A hydraulic system is only as strong as its weakest link, and often, that critical component is the hydraulic hose. Far from just a conduit for fluid, the material composition of your hydraulic hose is the true backbone of your system’s efficiency and reliability. Choosing wisely ensures optimal power transmission and prevents costly downtime.
Understanding the properties of various hydraulic hose materials—be it synthetic rubber, thermoplastic, or specialized compounds—is crucial for peak performance. This blog will delve into how the right material choice directly impacts pressure handling, temperature resistance, chemical compatibility, and overall longevity, ensuring your hydraulic system operates at its best.
What Are Hydraulic Hoses Made Of?
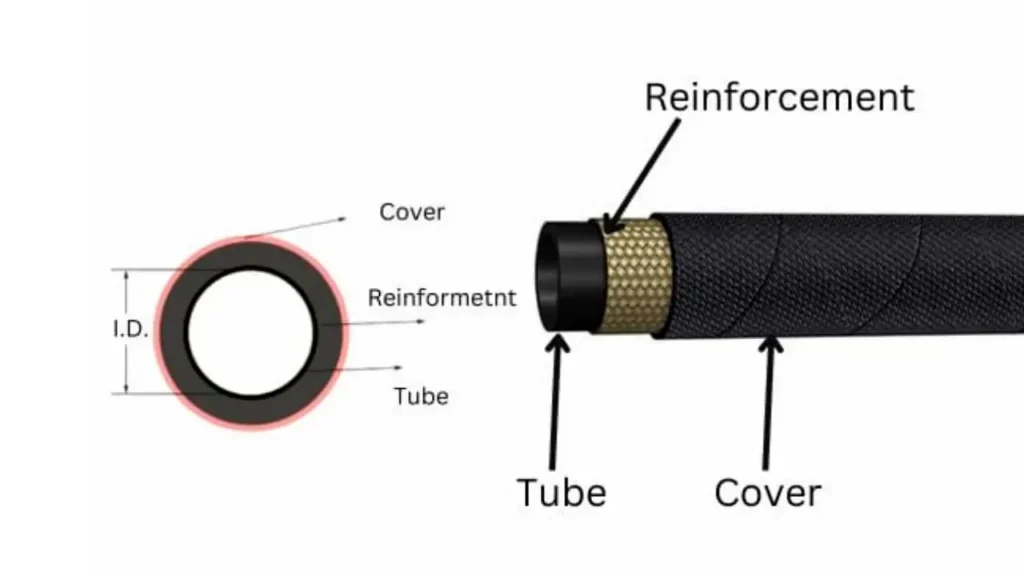
Hydraulic hoses are complex components, meticulously engineered to withstand the demanding conditions of hydraulic systems.
The hydraulic hose construction typically involves three key layers: an inner tube, a reinforcement layer, and an outer cover, each made from specialized materials to ensure flexibility, pressure resistance, and protection.
Here are common hydraulic hose materials:
- Synthetic Rubber: This is the most prevalent material for the inner tube and outer cover due to its excellent flexibility, good oil resistance (especially nitrile rubber for inner tubes), and abrasion resistance. Different synthetic rubbers, like EPDM for outer covers, offer varying levels of weather and ozone resistance, protecting the hose from external degradation.
- Thermoplastic: Known for being lightweight and highly flexible, thermoplastic hoses (often made from nylon or polyurethane) are ideal for applications requiring tight bend radii or where weight is a concern. They also offer good chemical resistance and can perform well in low-temperature environments, making them versatile for specific hydraulic needs.
- Steel Wire: The reinforcement layer, crucial for handling high internal pressures, is commonly made from high-tensile steel wire. This wire is either braided or spiraled in multiple layers, providing immense strength and preventing hose expansion or bursting under pressure. The number of wire layers determines the hose’s pressure rating.
- Teflon (PTFE): For demanding applications involving aggressive chemicals or extreme temperatures (up to 450°F), Teflon (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is the material of choice. Its exceptional chemical inertness and wide temperature range make it indispensable in industries like chemical processing and aerospace, despite its higher cost.
- Stainless Steel: Used for both reinforcement and sometimes as an outer covering, stainless steel offers superior durability, extreme temperature resistance, and excellent corrosion resistance. This makes stainless steel hoses, particularly those with a stainless steel braid, suitable for harsh environments where other materials might degrade rapidly.
