Kingdaflex supplies high-quality 3/8 hydraulic hose designed for reliable fluid transfer in medium to high-pressure hydraulic systems.
Available in multiple pressure ratings and configurations, our hoses meet international standards and are suitable for OEM and aftermarket use.

Our 3/8 inch hydraulic hose is manufactured with precision-controlled inner and outer diameters to ensure stable flow performance, secure fitting connections, and long service life. Each hose is tested according to applicable SAE and EN standards before delivery.
| Inside | Outside | Working Pressure | Burst Pressure | Min Bend Radius | Weight | ||||
| Min(mm) | Max(mm) | Max(mm) | Bar | Psi | Bar | Psi | mm | kg/m | |
| SAE 100R1AT / DIN EN853 1SN | 9.3 | 10.1 | 16.5 | 180 | 2610 | 720 | 10500 | 130 | 0.31 |
| SAE 100R2AT / DIN EN853 2SN | 9.3 | 10.1 | 18.2 | 330 | 4800 | 1320 | 19200 | 125 | 0.46 |
| SAE 100R1A / DIN EN853 1ST | 9.3 | 10.1 | 20.6 | 180 | 2610 | 720 | 10440 | 130 | 0.36 |
| SAE 100R2A / DIN EN853 2ST | 9.3 | 10.1 | 22.2 | 330 | 4785 | 1320 | 19140 | 130 | 0.54 |
| EN857 1SC | 9.3 | 10.1 | 16.9 | 180 | 2610 | 720 | 10440 | 90 | 0.26 |
| EN857 2SC | 9.3 | 10.1 | 18.3 | 330 | 4785 | 1320 | 19140 | 90 | 0.42 |
| DIN 1SNK | 9.3 | 10.1 | 15.8 | 230 | 3335 | 920 | 13340 | 90 | 0.25 |
| DIN 2SNK | 9.3 | 10.1 | 17.3 | 385 | 5585 | 1540 | 22340 | 90 | 0.42 |
| SAE 100R16 | 9.3 | 10.1 | 18.8 | 330 | 4785 | 1320 | 19140 | 65 | 0.42 |
| SAE 100R17 | 9.3 | 10.1 | 17 | 210 | 3045 | 840 | 12180 | 65 | 0.26 |
| PILOT HOSE | 9.5 | 9.5 | 15.9 | 125 | 1815 | 500 | 7250 | 50 | 0.25 |
| STEAM HOSE | 9.5 | 9.5 | 22 | 17 | 250 | 170 | 2500 | 100 | 0.49 |
| SAE 100R14 TEFLON (Smooth) | 9.5 | 9.5 | 12.6 | 132 | 1914 | 528 | 7656 | 100 | 0.17 |
| SAE 100R14 TEFLON (Corrugated) | 9.5 | 9.5 | 15.5 | 90 | 1305 | 360 | 5220 | 30 | 0.26 |
| SAE 100R3 | 9.2 | 10.1 | 19.8 | 78 | 1130 | 315 | 4570 | 100 | 0.31 |
| SAE 100R6 | 9 | 10 | 16.7 | 28 | 406 | 112 | 1624 | 75 | 0.2 |
| EN854 1TE | 9 | 10 | 16.3 | 28 | 406 | 112 | 1624 | 75 | 0.16 |
| EN854 2TE | 9 | 10 | 17.3 | 63 | 914 | 252 | 3656 | 60 | 0.19 |
| EN854 3TE | 9 | 10 | 19.3 | 110 | 1595 | 440 | 6380 | 70 | 0.28 |
| SAE 100R7 | 9.6 | 9.6 | 16 | 155 | 2248 | 620 | 8990 | 70 | 0.17 |
| SAE 100R8 | 9.6 | 9.6 | 16 | 300 | 4350 | 1200 | 17400 | 70 | 0.17 |
| EN856 4SP | 9.3 | 10.1 | 22.2 | 445 | 6450 | 1780 | 25810 | 180 | 0.7 |
| SAE 100R9 | 9.3 | 10.1 | 21 | 280 | 4060 | 1120 | 16240 | 130 | 0.7 |
| SAE 100R12 | 9.3 | 10.1 | 21 | 280 | 4060 | 1120 | 16240 | 130 | 0.7 |
| SAE 100R15 | 9.3 | 10.1 | 23.3 | 420 | 6090 | 1680 | 24360 | 150 | 0.8 |

