Hydraulic and pneumatic systems are widely used in industrial and mechanical applications to transmit power and control motion. While both rely on fluid or air to operate machinery, their principles, components, and performance characteristics differ. Understanding these differences helps in selecting the right system for specific tasks.
Hydraulic systems use pressurized liquid to generate strong, precise force, suitable for heavy-duty operations. Pneumatic systems rely on compressed air to create movement, ideal for lighter, faster applications. By comparing their efficiency, cost, and operational capabilities, engineers and operators can determine which system best meets their equipment and workflow requirements.
What is a Hydraulic System?

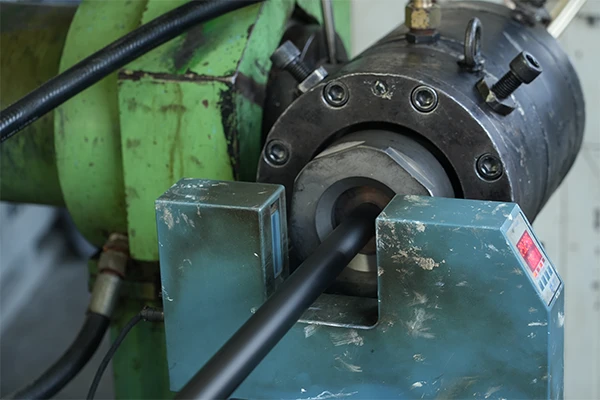
A hydraulic system is a technology that uses pressurized fluid to transmit power and perform mechanical work. It converts fluid pressure into controlled motion, enabling machinery to lift, push, or move heavy loads efficiently. Hydraulic systems are widely used in industrial, automotive, and construction applications.
- Power Transmission: Hydraulic systems transmit force through pressurized fluid, allowing precise control of machinery movement. The system can generate large amounts of force with minimal input, making it ideal for lifting, pressing, or moving heavy loads in various industrial and mechanical operations.
- Key Components: A hydraulic system typically consists of a pump, reservoir, valves, actuators, and hoses. The pump pressurizes the fluid, valves regulate flow and pressure, actuators convert pressure into motion, and hoses connect components, ensuring smooth and efficient fluid transfer throughout the system.
- Applications: Hydraulic systems are used in construction machinery, industrial presses, automotive brakes, and agricultural equipment. They provide high power density, precise control, and reliability in demanding environments. Their versatility allows them to perform heavy-duty tasks that would be impossible with purely mechanical systems.
- Advantages: Hydraulic systems offer high force output, smooth motion, and precise control. They can operate under extreme conditions, including high loads, temperatures, and pressures. Proper maintenance and high-quality components, especially hoses and seals, ensure safety, efficiency, and long-term reliability of the system.
What is a Pneumatic System?

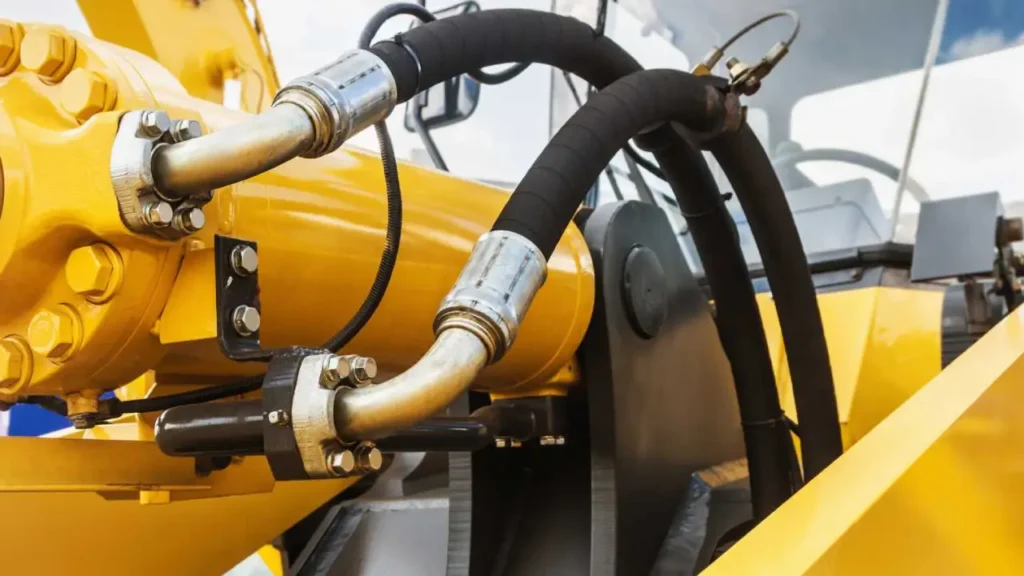
A pneumatic system uses compressed air or gas to transmit power and perform mechanical work. These systems are widely used in industrial automation, manufacturing, and light machinery. They offer fast operation, low cost, and simple maintenance, making them ideal for tasks requiring speed and repetitive motion.
