Rubber plays a vital role in the production of hydraulic hoses, serving as the core raw material that determines flexibility, durability, and performance. Different rubber types offer unique properties, making them suitable for handling varying pressures, temperatures, and fluids. Understanding these materials is essential for selecting the right hydraulic hose.
In this ultimate guide, we explore the most common rubber types used in hydraulic hose manufacturing, including synthetic and natural variations. Each type is engineered to meet specific application demands, from extreme weather resistance to chemical compatibility. Knowing their strengths helps ensure safety, reliability, and longer service life.
What Is Rubber?
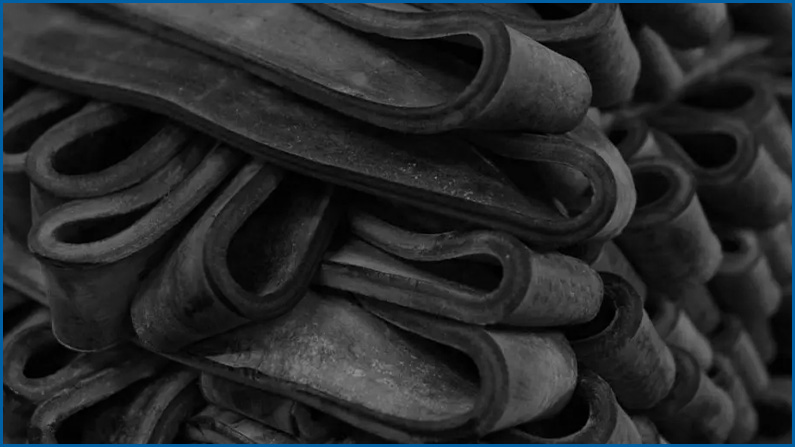

Rubber is an elastic material that can be produced naturally from plant sources or synthetically through a variety of chemical processes. And the rubber material has been in use for thousands of years, and the rubber material can be produced to numerous variations with distinct characteristics that make them suitable for different applications.
The hydraulic hose material properties include rubber material, to make the hydraulic hose as a whole, yes, the inner tube and outer cover of the hydraulic hose can be made of the rubber material, synthetic rubber.
Rubber History

Rubber has a fascinating history that stretches from ancient civilizations to modern industries. Originally discovered in natural form, it was used for simple waterproofing and practical tools. Over centuries, innovations such as vulcanization transformed rubber into one of the most versatile materials in industrial development.
Ancient use in Mesoamerica – Civilizations like the Mayans and Aztecs harvested latex from rubber trees to waterproof fabrics, create bouncing balls, and craft tools. These early applications showed the unique properties of elasticity and resilience long before industrial use.
European discovery in the 18th century – When explorers brought rubber to Europe, scientists and inventors experimented with its potential. However, the material was unstable in different climates, becoming sticky in heat and brittle in cold, which limited its use at the time.
Goodyear’s vulcanization process (1839) – Charles Goodyear’s discovery of vulcanization stabilized rubber through heating with sulfur, creating durable, flexible, and weather-resistant material. This breakthrough revolutionized rubber applications, making it suitable for tires, hoses, belts, and countless industrial products that reshaped modern manufacturing.
Industrial expansion in the 19th century – The demand for durable rubber surged with industrialization, especially for machinery belts, gaskets, and seals. Natural rubber plantations spread across Asia, ensuring large-scale supply and fueling global trade, while industries adopted rubber as an essential raw material.
Synthetic rubber in the 20th century – During World War II, shortages of natural rubber led to the development of synthetic alternatives. Materials like SBR and NBR offered enhanced resistance to chemicals, oil, and extreme conditions, ensuring continuous supply and expanding rubber’s role in technology and engineering.
What is Rubber Made of?
Rubber is made from both natural and synthetic sources, processed into durable, flexible, and resilient materials.
- Natural latex from rubber trees – Harvested from Hevea brasiliensis, natural latex provides elasticity, flexibility, and toughness.
- Petrochemical-derived synthetic polymers – Made from petroleum-based chemicals, synthetic rubbers resist heat, oils, and harsh chemicals effectively.