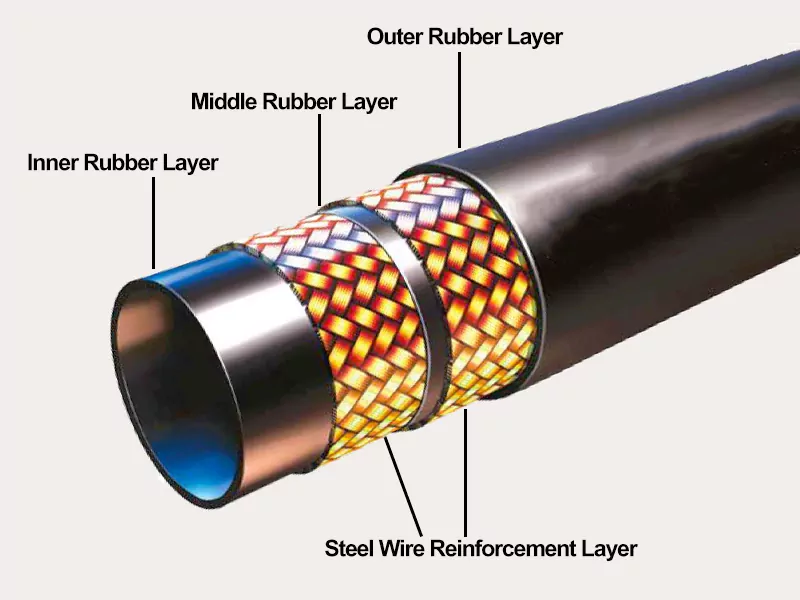
The inner tube is made from oil-resistant synthetic rubber (NBR), suitable for mineral-based hydraulic oils and stable operation under continuous pressure.
The outer cover uses weather- and abrasion-resistant synthetic rubber (CR) to protect the hose against ozone, UV exposure, and mechanical wear in industrial environments.

Working pressure capability varies depending on hose construction, reinforcement type, and applicable standards.
Standard braided designs are used for medium-pressure systems, while spiral-reinforced constructions are selected for high-pressure and high-impulse hydraulic applications.
Hoses are supplied in continuous coils or cut to length according to customer specifications and system layouts.
Professional hose assembly services, including cutting and crimping, are available to ensure dimensional accuracy and consistent assembly quality.
Braided reinforcement structures, such as single-wire and double-wire designs, provide a balance of flexibility and pressure resistance.
Spiral-reinforced constructions are used for applications requiring higher pressure capacity and extended impulse life.
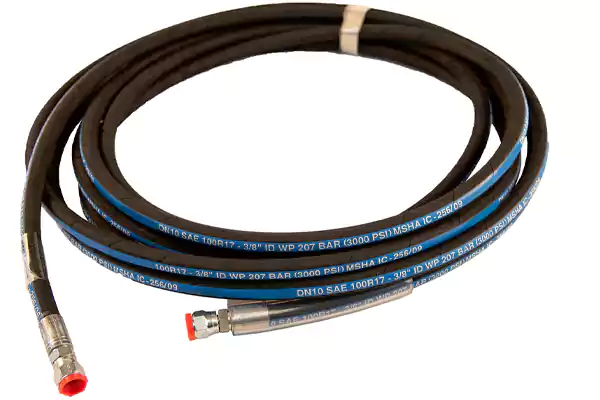

3/8 hydraulic hose rated at 3000 PSI is commonly used in agricultural machinery, tractors, and light industrial equipment.
It provides reliable pressure handling for hydraulic circuits with moderate flow requirements while maintaining flexibility and abrasion resistance.
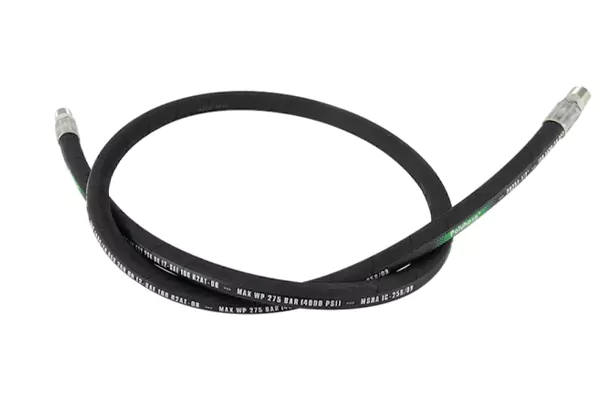

