Hydraulic and pneumatic systems are essential technologies in industrial and mechanical operations. While both use fluid or gas to transmit power, they function differently. Understanding the types of hydraulic systems and their advantages helps engineers and operators choose the right system for efficiency, precision, and performance in various applications.
Hydraulic systems use pressurized liquids to generate strong, controlled motion, making them ideal for heavy-duty tasks. Pneumatic systems rely on compressed air to produce movement, often suited for lighter, faster operations. Knowing the differences, along with system types like open-loop, closed-loop, and regenerative hydraulics, ensures optimal selection for specific machinery and workflow requirements.
What is a Hydraulic System?
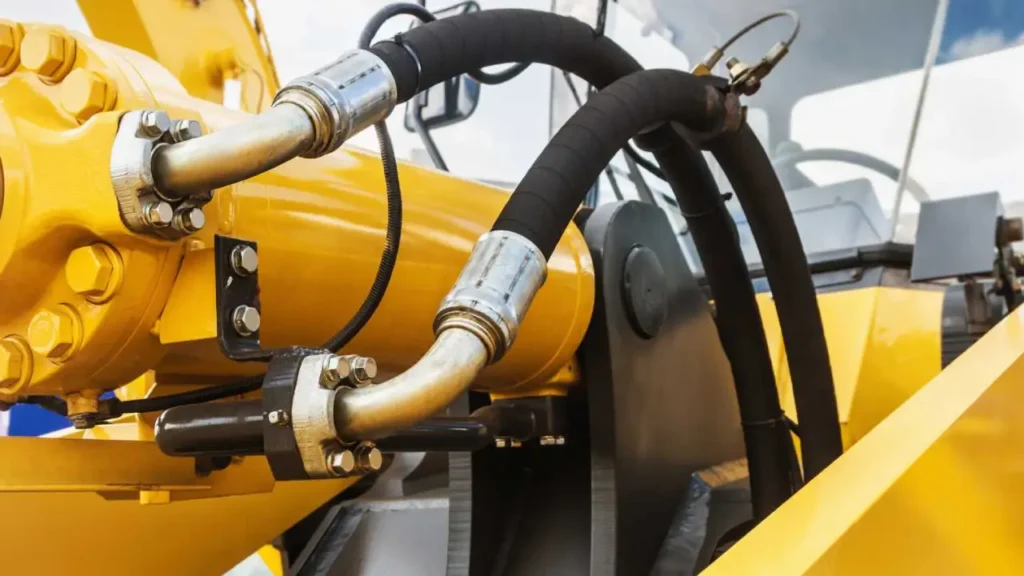

A hydraulic system is a technology that uses pressurized liquid to transmit power and perform mechanical work. It consists of key components such as pumps, valves, actuators, and hoses, which work together to convert fluid pressure into controlled motion, enabling machinery to lift, push, or move heavy loads efficiently and precisely.
How Does a Hydraulic System Work?
A hydraulic system works by using pressurized fluid to generate mechanical power and control motion. The fluid flows through pumps, valves, hoses, and actuators, enabling machinery to perform heavy-duty tasks with precision and efficiency. Proper design ensures smooth operation, safety, and durability across applications.
- Fluid Pressurization: The hydraulic pump pressurizes fluid, converting mechanical energy into hydraulic energy. This pressurized fluid carries force to actuators, allowing machinery to lift, push, or rotate heavy loads efficiently. High-quality pumps ensure consistent pressure and system reliability under varying operational conditions.
- Control via Valves: Valves regulate fluid flow, direction, and pressure within the hydraulic system. Directional valves determine movement, pressure relief valves prevent overload, and flow control valves adjust actuator speed. Proper valve selection guarantees precise, safe, and reliable operation in different machinery and industrial setups.
- Actuator Operation: Actuators, such as cylinders and motors, convert hydraulic energy into mechanical motion. Cylinders produce linear movement for lifting or pressing, while motors generate rotary motion. These components enable machinery to perform complex tasks efficiently, reducing manual effort and increasing operational productivity.
- Return Flow and Reservoir: After performing work, hydraulic fluid returns to the reservoir, where it cools, releases air, and is filtered for reuse. The reservoir ensures a continuous supply of fluid, maintains pressure, and protects system components, contributing to overall hydraulic system longevity and efficiency.
- Hoses and Seals: Hydraulic hoses and seals direct fluid flow while preventing leaks. They must withstand high pressure, temperature, and mechanical stress. Using durable hoses and reliable seals ensures safety, reduces maintenance, and prolongs the service life of the hydraulic system across various industrial applications.