- Additives for strength and stability – Fillers, sulfur, and accelerators improve durability, elasticity, and resistance to wear.
- Processing agents and plasticizers – These materials enhance flexibility, softness, and performance for diverse industrial hose applications.
- Carbon black reinforcement – Used as a strengthening agent, carbon black boosts wear resistance and extends hose life.
Natural Rubber vs Synthetic Rubber
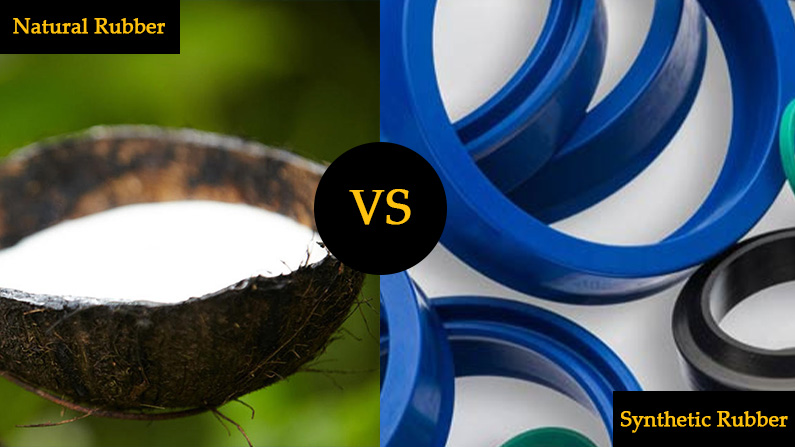

Rubber can be classified into natural and synthetic types, each offering distinct properties, benefits, and limitations. Natural rubber is harvested directly from rubber trees, while synthetic rubber is produced from petroleum-based chemicals. Both materials are widely used in hydraulic hoses, automotive parts, and industrial applications.
- Natural Rubber Origin – Derived from the latex of Hevea brasiliensis trees, natural rubber has been used for centuries. It is valued for its elasticity, tensile strength, and resistance to wear, making it ideal for tires, belts, and flexible industrial hose applications.
- Synthetic Rubber Origin – Produced through polymerization of petrochemical monomers, synthetic rubbers like NBR, EPDM, and SBR are engineered for specific performance. They resist oils, chemicals, and extreme temperatures, offering more versatility than natural rubber in modern industrial and hydraulic systems.
- Advantages of Natural Rubber – Natural rubber offers superior elasticity, resilience, and abrasion resistance, ensuring strong performance in dynamic and high-flex applications. Its renewable source also makes it environmentally favorable, though it can degrade under heat, sunlight, or chemical exposure without protective treatments.
- Advantages of Synthetic Rubber – Synthetic rubber provides resistance to oils, fuels, chemicals, ozone, and extreme conditions. Its engineered versatility allows precise performance in specialized environments, making it essential for hydraulic hoses, seals, and gaskets that must withstand heat and aggressive fluids.
- Applications Comparison – Natural rubber is widely used in products needing elasticity and cushioning, such as tires, gloves, and flexible hoses. Synthetic rubber dominates in environments with high temperatures, oils, or chemical exposure, ensuring performance in automotive, aerospace, and industrial fluid transfer systems.
Here are some differences between natural rubber and synethetic rubber in the following:
| Feature | Natural Rubber | Synthetic Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Harvested from latex of rubber trees | Produced from petroleum-based chemicals |
| Elasticity | High elasticity and resilience | Variable elasticity, engineered for application |
| Resistance | Weak against heat, oil, and chemicals | Strong resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals |
| Durability | Excellent tensile strength, less weather-resistant | High durability with ozone and UV stability |
| Common Uses | Tires, gloves, belts, flexible hoses | Hydraulic hoses, seals, gaskets, industrial parts |
Basic Properties of Rubber

Rubber exhibits a unique combination of flexibility, resilience, and durability, making it ideal for industrial and hydraulic applications. Its properties can be tailored through formulation, additives, and processing methods, allowing engineers to select the right type for specific temperature, pressure, and chemical conditions.