How to Choose the Best Hydraulic Hose Materials
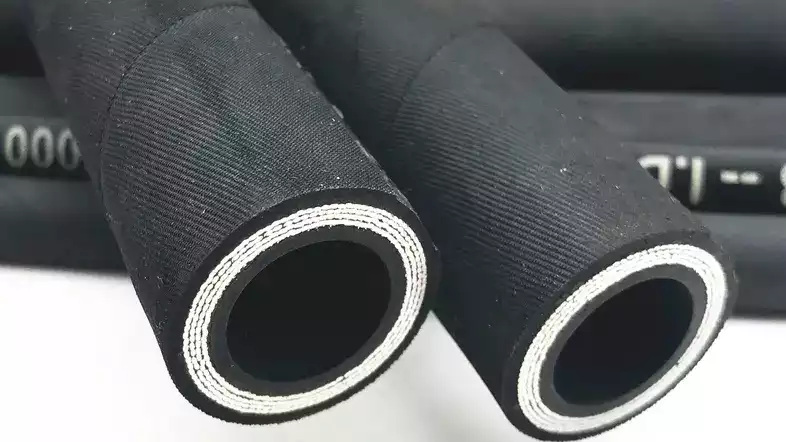

Choosing the best hydraulic hose material is a critical decision that impacts the entire system’s safety, efficiency, and longevity. It’s not a one-size-fits-all solution, as each application presents unique challenges regarding fluid type, operating conditions, and environmental factors.
A careful assessment of these parameters is essential to ensure optimal performance and prevent premature hose failure.
Here are the key factors to consider when selecting hydraulic hose materials:
- Fluid Compatibility: The inner tube material must be compatible with the hydraulic fluid being conveyed. Different fluids (e.g., petroleum-based oils, synthetic fluids, water-glycol solutions) can react with certain materials, leading to degradation, swelling, or hardening of the hose. Always cross-reference the fluid type with the hose manufacturer’s chemical resistance charts.
- Pressure Rating: The hose’s material and reinforcement directly determine its ability to withstand internal pressure. You need to consider both the system’s maximum working pressure and any potential pressure spikes or surges. Selecting a hose with a working pressure rating that exceeds your system’s maximum pressure, typically with a 4:1 safety factor, is paramount for safety.
- Temperature Range: Both the ambient temperature (surrounding environment) and the fluid temperature inside the hose are crucial. Materials have specific temperature limitations; some become brittle in cold or soften in heat. Ensuring the hose’s material can endure the full expected temperature range of your application is vital to prevent material degradation and maintain flexibility.
- Abrasion and Environmental Resistance: The outer cover material needs to protect the reinforcement layers from external damage. Consider the operating environment: will the hose be exposed to constant rubbing, impact, UV radiation, ozone, or corrosive chemicals? Materials like specialized synthetic rubbers or polyurethane offer enhanced resistance to abrasion and environmental elements.
- Flexibility and Bend Radius: The application’s physical constraints dictate the required flexibility and minimum bend radius. Some materials are inherently more flexible, allowing for tighter routing in confined spaces without kinking or stressing the hose. Thermoplastic hoses often excel in applications requiring a very tight bend radius.
Protective Hydraulic Hose UV Cover Material
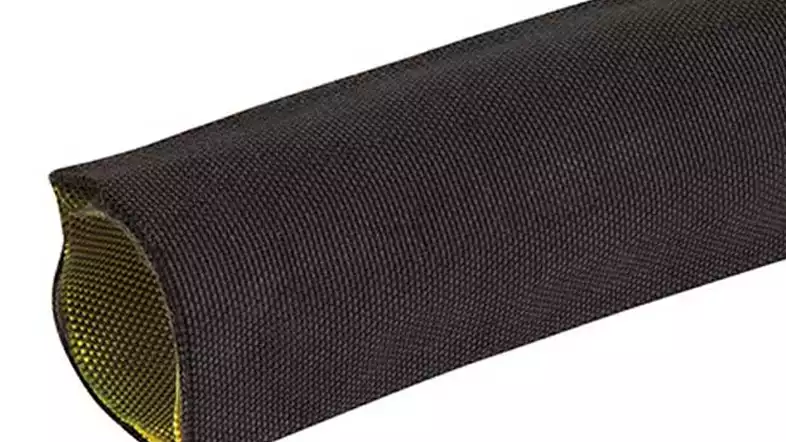

For hydraulic hoses operating outdoors or in environments with significant sun exposure, UV protection is paramount. Ultraviolet radiation can degrade the outer cover of a hydraulic hose over time, leading to cracking, hardening, and ultimately, premature failure of the hose assembly.