Types of Hydraulic Systems
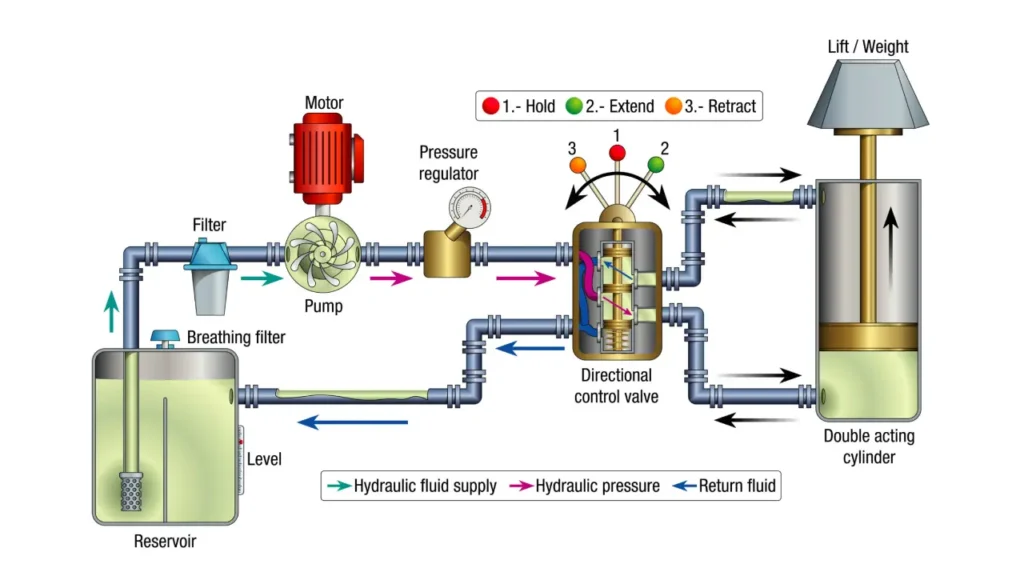
Hydraulic systems can be classified into different types based on design and operation, each suited for specific industrial and mechanical applications. Understanding these types helps in selecting the right system for efficiency, durability, and performance, ensuring smooth operation in construction, manufacturing, automotive, and other industries.
Open-Loop Hydraulic Systems
Open-loop systems circulate hydraulic fluid from a reservoir to the actuator and back through a pump without returning excess fluid to the pump. They are simple, cost-effective, and easy to maintain, making them ideal for light to medium-duty applications in construction and mobile machinery.
Open-loop systems offer benefits like lower cost, easy installation, and straightforward maintenance. Their applications include forklifts, small excavators, and agricultural machinery. These systems provide adequate force and control for most mobile operations, although they are less suitable for high-pressure, continuous-duty industrial machines.
Closed-Loop Hydraulic Systems
Closed-loop hydraulic systems recirculate fluid directly from the actuator back to the pump, creating a self-contained loop. They provide faster response, higher efficiency, and precise control, making them suitable for heavy machinery, industrial presses, and advanced mobile equipment.
Benefits include improved energy efficiency, smoother operation, and reduced heat generation. Closed-loop systems are widely applied in large construction equipment, industrial machines, and advanced material handling equipment. Their precise control makes them ideal for tasks requiring consistent, continuous power output.
Regenerative Hydraulic Systems
Regenerative hydraulic systems reuse fluid from one actuator to assist another, reducing energy consumption and improving efficiency. These systems are designed for applications where rapid actuator motion and energy recovery are critical, such as in lifting, lowering, or repetitive tasks in industrial machinery.
The main benefits include energy savings, faster cycle times, and reduced hydraulic pump load. Regenerative systems are commonly used in presses, automated machinery, and large lifting equipment. They enhance productivity while lowering operational costs and minimizing environmental impact through efficient fluid management.
Types of Hydraulic Power Steering Systems
Hydraulic power steering systems help drivers steer vehicles with minimal effort using hydraulic pressure. These systems enhance vehicle control, reduce driver fatigue, and improve maneuverability. Different types of hydraulic power steering systems are designed to suit various vehicle sizes, driving conditions, and performance requirements.
- Integral (Or Rack-and-Pinion) Hydraulic Power Steering: This system combines the steering rack and hydraulic assist into a single unit. The hydraulic fluid amplifies the driver’s input at the steering wheel, providing smooth, responsive control. It is commonly used in modern passenger cars for precise handling.
Integral hydraulic systems offer benefits like reduced steering effort, better road feedback, and improved safety. They are widely applied in compact and mid-sized vehicles, enhancing maneuverability in urban environments. Their compact design makes installation easier and maintenance relatively straightforward.
- Recirculating Ball Hydraulic Power Steering: This system uses a worm-and-sector gear mechanism with hydraulic assistance. Fluid pressure helps move the steering linkage, reducing the driver’s effort, especially in larger vehicles such as trucks and SUVs that require more steering force.
Recirculating ball systems provide benefits like durability, smooth steering under heavy loads, and enhanced reliability. They are commonly used in heavy-duty vehicles, off-road trucks, and commercial vehicles. Their robust design makes them ideal for vehicles that experience high steering torque and demanding road conditions.
- Variable-Assist Hydraulic Power Steering: This advanced system adjusts hydraulic assistance based on vehicle speed. At low speeds, more assist is provided for easier maneuvering, while at higher speeds, assistance is reduced to improve stability and control.
Variable-assist systems benefit drivers by offering both comfort and safety. They are used in modern cars, SUVs, and performance vehicles. The system improves steering feel, reduces effort during parking, and maintains control at highway speeds, providing a balanced and adaptable driving experience.
