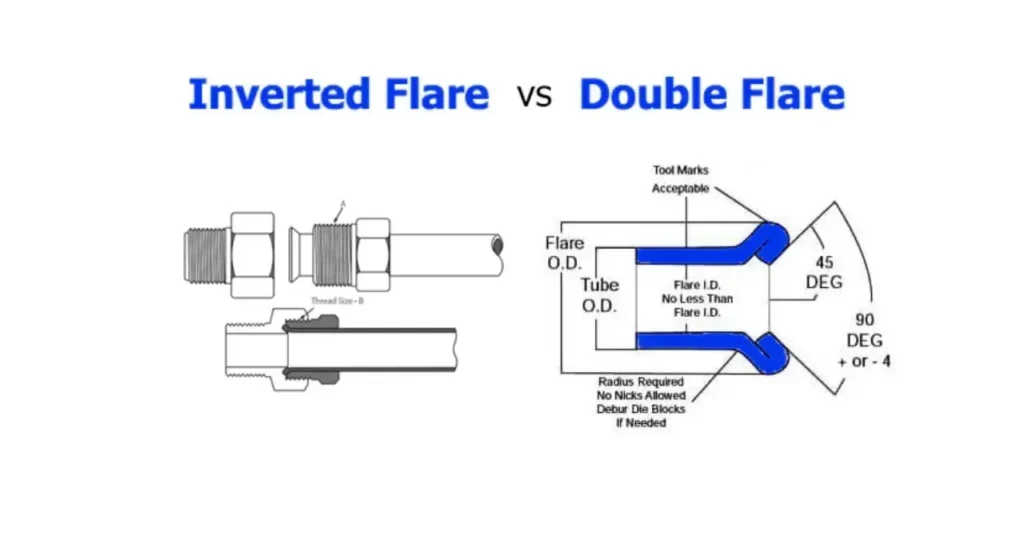
Flare connections are critical in automotive and plumbing systems, creating a seal by deforming tubing ends. Two common types are the inverted flare and the double flare, each with distinct advantages and applications.
Formation Process
An inverted flare is created by flaring the tubing outwards, forming a cone shape. This cone then seats into a corresponding concave surface on the fitting. A double flare, on the other hand, involves a two-step process where the tubing is first flared outwards and then folded back in on itself, creating a more robust, double-thickness cone.
Sealing Mechanism
Inverted flares rely on the direct compression of the single-layer flared tube against the fitting’s mating surface to create a seal. This single point of contact can be effective but may be more susceptible to leakage under high vibration or pressure fluctuations if not perfectly installed. Double flares provide a more substantial sealing surface due to the doubled-over material, offering enhanced leak resistance and durability.
Strength and Durability
Due to its single-wall construction, an inverted flare is generally less robust and more prone to cracking or deforming under stress, especially during repeated tightening or in high-vibration environments. The double flare, with its reinforced, folded-back design, offers significantly greater strength and resistance to fatigue and damage, making it suitable for more demanding applications.
Common Applications
Inverted flares are typically found in lower-pressure applications, such as some automotive brake lines on older vehicles, fuel lines, and certain plumbing connections where ease of assembly is prioritized over extreme durability. Double flares are widely used in critical high-pressure systems like modern automotive brake lines, hydraulic lines, and fuel injection systems where reliability and leak prevention are paramount.
Tools and Difficulty of Creation
Creating an inverted flare usually requires a basic flaring tool and is a relatively straightforward process. The simplicity makes it accessible for many DIY enthusiasts. Double flares, however, require a specialized double flaring tool kit and a more precise, two-step procedure, which can be more challenging for an inexperienced user to master.
| Feature | Inverted Flare | Double Flare |
| Formation | Single outward flare | Outward flare, then folded back |
| Sealing | Single point of contact, less robust | Doubled-over material, enhanced leak resistance |
| Strength | Less robust, prone to cracking | Significantly stronger, resistant to fatigue |
| Common Applications | Lower pressure, older brake lines, fuel lines | High pressure, modern brake lines, hydraulics |
| Creation Difficulty | Easier, basic flaring tool | More challenging, specialized double flaring tool |
What is SAE Flare Fitting

SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) is a global organization that develops engineering standards for the automotive industry. Naturally, this includes standards for fittings, and SAE flare fittings are a common type.
