Hydraulic systems rely on fluid transfer, and choosing between hoses and tubes is crucial. Both serve this purpose, but with distinct characteristics. This blog will explore the key differences between hydraulic hoses and tubes.
We’ll delve into their materials, flexibility, and pressure ratings. Understanding these distinctions will help you determine the optimal choice for your specific hydraulic applications.
What Are Hydraulic Hoses
Hydraulic hoses are flexible conduits designed to transport hydraulic fluid between components in a hydraulic system. They are engineered to withstand high pressures and varying temperatures, ensuring efficient power transfer. These hoses are crucial for enabling movement and flexibility in machinery, allowing for dynamic operation where rigid tubing would be impractical.
Constructed with multiple layers, including an inner tube, reinforcement layers (typically braided wire or textile), and an outer cover, hydraulic hoses are built for durability and resilience. Their flexibility allows them to bend and flex, accommodating movement in machinery while maintaining a secure fluid path.
What Are Hydraulic Tubes
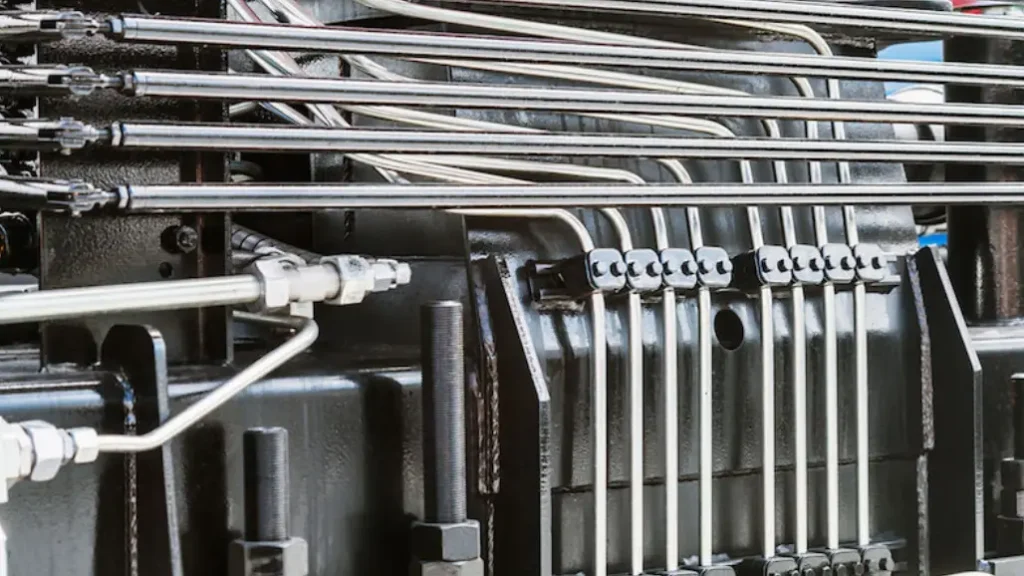
Hydraulic tubes are rigid conduits used to transport hydraulic fluid within a system. Unlike flexible hoses, tubes are designed for fixed applications where movement is minimal or nonexistent. They offer a stable, direct pathway for fluid flow, particularly in high-pressure environments.
Typically made from steel, stainless steel, or copper, hydraulic tubes provide excellent pressure resistance and durability. Their rigid structure minimizes expansion and contraction, ensuring consistent performance in demanding hydraulic systems. They are often preferred for applications requiring precise fluid control and minimal energy loss.
Hydraulic Hose vs Tube
Alright, let’s delve deeper into the distinctions between hydraulic hoses and tubes, exploring their nuances and applications.
Hydraulic Hoses: Flexibility and Dynamic Applications
Hydraulic hoses are the workhorses of dynamic hydraulic systems. Their defining characteristic is flexibility, enabling them to bend and flex to accommodate movement, vibrations, and changes in machine configuration. This flexibility is achieved through their multi-layered construction, which typically includes:
- Inner Tube: This layer, often made of synthetic rubber or thermoplastic, is in direct contact with the hydraulic fluid. It must be compatible with the fluid and resistant to degradation.
- Reinforcement Layers: These layers, typically braided wire, spiral wire, or textile, provide the hose with its pressure-holding capacity. The number and type of reinforcement layers determine the hose’s pressure rating.
- Outer Cover: This layer protects the reinforcement layers from abrasion, weather, and other environmental factors.
Hoses are ideal for applications where:
- Movement is required, such as in construction equipment, agricultural machinery, and robotic systems.
- Vibrations are present, as the hose can absorb these vibrations and prevent damage to the system.
- Routing is complex, as the hose can be easily bent and routed around obstacles.