- Compressed Air Supply: Pneumatic systems rely on compressors to generate pressurized air. This air is stored in tanks and distributed through pipelines to actuators and valves. A stable air supply ensures consistent force, smooth operation, and reliable performance across various pneumatic applications.
- Actuators and Cylinders: Pneumatic actuators, including cylinders and rotary motors, convert compressed air into mechanical motion. Cylinders provide linear motion, while rotary actuators create rotation. These components enable precise and rapid movement in tasks like assembly, packaging, and material handling.
- Valves and Control Components: Valves regulate air flow, pressure, and direction in a pneumatic system. Directional control valves manage actuator movement, pressure relief valves prevent overload, and flow control valves adjust speed. Proper valve selection ensures efficiency, accuracy, and safety in operation.
- Air Treatment and Filtration: Air must be filtered, lubricated, and dried before reaching components. Filters remove contaminants, lubricators reduce friction, and dryers prevent moisture-related issues. Proper air treatment extends component life, maintains performance, and prevents downtime in pneumatic systems.
- Hoses and Tubing: Pneumatic hoses and tubing transport compressed air between system components. They must withstand pressure, be flexible, and resist wear. Using high-quality hoses ensures leak-free operation, smooth airflow, and reliable performance in automated and industrial applications.
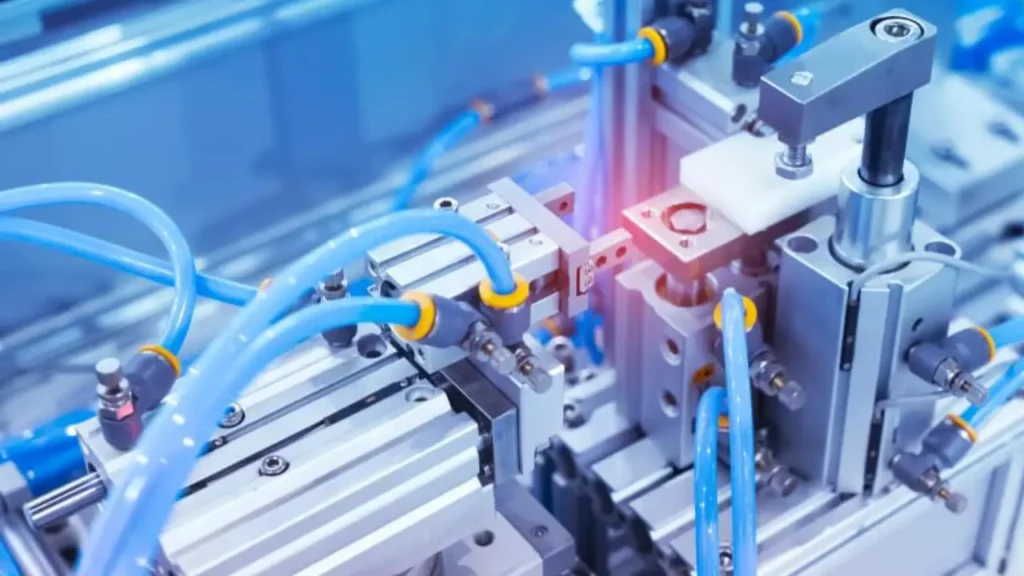
Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems
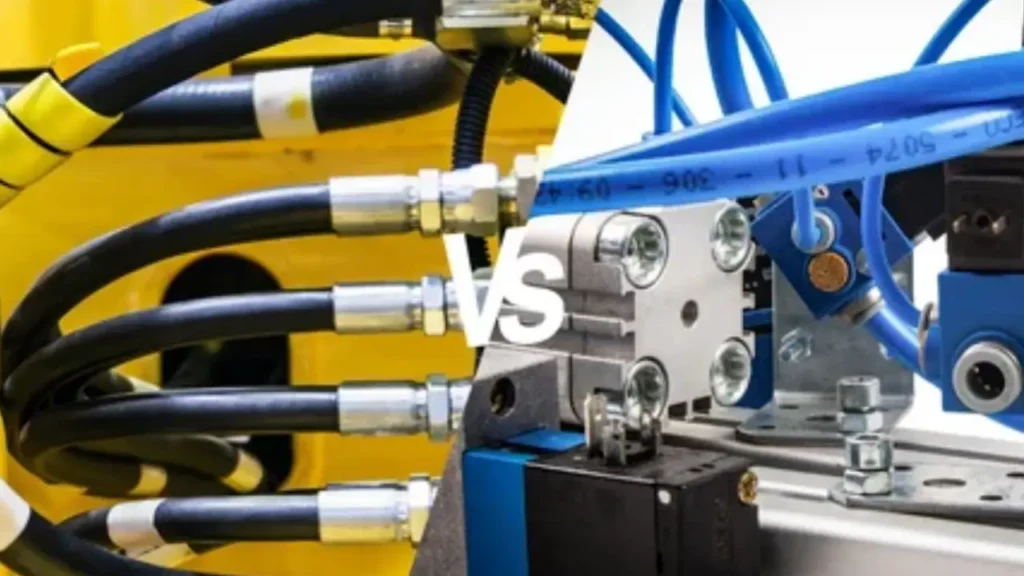
Hydraulic and pneumatic systems are widely used to transmit power and control machinery. Hydraulic systems use pressurized liquid, while pneumatic systems use compressed air. Both have unique advantages, applications, and operational characteristics, making them suitable for different industrial and mechanical tasks.
1. Power Source