- Elasticity – Rubber can stretch and return to its original shape, providing excellent flexibility and resilience.
- Tensile Strength – It resists breaking under tension, ensuring durability in hoses, belts, and seals.
- Abrasion Resistance – Rubber withstands surface wear, extending the lifespan of hoses and industrial components.
- Chemical Resistance – Certain rubbers resist oils, fuels, and chemicals, maintaining integrity in harsh environments.
- Temperature Tolerance – Rubber types can perform under extreme heat or cold without losing functionality.
- Waterproofing – Rubber naturally repels water, making it suitable for sealing and fluid transfer applications.
Rubber Applications
Rubber Applications
Rubber is a versatile material widely used across industries due to its elasticity, durability, and chemical resistance. Its applications range from everyday products to specialized industrial equipment, including hydraulic hoses. Understanding its diverse uses helps industries select the right rubber type for performance, longevity, and safety requirements.
- Automotive Industry – Rubber is used in tires, seals, gaskets, and hoses. Its elasticity absorbs shocks, reduces vibration, and ensures reliable sealing, improving vehicle safety and efficiency under varying temperature and pressure conditions in engines and hydraulic systems.
- Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems – Hydraulic hoses, O-rings, and seals rely on rubber’s flexibility and pressure resistance. Proper rubber selection prevents leaks, withstands high pressures, and ensures long-term performance in demanding industrial and construction applications.
- Industrial Machinery – Rubber components such as belts, gaskets, and vibration isolators protect machines from wear, shock, and chemical exposure. Their durability and flexibility reduce maintenance costs and enhance operational efficiency across manufacturing plants.
- Consumer Goods – Everyday products like footwear, gloves, and waterproof clothing utilize rubber for comfort, elasticity, and protection. Its resilience ensures repeated use while maintaining shape, flexibility, and functional performance over time.
- Medical and Laboratory Equipment – Rubber is used in tubing, seals, stoppers, and gloves. Its chemical resistance and elasticity ensure safe fluid transfer, prevent contamination, and maintain reliable performance under sterilization and varying environmental conditions.
Rubber Types

Rubber can be classified into natural and synthetic types, each designed for specific performance needs. Different rubber types offer unique properties such as elasticity, chemical resistance, heat tolerance, and durability. Selecting the right type is crucial for hydraulic hoses, industrial components, and specialized applications.
- Natural Rubber (NR) – Derived from latex of rubber trees, NR offers excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and wear resistance. It is ideal for dynamic applications like hydraulic hose inner tubes, flexible seals, and vibration-absorbing parts, although it is less resistant to oils, chemicals, and extreme temperatures.
- Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) – A synthetic rubber made from styrene and butadiene, SBR has good abrasion resistance and moderate heat resistance. It is widely used in tires, belts, and hose covers, providing durability and flexibility while maintaining performance under varying mechanical stress.
- Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) – NBR is resistant to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it perfect for hydraulic hoses, seals, gaskets, and industrial tubing. Its durability under harsh conditions ensures leak-free operation and long-term reliability in automotive, aerospace, and industrial fluid transfer systems.
- Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) – EPDM excels in heat, ozone, and weather resistance, commonly used in hoses, gaskets, and seals exposed to outdoor or high-temperature environments. It provides long-term stability, flexibility, and chemical resistance in automotive and industrial applications.
- Chloroprene Rubber (CR / Neoprene) – Neoprene combines chemical, oil, and weather resistance with moderate flexibility. It is suitable for hose covers, industrial belts, gaskets, and protective coatings, offering durability and stability under mechanical and environmental stress.
- Silicone Rubber (SI) – Silicone rubber is heat resistant and chemically stable, ideal for high-temperature hoses, sealing applications, and medical tubing. Its flexibility and resilience allow reliable performance in extreme environments, including automotive engines and industrial machinery.
- Fluoroelastomer (FKM / Viton) – FKM rubber is highly resistant to heat, oils, fuels, and chemicals. It is commonly used in hydraulic hose inner linings, seals, and gaskets for high-performance applications requiring extreme chemical and temperature durability.