Hydraulic Hoses Used in Hydraulic Systems
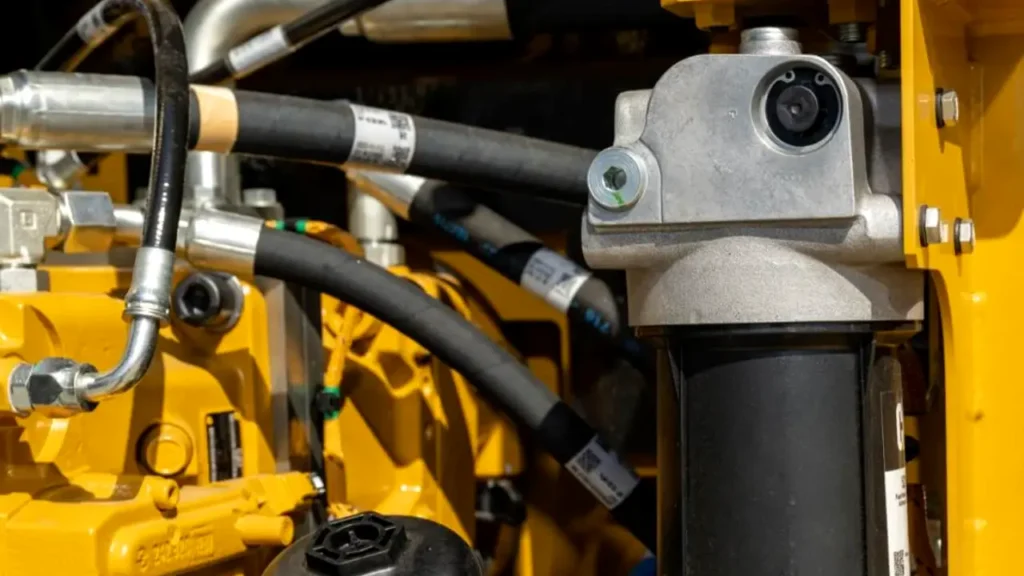

Hydraulic hoses are critical components in hydraulic systems, responsible for transmitting pressurized fluid between pumps, valves, and actuators. They ensure efficient power transfer, flexibility, and safety. Choosing the right hydraulic hose type is essential to maintain system performance, prevent leaks, and withstand pressure, temperature, and environmental conditions.
- Rubber Hydraulic Hoses: Rubber hoses are flexible, durable, and resistant to abrasion and moderate pressures. They consist of an inner tube, reinforcement layers, and an outer cover, making them ideal for mobile machinery, construction equipment, and general industrial applications.
Rubber hoses provide vibration absorption, reduce stress on system components, and handle various hydraulic fluids, including mineral oils and water-glycol solutions. Proper selection of diameter, pressure rating, and reinforcement ensures long-lasting performance, minimizing maintenance requirements and ensuring reliable system operation.
- Thermoplastic Hydraulic Hoses: Thermoplastic hoses are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and chemically compatible with a wide range of fluids. Their layered construction provides flexibility and durability while reducing system weight, making them suitable for mobile and compact machinery.
Thermoplastic hoses enhance fluid flow efficiency due to their smooth inner surface, reducing friction and contamination risk. They excel in applications requiring tight bends or continuous movement, such as agricultural equipment, material handling, and light industrial machines, where flexibility and chemical resistance are critical.
- Steel Braided Hydraulic Hoses: Steel braided hoses offer high pressure resistance and durability. A steel wire braid reinforces the inner tube, providing strength while maintaining flexibility. They are widely used in heavy-duty industrial machinery and equipment requiring reliable performance under extreme pressures.
Steel braided hoses resist kinking, abrasion, and external damage, making them suitable for demanding environments. They provide consistent performance, maintain hydraulic pressure, and ensure safety in construction machinery, manufacturing equipment, and other high-pressure industrial applications, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Spiral Hydraulic Hoses: Spiral hoses handle extremely high pressures and are reinforced with multiple steel wire layers. They are designed for heavy-duty applications, including large construction machinery, industrial presses, and mining equipment, where high-pressure performance and reliability are critical.
Spiral hoses provide maximum strength, flexibility, and resistance to burst or collapse under high-pressure conditions. They ensure long-term reliability in demanding environments, supporting continuous operation of heavy machinery while preventing leaks, maintaining efficiency, and enhancing system safety.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of hydraulic systems and how they differ from pneumatic systems is crucial for selecting the right technology. Hydraulic systems offer strength and precision for heavy loads, while pneumatic systems excel in speed and lightweight tasks. Both have unique applications across industries.
Choosing high-quality hydraulic components, especially hoses, is vital for system performance and longevity. At Kingdaflex, we provide wholesale hydraulic hoses designed for durability, pressure resistance, and flexibility. Our hoses ensure smooth fluid flow, prevent leaks, and maintain reliable operation in all types of hydraulic systems.
Whether upgrading existing machinery or designing a new system, sourcing hydraulic hoses from Kingdaflex guarantees quality and efficiency. Our products comply with international standards, reducing maintenance issues, enhancing safety, and maximizing productivity in industrial, construction, and manufacturing applications worldwide.