Therefore, selecting a cover material specifically designed to resist UV degradation is crucial for extending the hose’s lifespan and maintaining system integrity, especially in agricultural, construction, marine, and mobile equipment applications.
Here are common materials and methods used for protective hydraulic hose UV covers:
- Thermoplastic Materials (e.g., Polyurethane, Nylon): Many thermoplastic hoses inherently offer excellent UV resistance. Materials like polyurethane and nylon, used for the outer cover, are engineered to resist degradation from sunlight, chemicals, and abrasion. This makes thermoplastic hoses a durable choice for outdoor applications where UV exposure is a consistent factor.
- UV-Stabilized Synthetic Rubber: While natural rubber can degrade rapidly in UV, synthetic rubbers used for hydraulic hose covers are often compounded with UV stabilizers. These additives prevent the molecular breakdown caused by ultraviolet light, maintaining the rubber’s flexibility and integrity over extended periods of sun exposure.
- Protective Sleeves (e.g., Nylon, Polyester, Polyethylene): Beyond the hose’s inherent cover material, external sleeves made from UV-resistant fabrics like ballistic nylon, heavy-duty polyester, or high-density polyethylene (HDPE) are commonly used. These sleeves offer an additional layer of protection against UV, abrasion, and other environmental stressors, effectively extending the hose’s service life.
- Spiral Wraps (e.g., HDPE): Similar to sleeves, spiral wraps, often made from UV-stabilized HDPE, are wrapped around the hose to provide physical protection from abrasion, crushing, and UV rays. Their design allows for easy installation and replacement, making them a popular choice for enhancing durability in exposed conditions.
- Specialized Coatings: Some hydraulic hoses may feature specialized coatings on their outer cover designed to enhance UV resistance. These coatings can act as a barrier, reflecting or absorbing UV radiation before it can damage the underlying hose material, thereby prolonging its operational life in sun-intensive environments.
Hydraulic Hose Material Properties

Understanding the specific properties of hydraulic hose materials is essential for engineers and technicians to select the optimal hose for any given application. These properties dictate the hose’s ability to withstand internal pressure, resist chemical degradation, endure temperature extremes, and resist external abrasion, all of which directly impact the safety, efficiency, and longevity of the hydraulic system.
Each component—the inner tube, reinforcement, and outer cover—is designed with distinct material properties to fulfill its critical role.
Here are key hydraulic hose material properties:
- Chemical Resistance: This refers to the ability of the inner tube (and to some extent, the outer cover) material to resist degradation, swelling, or hardening when exposed to various hydraulic fluids, lubricants, and external chemicals. For instance, nitrile rubber is excellent for petroleum-based fluids, while PTFE (Teflon) offers superior resistance to aggressive chemicals and high temperatures.
- Temperature Range: Hydraulic hoses must maintain their integrity and flexibility across a wide spectrum of temperatures, both ambient and internal fluid temperatures. Materials like certain synthetic rubbers perform well in cold or moderate heat, while others, such as PTFE, are necessary for extreme high-temperature applications (e.g., steam or hot chemicals), preventing material breakdown or embrittlement.
- Pressure Resistance (Burst and Working Pressure): This is primarily determined by the reinforcement layers. High-tensile steel wire (braided or spiraled) provides the strength to contain high internal pressures, preventing bursting. The working pressure is the maximum continuous pressure the hose can safely handle, typically with a safety factor (e.g., 4:1) of its burst pressure.
- Abrasion Resistance: The outer cover’s ability to withstand rubbing, scuffing, and cutting from external contact is crucial, especially in dynamic environments. Materials like polyurethane and specialized synthetic rubber compounds are formulated to offer superior abrasion resistance, protecting the underlying reinforcement and extending the hose’s service life.
- Flexibility and Bend Radius: The inherent pliability of the hose material dictates its flexibility and the minimum radius to which it can be bent without kinking or sustaining damage. Thermoplastic hoses often excel in applications requiring tight routing or continuous flexing, while multi-spiral wire hoses, though offering higher pressure ratings, tend to be less flexible.