- Butyl Rubber (IIR) – Butyl rubber has excellent gas impermeability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for inner tubes, seals, and hoses where airtight properties and chemical stability are essential.
- Polyurethane Rubber (PU) – PU offers high abrasion and tear resistance. It is used in hoses, rollers, seals, and industrial components where mechanical wear is a concern.
- Other Specialty Rubbers – Includes HNBR, ACM, EPDM blends, and other engineered rubbers designed for specific chemical, temperature, or mechanical requirements in advanced hydraulic or industrial applications.
Natural Rubber
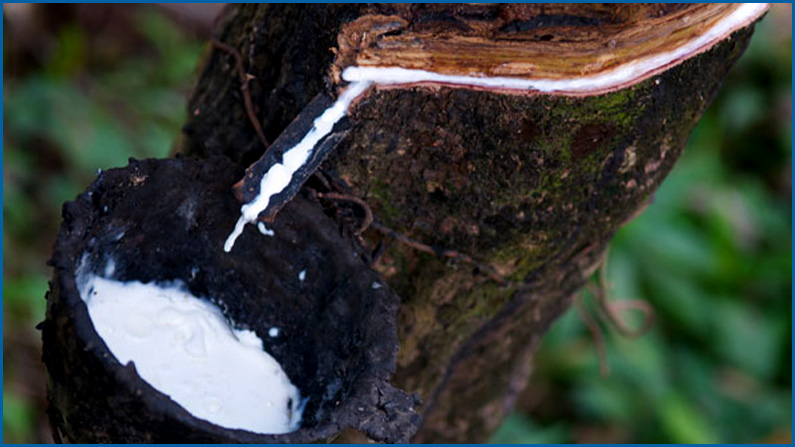

Natural rubber is the elasticity substance derived from the milky liquid from the Hevea brasiliensis tree, Brazilian tree, commonly the rubber tree. And rubber trees are from India, Thailand, Vietnam where have environmental conditions suitable for rubber tree growth.
And natural rubber is extracted from the rubber tree latex sap, and rubber farmers knot a cup to collect the rubber tree sap to the raw material for extracting natural rubber.
Natural Rubber Properties
The natural rubber consists of long, loosened isoprene polymer chains, and the chain reconnects once separated, and this structure gives elasticity to the natural rubber.
The natural rubber has flexibility and strength, as well as impurities and vulnerability to environmental conditions and hydrocarbons. Compared to other rubbers, natural rubber is one of the most flexible types, and it’s resistant to water and certain chemicals. It’s also resistant to cutting, tearing, wear, fatigue, and abrasion, with a working range between -58 to 212 degrees F. Additionally, it has a lot of tensile strength and adheres easily to other materials. However, natural rubber isn’t as effective at resisting heat, light, and ozone as other rubbers like neoprene. The material also varies with the tree it’s produced from, as well as containing natural impurities. While natural rubber is resistant to water and some chemicals, it’s still vulnerable to fuel, oil, and non-polar solvents.
Natural Rubber Application
Natural rubber is used in applications requiring a high level of wear and heat resistance. Thanks to its strength and compressibility, natural rubber is used in engineering applications, like anti-vibration mounts, drive couplings, springs, bearings, rubber bands, and adhesives. But the majority- 50% of natural rubber- is used in high-performance tires for race cars, buses, and aircraft thanks to its strength and heat resistance. It’s also used in hoses, automotive parts, foam mattresses, and battery boxes.
However, thanks to its adhesive properties, natural rubber is also found in rubber cement and the soil stabilization materials used around new roads. Even raw rubber is sometimes used for adhesives and as part of shoe soles. Additionally, about 10% of latex harvested from trees is simply reduced down to 60% rubber solution to make products like latex gloves or to use as a coating.
Neoprene Rubber (CR)
Neoprene rubber, also called chloroprene, is one of the most popular rubber materials, which has a wide application. Neoprene rubber is a synthetic rubber compound, and it can be widely applied in many industry fields.