Hydraulic Tubes: Rigidity and High-Pressure Stability
Hydraulic tubes, in contrast, are rigid conduits designed for fixed installations. Their primary advantage is their ability to withstand high pressures and maintain a consistent fluid flow path. Typically made from steel, stainless steel, or copper, tubes offer:
- High-pressure resistance: Their rigid structure minimizes expansion and contraction, ensuring consistent performance in demanding applications.
- Durability: Tubes are resistant to abrasion, corrosion, and other forms of damage, making them ideal for long-term use.
- Precise fluid control: The rigid nature of tubes minimizes energy loss and provides precise control over fluid flow.
Tubes are preferred for applications where:
- High pressures are involved, such as in stationary industrial machinery and hydraulic presses.
- Rigid, fixed installations are required, such as in piping systems and manifold assemblies.
- Precise fluid control is essential, such as in precision machining and hydraulic testing.
To further clarify the distinctions, here’s a comparative chart about the differences between hydraulic hose and tubing:
| Feature | Hydraulic Hose | Hydraulic Tube |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High | Low (Rigid) |
| Pressure Rating | Variable (dependent on reinforcement) | High |
| Applications | Dynamic, mobile applications | Static, fixed applications |
| Material | Synthetic rubber, thermoplastic, reinforced with wire or textile | Steel, stainless steel, copper |
| Vibration Resistance | Good | Poor |
| Routing Complexity | High (easy to route) | Low (difficult to route) |
| Connection method | Crimp fittings, reusable fittings | welded, flared, compression fittings |
| Cost | Generally higher | Generally lower |
How to Choose Hydraulic Hose and Tubes
Choosing the right hydraulic hose or tube is crucial for the efficiency and safety of your hydraulic system. Here’s a breakdown of the key factors to consider:
1. Application and System Requirements:
Movement and Flexibility:
- If your application involves movement, vibration, or complex routing, a hydraulic hose is essential. Think construction equipment, mobile machinery, or robotic arms.
- For stationary systems with minimal movement, like industrial presses or fixed piping, hydraulic tubes are the better choice.
- Determine the maximum operating pressure of your system. Select hoses or tubes with a pressure rating that exceeds this value, with a safety margin.
- High-pressure applications generally favor rigid tubes, while hoses can handle varying pressures depending on their reinforcement.
Consider the operating temperature of the hydraulic fluid and the surrounding environment. Choose hoses or tubes made from materials that can withstand these temperatures.
Fluid Compatibility:
Ensure the hose or tube material is compatible with the hydraulic fluid being used. Incompatible materials can degrade, leading to leaks and system failures.
Environmental Conditions:
Consider factors like abrasion, chemical exposure, UV radiation, and moisture. Select hoses or tubes with appropriate protective coatings or materials.
2. Hydraulic Hose Selection:
Size and Length:
- Determine the correct inside diameter (ID) of the hose to ensure adequate fluid flow.
- Measure the required length of the hose, accounting for bends and routing.
Reinforcement Type:
Choose the appropriate hydraulic hose reinforcement type (braided wire, spiral wire, textile) based on the pressure rating and flexibility requirements.
Fitting Type:
Select compatible fittings for the hose and system components. Common types include crimp fittings and reusable fittings.
3. Tube Selection:
Material:
Choose the appropriate tube material (steel, stainless steel, copper) based on pressure, corrosion resistance, and fluid compatibility.
Size and Wall Thickness:
Determine the correct outside diameter (OD) and wall thickness of the tube based on pressure and flow requirements.
Connection Method:
Choose the appropriate connection method, such as welding, flaring, or compression fittings, based on the application and installation requirements.
Routing and Bending:
Plan the routing of the tubes carefully, minimizing bends and restrictions.
Use appropriate bending tools to avoid kinking or damaging the tubes.
4. Safety Considerations:
Always pressure test hydraulic systems after installation or maintenance to ensure leak-free operation.
Regular Inspections:
Conduct regular inspections of hoses and tubes for signs of wear, damage, or leaks.
Proper Installation:
Ensure that hoses and tubes are installed correctly, with proper support and protection.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select the appropriate hydraulic hoses or tubes to optimize the performance, reliability, and safety of your hydraulic system.
Get Hydraulic Hoses Wholesale from Kingdaflex
Ultimately, choosing between hydraulic hoses and tubes hinges on your system’s specific demands. Hoses prioritize flexibility and movement, while tubes excel in rigid, high-pressure scenarios. Careful consideration of these differences ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Understanding these distinctions allows for informed decisions in hydraulic system design and maintenance. Matching the right component to the application is vital for efficiency and safety.
For reliable wholesale hydraulic hoses that meet diverse industrial needs, consider Kingdaflex. Explore our extensive range and contact us today for competitive pricing and expert support.