For construction equipment and mobile hydraulic systems, the 3/8 hydraulic hose with a 4000 PSI working pressure offers enhanced strength and safety margin.
This option is widely used in excavators, loaders, and material handling machinery.
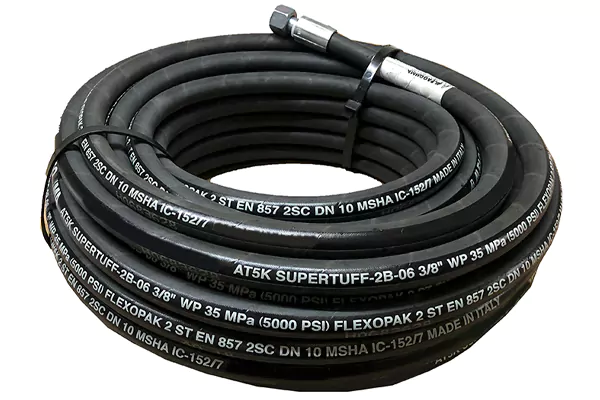

High-pressure 3/8 hydraulic hose rated up to 5000 PSI is designed for demanding hydraulic environments where pressure spikes and continuous operation are expected.
It is suitable for heavy-duty industrial systems and specialized hydraulic applications.
To ensure compatibility with different hydraulic systems, Kingdaflex offers a wide range of fitting options for 3/8 hydraulic hose assemblies.
All fittings are precisely machined to provide leak-free connections and long-term performance.
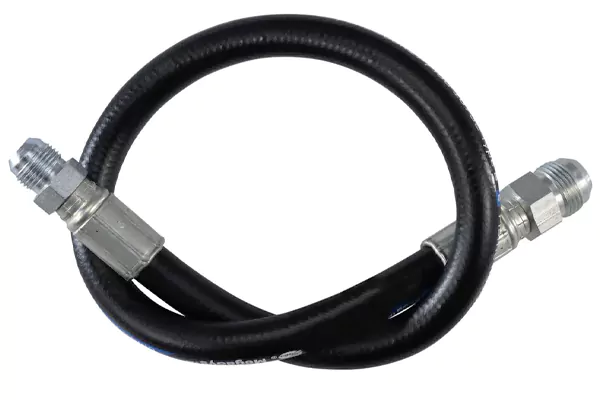

3/8 JIC hydraulic hose assemblies are commonly used in North American hydraulic systems.
The 37-degree flare design ensures reliable sealing under high pressure and repeated assembly.
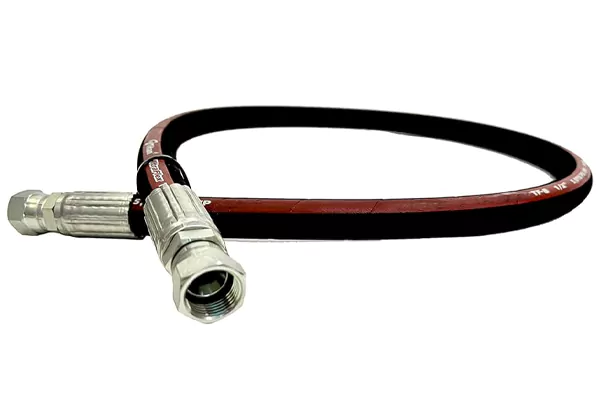

3/8 NPT hydraulic hose fittings provide tapered thread connections suitable for various industrial and aftermarket hydraulic installations.
Proper sealing compounds are recommended for optimal performance.
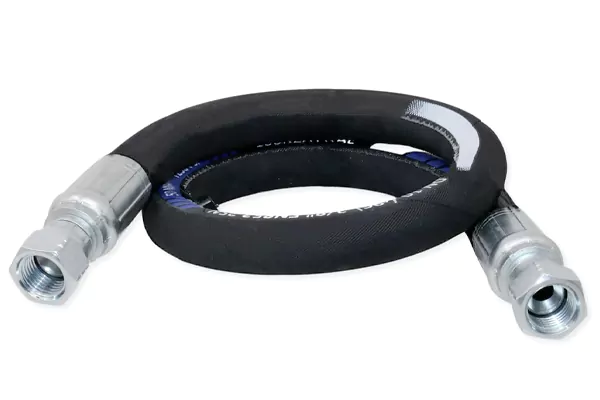