Neoprene Rubber Properties
Compared with other types of rubber, and regular synthetic rubber, Neoprene rubber exhibits an exceptionally low susceptibility to burning, corrosion, and degradation. So Neoprene rubber is the perfect material for adhesives and corrosion-resistant coatings.
Neoprene Rubber Application
Neoprene rubber has a wide range of uses, mainly used as wire and cable sheaths, hoses, oil-resistant rubber products, heat-resistant conveyor belts, printing rubber sticks, rubber dams, construction sealing strips, road caulking sealants, bridge bearings, Oil field wire waterproof caps, flame-retardant rubber products, various gaskets, anti-corrosive linings for chemical equipment, and neoprene adhesives, etc. In recent years, neoprene has been developed for new uses in building waterproof materials, sealing materials, adhesives, marine development, medical and health, energy development, and people’s lives, and has expanded its application fields.
Silicone Rubber
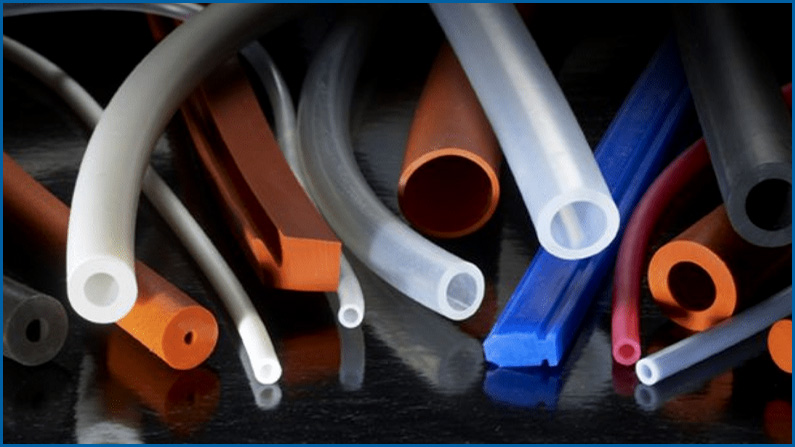

Silicone rubber—also referred to as polysiloxane—is known for its malleability, biocompatibility, and resistance to extreme temperatures, fire, ozone, and ultraviolet (UV) radiation. It is available in both solid and liquid forms in a variety of colors. Its chemically inert nature makes it ideal for use in parts and products that demand biocompatibility (such as gloves, respiratory masks, implants, and other medical products) and chemical resistance (such as baby care items, cosmetic applicators, and food containers and instruments).
Silicone rubber properties
- High and low-temperature resistance: Silicone rubber has the widest operating temperature range (-100~350℃). However, it must be pointed out that silicone rubber has poor resistance to high temperature and temperature sealing and aging. That is, when the air is isolated, especially when water is present, it will cause The mechanical strength to drop rapidly, and even breaks down into low-molecular-weight substances. This shortcoming can be achieved by adding a special heat-resistant stabilizer-a compound of cerium.
- Ozone aging resistance, oxygen aging resistance, weathering resistance performance: The performance of the silicone rubber vulcanized rubber has not changed significantly after being exposed to outdoor exposure in a free state for several years.
- Electrical insulation performance: The silicon dioxide produced after burning is still an insulator, and its corona resistance and arc resistance are extremely good.
- Special surface properties and physiological inertia: The surface energy of silicone rubber is lower than that of most organic materials. Therefore, it has low moisture absorption. Its water absorption rate is only 1% when immersed in water for a long time. The physical and mechanical properties are not reduced. Can play an isolation role. Silicone rubber is odorless, non-toxic, and has no adverse effects on the human body.
- High air permeability: The permeability of N2, O2, and air at room temperature are 30-40 times higher than that of NR. It also has the selective performance of gas permeability, and the permeability of O2 is 1 times that of N2.
The oil resistance, radiation resistance, and combustion resistance of special silicone rubber.
- Oil resistance: It has good stability to aliphatic, aromatic, and chlorinated hydrocarbon solvents, various petroleum-based fuel oils, lubricating oils, hydraulic oils, etc. at room temperature and high temperature, and has good resistance to ethanol, acetone, etc.