Key Characteristics of SAE Flare Fittings:
- 45-degree flare angle: This distinguishes them from JIC fittings, which have a 37-degree angle.
- Wide range of applications: Commonly used in automotive, plumbing, refrigeration, and air conditioning systems.
- Versatility: Available in various materials, sizes, and configurations.
- Cost-effective: Often more economical than other fitting types.
Common Applications:
- Automotive brake systems
- Fuel lines
- Hydraulic systems
- Refrigeration and air conditioning systems
- Plumbing systems
What is an Inverted Flare Fitting?
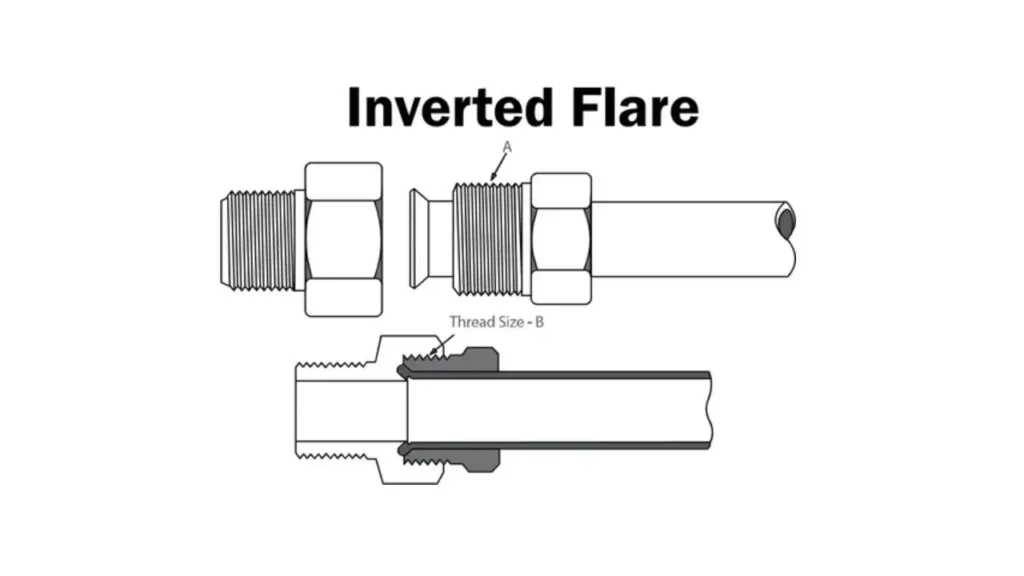
The term “inverted” might be a bit misleading. It doesn’t refer to the orientation of the flare itself but rather to the way the tube is prepared before flaring. The tube is folded inward or “inverted” before the flaring process, hence the name.
Benefits of Inverted Flare Fittings:
- Superior seal: The reinforced connection creates a more reliable and leak-tight seal.
- Resistance to leaks: Less prone to leaks compared to single flare fittings, especially under high pressure conditions.
- Longer lifespan: The increased durability extends the life of the fitting.
In conclusion, inverted flare fittings, or double flare fittings, offer a robust and dependable solution for connecting tubing in high-pressure applications. Their superior performance makes them a preferred choice in many industries, particularly in automotive brake systems.
What is a Flare Fitting Used For?

Flare fittings are versatile connectors with a wide range of applications across various industries. Their ability to create a reliable, leak-tight seal under pressure makes them ideal for:
Automotive Industry
- Brake lines: The high pressures involved in braking require the robust and secure connection provided by flare fittings.