3/8 hydraulic hose with female ends is widely used in replacement and repair applications.
Pre-crimped female fittings allow fast installation and reduce assembly time on site.
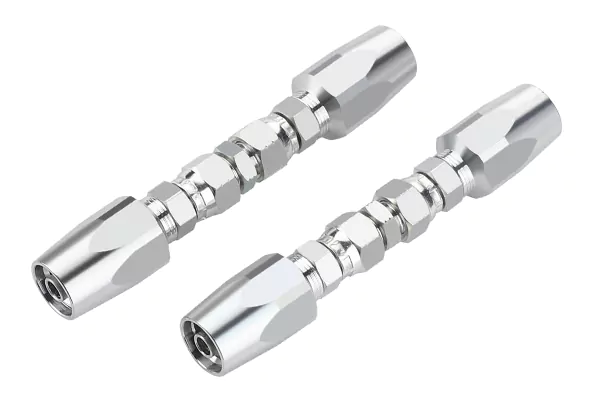

Reusable 3/8 hydraulic hose fittings are designed for maintenance and field repair situations where crimping equipment is not available.
They allow hose replacement without specialized tools while maintaining safe pressure performance.
Kingdaflex supplies premade 3/8 hydraulic hose assemblies with fittings installed according to customer specifications.
Each assembly is pressure tested to ensure safety and performance before shipment.
For distributors and OEM customers, 3/8 hydraulic hose is available in bulk coils or by the foot.
Bulk supply allows flexible cutting and assembly based on specific application requirements.
We also provide 3/8 hydraulic hose repair kits, clamps, splices, and related tools to support maintenance and emergency repairs.
These accessories are compatible with standard 3/8 inch hydraulic hose dimensions.
The price of a 3/8 hydraulic hose depends on several technical and commercial factors rather than a fixed unit cost.
Understanding these factors helps buyers select the most cost-effective solution for their application.
Kingdaflex is a professional hydraulic hose manufacturer with years of experience serving global industrial markets.
All 3/8 hydraulic hoses are produced according to SAE and EN standards and tested for pressure, leakage, and durability.
Our products are exported to multiple countries and regions, supporting distributors, OEMs, and industrial users worldwide.
We provide OEM and customization services including hose length, fittings, branding, and packaging.
Quick Reference: Working Pressure for 3/8″ (DN10) Hoses
The following table categorizes our hoses from standard to high-pressure applications.
| Hose Standard | Construction Type | Working Pressure | Working Pressure | Common Application |
| SAE 100R6 | 1 Textile Braid | 28 Bar | 406 PSI | Low-pressure return lines |
| SAE 100R3 | 2 Textile Braids | 78 Bar | 1,130 PSI | Low-pressure return/suction |
| SAE 100R1AT / 1SN | 1 Wire Braid | 180 Bar | 2,610 PSI | Standard hydraulic lines |
| SAE 100R17 | 1 Wire Braid (Compact) | 210 Bar | 3,045 PSI | Compact/tight routing areas |
| SAE 100R2AT / 2SN | 2 Wire Braids | 330 Bar | 4,785 PSI | High-pressure equipment (Most Popular) |
| SAE 100R16 | 2 Wire Braids (Compact) | 330 Bar | 4,785 PSI | High-pressure, tighter bend radius |
| DIN 2SNK | 2 Wire Braids (Compact) | 385 Bar | 5,585 PSI | Demanding compact applications |
| SAE 100R12 | 4 Wire Spirals | 280 Bar | 4,060 PSI | Heavy-duty, high impulse |
| EN856 4SP | 4 Wire Spirals | 445 Bar | 6,450 PSI | Very high pressure, mining/excavators |
| SAE 100R15 | 4-6 Wire Spirals | 420 Bar | 6,090 PSI | Extreme pressure, heavy duty |
Yes, 3/8 hydraulic hose is available by the foot or in bulk coils for flexible cutting and assembly.
The minimum order quantity for our 3/8 inch Hydraulic Hose is 200 meters.
Common options include JIC, NPT, and female end fittings designed for standard 3/8 inch hydraulic hose dimensions.
The working pressure of the hose should always be equal to or higher than the maximum system pressure, including pressure spikes. In most applications, a safety factor is applied according to industry standards. Our technical team can help evaluate your system pressure, duty cycle, and operating conditions to recommend the appropriate hose construction.
Each hydraulic hose is manufactured under controlled processes and tested according to applicable standards. Typical tests include dimensional inspection, pressure testing, leakage checks, and visual inspection to ensure consistent performance and safety before delivery.
To produce a correct hose assembly, we typically need the hose size, working pressure, hose length, fitting types, fitting orientation, and application details. Providing accurate information ensures the assembly performs reliably in your hydraulic system.