- Aging and Weather Resistance: This property relates to the material’s ability to resist degradation from environmental factors such as ozone, UV radiation, moisture, and general atmospheric exposure over time. UV-stabilized synthetic rubbers and certain thermoplastics are designed to prevent cracking, hardening, or color fading when exposed to outdoor conditions.
Rubber Hydraulic Hose
Rubber hydraulic hoses are the most common type of hydraulic hose. They are flexible and durable, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Rubber hydraulic hoses are resistant to oil, weather, and abrasion. They are also relatively low-cost and easy to install. However, they may not be suitable for high-temperature applications.
Thermoplastic Hydraulic Hose
Thermoplastic hydraulic hoses are made from a plastic polymer that is flexible and lightweight. They have a high resistance to abrasion and can withstand high-pressure applications. They are also resistant to UV rays and chemicals, making them suitable for harsh environments. However, thermoplastic hoses are not as durable as rubber hoses and may not be suitable for high-temperature applications.
Teflon Hydraulic Hose
Teflon hydraulic hoses are made from a synthetic polymer that is highly resistant to chemicals and high temperatures. They are suitable for applications where the hydraulic system operates at high temperatures and corrosive environments. Teflon hoses have excellent chemical resistance and are highly durable. However, they are not as flexible as rubber or thermoplastic hoses and are relatively expensive.
Stainless Steel Hydraulic Hose
Stainless steel hydraulic hoses are made from a braided stainless steel outer covering with a Teflon inner tube. They are highly resistant to corrosion and can withstand high-pressure applications. Stainless steel hoses are suitable for applications where there is a risk of abrasion or impact. However, they are relatively expensive and may not be suitable for all applications.
Hybrid Hydraulic Hose
Hybrid hydraulic hoses are made from a combination of different materials, such as rubber and thermoplastic. These hoses are designed to provide the advantages of both materials and are suitable for applications requiring flexibility and durability. Hybrid hoses are relatively new and may not be as widely available as other types of hydraulic hoses.
What to Consider When Choosing Hydraulic Hoses

Choosing the right hydraulic hose is a critical engineering decision that directly impacts the safety, efficiency, and lifespan of any hydraulic system. It requires a thorough understanding of the application’s demands, as a mismatched hose can lead to premature failure, fluid leaks, system downtime, and potential safety hazards. The process often involves a comprehensive evaluation of several key parameters to ensure the selected hose can reliably perform under the specific operating conditions.
Here’s what to consider when choosing hydraulic hoses:
- Size (Inner Diameter and Length): The inner diameter (ID) must be correctly sized to ensure optimal fluid flow velocity. Too small an ID can cause excessive pressure drops, heat generation, and turbulence, while too large can lead to sluggish system response. Length is also crucial; it must allow for machine movement and flex without kinking or stressing the hose or fittings, yet not be excessively long to avoid unnecessary pressure loss.
- Temperature (Fluid and Ambient): Both the temperature of the hydraulic fluid passing through the hose and the external ambient temperature of the operating environment are critical. Hoses have specific temperature ratings, and exceeding these limits, even briefly, can degrade the material, leading to cracking, hardening, or softening, and ultimately premature failure.
- Application: The specific use of the hydraulic hose dictates many selection criteria. Factors like exposure to external elements (UV, ozone, chemicals), abrasion, bending cycles, and whether the hose will experience continuous flexing or static conditions all influence the required hose construction and material properties. For instance, mobile equipment often requires highly abrasion-resistant covers.
- Media (Fluid Compatibility): The inner tube material must be chemically compatible with the hydraulic fluid being conveyed. Different fluids (e.g., petroleum-based, synthetic, water-based) can react differently with hose materials. Incompatibility can lead to inner tube degradation, swelling, or breakdown, contaminating the fluid and causing system damage.
- Pressure (Working and Burst): This is paramount for safety. The hose’s working pressure rating must always meet or exceed the maximum operating pressure of the hydraulic system, including any potential pressure spikes or surges. The burst pressure, typically four times the working pressure, indicates the hose’s ultimate strength before catastrophic failure.
- Ends/Couplings: The type of end fittings and couplings must be compatible with both the hose and the system’s ports to ensure a secure, leak-free connection. Factors like thread type (e.g., JIC, ORB, BSP) and sealing methods are crucial for proper assembly and long-term reliability.