Hydraulic systems rely on incompressible liquids, typically oil, to generate high force and precise motion. This allows heavy machinery to lift, push, or rotate large loads efficiently and reliably, even under continuous operation in demanding industrial settings.
Pneumatic systems use compressed air as their energy source, offering lighter and faster motion. While they cannot generate the same force as hydraulics, they are ideal for rapid, repetitive tasks, such as in packaging, automation, and light assembly lines, where speed and simplicity are important.
2. Force and Pressure
Hydraulic systems can operate at very high pressures, often exceeding 3000 psi, enabling heavy-duty applications with precise force control. They are suitable for construction machinery, presses, and automotive systems that demand strength and accuracy.
Pneumatic systems generally operate at lower pressures, around 100–150 psi. This limits their lifting power but allows for safer, faster operation. They are commonly used in light industrial equipment, robotics, and material handling where moderate force is sufficient.
3. Components and Complexity
Hydraulic systems involve pumps, valves, actuators, hoses, and reservoirs, requiring precise design and maintenance. While more complex, they provide high efficiency, smooth motion, and robust performance for heavy-duty applications.
Pneumatic systems use compressors, valves, actuators, filters, and tubing. They are simpler, lighter, and easier to maintain, making them suitable for automation, conveyors, and repetitive operations where high precision and extreme force are not necessary.
4. Speed and Responsiveness
Hydraulic systems provide smooth, controlled motion but can be slower due to fluid compressibility and system inertia. They excel where precision, heavy loads, and consistent force are critical.
Pneumatic systems are faster and highly responsive, ideal for applications requiring rapid, repetitive movements. Compressed air can accelerate and decelerate actuators quickly, making pneumatics suitable for packaging, pick-and-place, and fast automated machinery.