Flame retardant: Can be made using flame retardants.
Silicone Rubber Applications
high-temperature resistant insulation and sealing, medical materials, high voltage cables, adhesives, precision molds, isolating glue. Silicone rubber is mainly used in the aviation industry, electrical industry, food industry, and medical industry. Introduction to the application of silicone rubber is a linear polymer elastomer containing silicon-oxygen bonds (Si-O), so it has high thermal stability. It also has excellent resistance to ozone aging, oxygen aging, light aging, and weather aging. It also has excellent electrical insulation, mildew resistance, and high air permeability. It can be used to make many model products, such as various O-rings and gaskets. , Leather cups, oil seals, valves, shock absorbers, and diaphragms, etc. Because silicone rubber is physiologically inert, non-toxic, has no adhesion to other materials, and can withstand repeated cooking and sterilization, it is widely used in the medical and health, and food industries, such as artificial heart valves, artificial throats, artificial blood vessels, pacifiers and Medicine bottle stopper, etc. As the coating and sealing of various electronic tubes or electrical components, it has the effects of moisture-proof, dust-proof, shock-proof, and improved electrical performance.
Nitrile Rubber (NBR)

Nitrile rubber—also known as Buna-N rubber or nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR)—demonstrates several desirable mechanical and chemical properties, such as resistance to compression set, heat, oil and gas, and wear. These traits make it suitable for use in automotive gaskets and seals, O-rings, and engine hoses. It is also used in medical products (e.g., surgical gloves) since it lacks the allergenic proteins of latex-based rubbers and maintains its structural integrity better than silicone rubber.
Nitrile Rubber Properties
- Excellent abrasion resistance
- Good rebound, tear resistance, and non-polar solvent resistance
- Good water and oil resistance.
- Good resistance to gas permeability
- Good elongation properties and excellent compression set resistance
- Adequate resilience and tensile strength
- Good resistance to aliphatic hydrocarbons
- Excellent adhesion to metal and rigid materials
- Excellent colorability
Nitrile Rubber Application
EPDM Rubber

The main chain of EPDM rubber is composed of chemically stable saturated hydrocarbons, and only contains unsaturated double bonds in the side chain, so it is basically a kind of saturated rubber. Since there are no polar substituents in the molecular structure and the cohesive energy between molecules is low, the molecular chain can maintain flexibility in a wide temperature range. The chemical structure of ethylene propylene rubber makes its vulcanized products have unique properties.
EPDM Rubber Properties
Low density and high filling: EPDM rubber is a relatively low-density rubber with a density of 0.87. In addition, it can be filled with a large amount of oil and fillers, which can reduce the cost of rubber products and make up for the high price of EPDM rubber. The physical and mechanical properties are not significantly reduced.
Aging resistance: Ethylene-propylene rubber has excellent weather resistance, ozone resistance, heat resistance, acid and alkali resistance, water vapor resistance, color stability, electrical properties, oil-filling properties, and fluidity at room temperature. EPDM rubber products can be used for a long time at 120 ℃, at 150~200. C can be used briefly or intermittently. Adding suitable antioxidants can increase its use temperature. EPDM rubber crosslinked with peroxide can be used under more severe conditions. EPDM rubber does not crack when the ozone concentration is 50×10~ and is stretched by 30% for more than 150 hours.
Corrosion resistance: Because ethylene-propylene rubber lacks polarity and a low degree of unsaturation, it has good resistance to various polar chemicals such as alcohols, acids, alkalis, oxidants, refrigerants, detergents, animal and vegetable oils, ketones, and greases. ; But the stability is poor in fatty and aromatic solvents (such as gasoline, benzene, etc. and mineral oil. The performance will also decrease under the long-term action of concentrated acid.
EPDM Rubber Application
Where is EPDM used? EPDM rubber is used in seals, o-rings, glass-run channels, radiators, garden and appliance hoses, tubing, pond liners, washers, belts, electrical insulation, solar panel heat collectors, and speaker cone surrounds.