- Delivery (Flow Rate and Velocity): While related to size, delivery specifically considers the required fluid volume and velocity for efficient system operation. An adequately sized hose ensures the system can deliver the necessary flow rate with minimal pressure drops and energy loss.
Benefits of Choosing the Right Hydraulic Hose Material
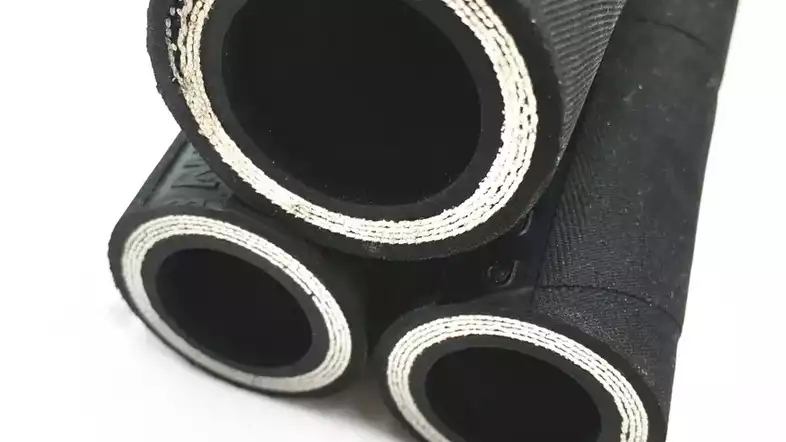

Choosing the correct hydraulic hose material offers a multitude of benefits, directly impacting the operational efficiency, safety, and lifespan of your entire hydraulic system. It transforms a potential weak link into a reliable component, capable of enduring the harsh conditions inherent in fluid power applications. This strategic selection leads to reduced maintenance, prolonged equipment life, and ultimately, significant cost savings by minimizing downtime and the need for frequent replacements.
Here are the key benefits of choosing the right hydraulic hose material:
- Enhanced Safety: The most crucial benefit is increased safety. A hose made from the appropriate material for its pressure, temperature, and fluid environment is far less likely to burst, leak, or fail, preventing potential injuries to personnel, damage to machinery, and environmental contamination from fluid spills.
- Extended Hydraulic Hose Service Life: Hoses designed with materials resistant to specific operational stressors—be it extreme heat, abrasive environments, or corrosive fluids—will last significantly longer. This means fewer hose replacements, reducing both material costs and labor associated with downtime.
- Improved System Performance: The right hose material ensures optimal fluid flow and pressure transmission, leading to more efficient system operation. Hoses that can handle the required pressure without undue expansion, or maintain flexibility in cold, contribute to consistent and responsive hydraulic performance.
- Reduced Maintenance and Downtime: By preventing premature failures, choosing suitable materials drastically cuts down on unscheduled maintenance and costly downtime. Equipment remains operational for longer periods, maximizing productivity and profitability.
- Cost Savings: While a higher-quality, specialized hose material might have a higher initial cost, the long-term savings from extended lifespan, reduced maintenance, improved safety, and enhanced performance far outweigh the initial investment. It’s a true investment in system reliability.
- Chemical and Environmental Compatibility: Correct material selection guarantees that the hose will not degrade due to chemical reactions with the hydraulic fluid or external environmental factors like UV radiation, ozone, or chemical splashes, ensuring the integrity of the fluid and the hose structure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the significance of selecting the appropriate hydraulic hose material cannot be overstated. It’s the silent workhorse, enduring immense pressures, extreme temperatures, and harsh environments to keep your machinery running smoothly. Investing time in understanding these materials ultimately translates to a more robust, efficient, and reliable hydraulic system, safeguarding your operations and bottom line.
Remember, the longevity and performance of your hydraulic system hinge directly on the quality and suitability of its components, especially the hoses. Don’t compromise on this critical element. Making an informed decision about the hydraulic hose material will save you headaches, reduce maintenance costs, and ensure consistent productivity for years to come.
For all your hydraulic hose needs, consider Kingdaflex. We offer a comprehensive range of wholesale hydraulic hoses crafted from diverse materials to meet every application’s specific demands. Get wholesale hydraulic hoses from our Kingdaflex and build a hydraulic system that truly stands the test of time.