5. Cost and Maintenance
Hydraulic systems are more expensive to design and maintain due to complex components and fluid management. However, their durability, high force output, and precision justify the cost for heavy-duty industrial applications.
Pneumatic systems are generally less expensive and easier to maintain. Air leaks are easier to manage than fluid leaks, and components are lighter and simpler. They are cost-effective for light-duty, high-speed, and repetitive tasks.
| Aspect | Hydraulic System | Pneumatic System |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Pressurized liquid (oil) | Compressed air |
| Maximum Pressure | High (up to 3000+ psi) | Low (100–150 psi) |
| Force Capability | Very high, suitable for heavy loads | Moderate, suitable for light loads |
| Components Complexity | Complex (pumps, valves, hoses) | Simple (compressors, valves, tubing) |
| Speed & Responsiveness | Moderate, smooth motion | Fast, rapid repetitive motion |
| Cost & Maintenance | Higher cost, needs careful maintenance | Lower cost, easier maintenance |
Hydraulic Hoses for Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems
Hydraulic hoses are vital components in both hydraulic and pneumatic systems, responsible for transmitting fluid or air under pressure. They ensure smooth operation, flexibility, and safety. Selecting the right type of hose is essential for performance, durability, and preventing leaks or system failure in industrial and mobile applications.
- Rubber Hydraulic Hoses: Rubber hoses are flexible and durable, suitable for medium to high-pressure hydraulic applications. Their reinforced construction allows them to handle oil-based fluids and resist abrasion, making them ideal for construction equipment, mobile machinery, and general industrial operations.
Rubber hoses provide excellent vibration absorption, reducing stress on system components and extending their lifespan. They can operate under a wide range of temperatures and pressures, ensuring reliable performance in dynamic environments while minimizing maintenance requirements.
- Thermoplastic Hoses: Thermoplastic hoses are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and chemically compatible with a variety of fluids. Their flexible design makes them suitable for tight spaces, mobile equipment, and pneumatic systems requiring smooth airflow and precise control.
Thermoplastic hoses reduce friction and contamination risks due to their smooth inner surface. They provide excellent flexibility for frequent bends or movements and are ideal for applications such as automated machinery, material handling systems, and light industrial equipment.
- Steel Braided Hoses: Steel braided hoses offer high pressure resistance and durability. The steel wire reinforcement supports heavy-duty hydraulic systems, ensuring consistent fluid flow and reliable performance under extreme pressure conditions in industrial machinery and mobile equipment.
Steel braided hoses resist kinking, abrasion, and external mechanical damage. Their strength and durability make them ideal for high-pressure hydraulic applications in construction, manufacturing, and mining, ensuring safety, longevity, and reduced downtime in demanding environments.
- Pneumatic Hoses: Pneumatic hoses are designed to carry compressed air in pneumatic systems. They are lightweight, flexible, and resistant to pressure and environmental factors. These hoses ensure smooth airflow and reliable performance in automation, packaging, and light machinery applications.
Pneumatic hoses provide rapid actuator response and maintain consistent pressure, allowing fast and repetitive movements. Using high-quality hoses prevents leaks, reduces maintenance, and ensures long-term performance in industrial automation, conveyor systems, and other air-powered equipment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hydraulic and pneumatic systems serve different purposes in industrial and mechanical operations. Hydraulic systems provide high force and precision, while pneumatic systems offer speed and simplicity. Understanding their differences ensures optimal equipment selection, safety, and performance across various industries and applications.
Choosing high-quality hydraulic components is critical for system reliability. At Kingdaflex, we offer wholesale hydraulic hoses designed for durability, pressure resistance, and flexibility. Our hoses ensure smooth fluid flow, prevent leaks, and maintain efficient operation in all types of hydraulic systems, supporting both new installations and system upgrades.
Sourcing hydraulic hoses from Kingdaflex guarantees quality, compliance with international standards, and long-lasting performance. Whether for construction, automotive, or industrial machinery, our hoses reduce maintenance, enhance safety, and maximize productivity, making them a trusted choice for professionals who demand reliable hydraulic system components.