- Fuel lines: To safely transport fuel, flare fittings offer a reliable and leak-proof solution.
- Hydraulic systems: In power steering and suspension systems, flare fittings ensure efficient fluid transfer.
How to Determine Flare Fitting Size?
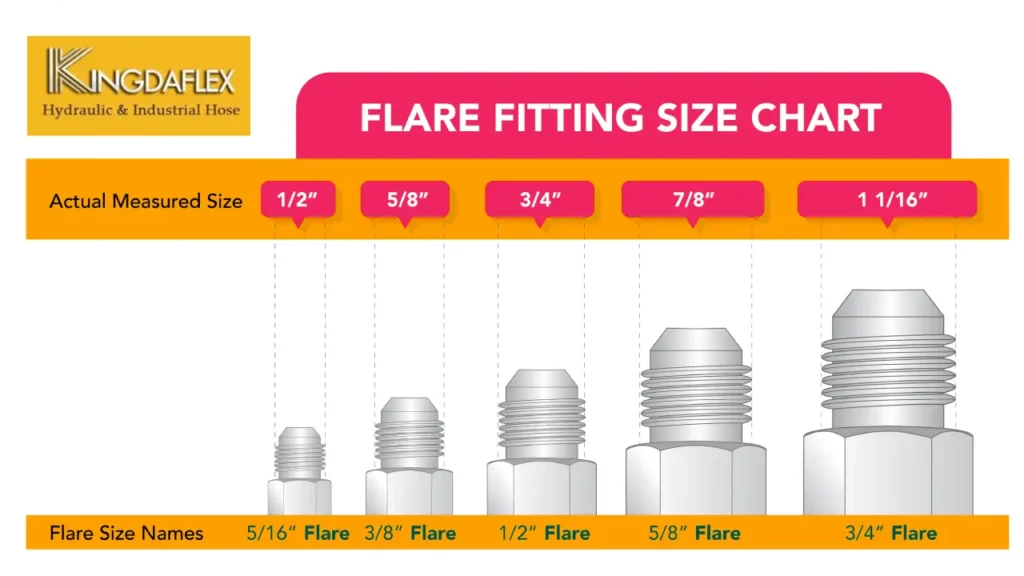
Determining the correct size of a flare fitting is crucial for ensuring a proper and leak-free connection. Here’s a breakdown of the key factors to consider:
1. Thread Size and Type
- Measure the thread diameter: Use a caliper to measure the outside diameter (OD) of the male threads or the inside diameter (ID) of the female threads.
- Identify the thread type: Common thread types include NPT (National Pipe Thread), SAE, and metric.
2. Flare Angle
Measure the flare angle: This is the angle of the conical surface where the tube meets the fitting. Common angles are 37 degrees (JIC) and 45 degrees (SAE). Use a protractor for accurate measurement.
3. Tube Size
Measure the tube’s outer diameter: This will help determine the appropriate fitting size to accommodate the tube.
4. Fitting Type
Identify the fitting type: Determine if it’s a male or female fitting, and whether it’s a straight, elbow, or other configuration.
Additional Tips:
- Refer to a fitting chart: Many manufacturers provide charts that correlate thread size, flare angle, and tube size with fitting dimensions.
- Consider the application: The type of fluid, pressure, and temperature will influence the choice of fitting material and size.
- Check for markings: Some fittings may have size and type information stamped on them.
Conclusion
Flare fittings are indispensable components in a wide range of applications, from automotive and hydraulic systems to refrigeration and plumbing. Their ability to create secure, leak-tight connections under pressure makes them a preferred choice for many industries.
By understanding the different types of flare fittings, their materials, and proper installation techniques, you can ensure the optimal performance and longevity of your systems. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional technician, mastering the art of flare fitting is essential for achieving reliable and efficient connections.
Remember, proper installation and maintenance are key to preventing leaks and ensuring the safety of your systems. If you’re unsure about any aspect of flare fittings, consult with a qualified professional.