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR)

Styrene-Butadiene Rubber Properties
SBR is a copolymer of styrene and butadiene and has properties similar to Natural Rubber. It has good abrasion resistance, excellent impact strength, very good resilience, and high tensile strength.
Solution polymerized styrene-butadiene rubber has excellent wear resistance, groove crack resistance, and good grip on wet roads, heat resistance, and good flex resistance after prolonged exposure at high temperatures. In addition, it is mixed in an internal mixer. The characteristics of low heat generation during refining, low extrusion expansion rate, high filling volume, etc.
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber Application
Mainly used in tires, accounting for about 80% of the total output of solution polymerized styrene-butadiene rubber, such as the manufacture of car tires, large tire treads, snow tire carcasses, etc.
Butyl Rubber

Butyl Rubber Properties
Butyl rubber, or polyisobutylene, is a vinyl elastomer very similar to polyethylene and polypropylene in its structure, except that every other carbon atom is substituted with two methyl groups rather than one. It is made by a process called cationic vinyl polymerization from the monomer isobutylene. Usually, 1-2% isoprene is added to the isobutylene. The reaction is very fast so it is usually synthesized at very low temperatures. The addition of isoprene creates double bonds that allow the material to be crosslinked by vulcanization, just like natural rubber. This was an important step in making the original material useful during World War II as a substitute for natural rubber in the manufacturing of tires and tank treads. Polyisobutylene was first synthesized in 1931 and developed into butyl rubber in 1937. Curing rates improved in the 1960s with the development of halogenated, chlorinated, and brominated forms. These forms are often abbreviated as CIIR (for chlorinated isobutylene isoprene rubber) and BIIR (for brominated isobutylene isoprene rubber).
Put simply, vulcanizing is a process that ties all the rubber molecules together to form a single large molecule that does not melt as it gets warm and does not embrittle as it gets cold. Vulcanizing was invented by Charles Goodyear in 1839. It is a thermosetting process, so vulcanizing takes place after the product is formed.
Butyl Rubber Application
Butyl rubber can be applied for the production of automotive tires, healthcare products, such as latex rubber gloves. The excellent properties of high damping, resistance to heat aging, resistance to ozone, and barrier properties make them perfect for manufacturing automotive vibration control, hoses, and gaskets. Butyl rubbers are also used to improve formulations for conveyor belts, tank linings, and condenser packaging. Construction Butyl rubber is also used in the construction industry. Using butyl rubbers, the weather ability of asphalt, contact cement, and sealant tapes can be improved. Adhesives Use butyl rubbers to provide adhesive properties in tapes, valve cement, and flooring adhesives. Consumer products Butyl rubbers are used in ball bladders for sports goods and electrical appliance condenser packing. Excellent air retention properties make butyl rubber a major component in bladders used in the sporting goods industry. Similarly, the low permeability and chemical inertness of butyl rubber make it ideal to make condenser packing for electrical appliances. Butyl rubber is used for making the gum base in chewing gums.
Fluorosilicone Rubber

Fluorosilicone Rubber Properties
Like silicone, fluorosilicone rubber is a long-lasting elastomer that is stable and compression set resistant across temperature extremes, but unlike silicone, fluorosilicone contains trifluoropropyl groups that enhance its chemical resistance to non-polar solvents, fuels, oils, acids, and alkaline chemicals.
Fluorosilicone Rubber Application
For automotive applications, a range of silicone/ fluorosilicone polymers are also used to provide a combination of fluid resistance, moulding, and economy. The primary uses are for static seals in hydraulic and fuel systems.Natural Rubber
Latex Rubber

The latex rubber is the milky white liquid emulsion contained in some flowering plant cells, such as the rubber tree-Hevea brasiliensis, or any other synthetic rubber or plastic-based water emulsions.
The plant product is a complex mixture of substances suspended in a watery medium in which salts, sugars, tannins, alkaloids, enzymes, and other substances are dissolved including various gum resins, fats, or waxes and, in some cases poisonous compounds.
It is produced mainly by the cells of plants in the Asclepiadoideae subfamily and others in the Apocynaceae family but also by plants in the Sapotaceae, Euphorbiaceae, Papaveraceae, Moraceae, and Asteraceae families
A mature rubber tree’s latex is a soft white material found under the bark. Given the intensity and man-made feel of so many of its final uses, such as tires, rubber gloves, and tennis shoes, you might be shocked to think of latex as a natural material.
The reality is that natural rubber latex is derived from nature. Rubber tappers collect latex from trees using a procedure that has been passed down over centuries until it is processed.
Latex Rubber Properties
Latex is an excellent rubber substance after processing. Latex’s tensile and elongation properties, as well as tear resistance and overall durability, are well known.
Latex is unaffected by the majority of modern abrasives. Low temperatures are not a problem but high temperatures can be. Latex can corrode at temperatures above 82 degrees.
To protect latex from corrosion caused by heat, sunlight, and oxygen, treatment chemicals can be added. Latex should not be used in conjunction with petroleum products or solvents. This will cause the latex to break down.
Latex Rubber Application
Latex has a wide range of uses, from everyday objects to more advanced applications. The gloves swim caps, chewing gum, mattresses, catheters, rubber bands, balloons, tennis shoes, and a number of other sporting goods are all manufactured of natural rubber latex.
Coatings containing synthetic latexes, such as latex paint are popular. They are also used in glues because of their tendency to solidify when water evaporates from the latex polymer particles.
Synthetic latex can also be mixed into cement for resurfacing and repairing cracks in concrete.
Liquid Silicone Rubber

Liquid silicone rubber is a high purity, two-component platinum cured silicone that is suitable for the manufacture of technical parts that require strength, resistance and high quality.
LSRs are viscous, pumpable products that are primarily manufactured using liquid injection molding. Liquid Silicone rubber is used in a wide range of applications in the elastomer industry, from consumer goods to medical devices and anything in between.
Liquid Silicone Rubber Properties
Silicone rubber comes in a variety of grades, each with its own set of material properties. One of the reasons LSR is used in so many different applications is because of its flexibility.
Liquid silicone’s mechanical properties make it a great place to start if you need a medical or food-grade product with superior bacteria resistance or an automotive part that can withstand extreme heat.
The quick curing and low compression collection of silicone and its resistance to tearing, heat, water and oil, and electrical conductivity, and overall strength are all essential material properties.
LSR can be used at temperatures ranging from -100 to 200 degrees Celsius, exposed to wind, rain, and UV light for long periods of time, and immersed in water, oil or solvents.
LSR comes in a range of grades with material properties that can withstand even the most challenging applications.
Liquid Silicone Rubber Application
The manufacturing of LSR parts is the most common application for silicone rubber. LSR components are used in a variety of industries.
They are ideal for gaskets and hardware in consumer appliances like microwaves because of steam resistance and low compression set. They are suitable for electronic interfaces on keyboards and touchpads because of their conductivity and fatigue resistance.
Their oil resistance ensures that automotive components last long. Liquid silicone rubber is a highly adaptable material, with new uses being found and tested regularly.
It’s used in a variety of industries, including healthcare, automobile parts manufacturing, electronics, and consumer goods, gaskets and other hardware, and many others.
Conclusion
Rubber is the backbone of hydraulic hose construction, and the right choice of material guarantees long-lasting performance in demanding applications. By understanding natural rubber, synthetic blends, and specialized compounds, you can match your hoses with the exact conditions they will face, ensuring durability and efficiency.
Selecting the right rubber type not only improves hose performance but also reduces maintenance costs and downtime. With countless applications across industries, having the correct raw material ensures safety, stability, and productivity, especially in high-pressure environments where reliability is non-negotiable.
At Kingdaflex, we manufacture and supply wholesale hydraulic hoses made from premium rubber materials tailored to your needs. Whether you require hoses for construction, agriculture, mining, or industrial use, our products deliver strength and dependability. Partner with Kingdaflex today to get durable hydraulic hoses at competitive wholesale prices.




